
(a)
Interpretation: The value of
Concept introduction:Thermodynamics is a study of energy transfers that can be done by either heat or work. The energy transferred through work involves force. When work is positive then system gains energy while when work is negative then system loses energy. Heat is not a state function and therefore change in enthalpy of reaction
(b)
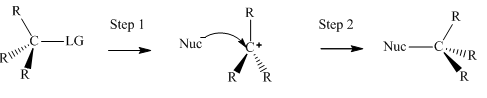
Interpretation: The mechanism using curved arrows should be indicated for below reactions.
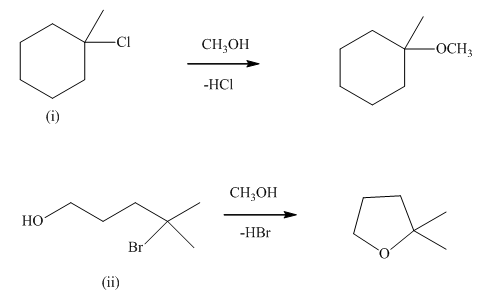
Concept introduction:Unimolecuar substitution or
A general
(c)
Interpretation: The effect observed on the rate of methanolysis when the concentration of tertiary
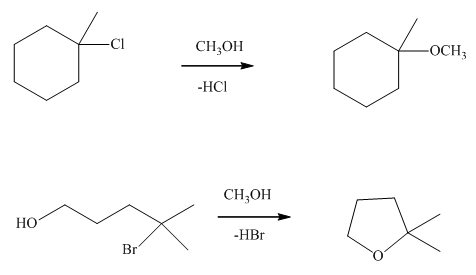
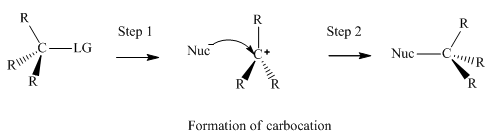
Concept introduction:Unimolecuar substitution or
A general
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- 1. Would you expect the following compounds to dissolve in the water layer or 1-hexanol layer, or neither layer? Use a couple sentences to justify each choice you made. (a) KPO. (b) SrSO. (c) FeCl, (d) CH2=CH-CH2-CH3 NO, (e) (f) CH3 0Na® CH H но но HO, O:5=0arrow_forward(b) The activating and deactivating groups could affect the position(s) of the next incoming group(s) to the benzene ring. Based on the structure below, analyze and explain the group(s) on the benzene ring is activating or deactivating group. Then, identify the product(s) formed from the following reactions. NH, CC, CH;CH,COCI AICI, (i) NH, HNO, H,SO, (ii) H Br AICI, (iii) Page 3 of 4arrow_forward4. A student has prepared 0.05 M solution of CH3-C=CH and has added to it 0.05 M solution of potassium tert-butoxide (K" O-C(CH3)3). (iv) Calculate the percentage of deprotonated methyl acetylene taking into account that pKa of the conjugate acid of potassium tert-butoxide equals 18 and pKa of methyl acetylene equals 24.arrow_forward
- (C) ntify the reagen out) in Scheme 6. (D) Another repeating transformation is the reductive amination that shows up in the Schemes 3, 5 and 6. This takes Ar-NH₂ to Ar-N(CH3)2 with NaBH4/HCHO (formaldedyde). This provides the “rear" dipole that drives the nanocar. Show the mechanism for converting Ar-NH2 → Ar-N(CH3)2 with two formaldehyde molecules and NaBH4. You will need to review your notes from lab5 in chem210L that used NaBH4.arrow_forwardIII. It is known that the solvolysis of 2-bromo-2-methylbutane in ethanol at 25 °C produces a mixture of substitution (64% mole) and elimination (36% mole) products. If the same alkyl halide is allowed to undergo solvolysis at the same temperature in tert-butyl alcohol, please predict (qualitatively) how the composition of the mixture will change and rationalize your prediction. You only need to consider nucleophilic substitution and elimination. ts)arrow_forward5. Consider the synthesis of 2-butanone from butyne: Hg2+ CH3CH,-C=C–H CH3CH, Ĉ -CH3 H3o* (i) Draw the structure of the compound D. (ii) Compound D isomerizes to form 2-butanone. What is this isomeric process called? (iii) Use the mechanism to show the conversion of compound D to 2-butanone.arrow_forward
- The following two sets of reactions, ((a) and (b)), show possibilities for arrow pushing in individual reaction steps. Identify which is wrong and explain why. Next, using the correct arrow pushing, label which molecule is the nucleophile and which is the electrophile. (a) (b) H3C :Cl: H3C H,c-i: – →: I-CH3 + :Cl: C-C: H3C / H3C H3C-Cl: C-CH3 H3C : H,C-Cl: H3C-CI: →: I-CH3 + :Cl: H3C :Cl: H3C C-CH3 C-CI: H3C/ H3C H3Carrow_forwardChemistry (ii) Would you expect the rate of hydrolysis of methyl-p-fluorobenzoate (X = F) to be substantially greater than, significantly less than, or about the same as that of the unsubstituted compound; Ox (p-F) = 0.06? Give a short justification of your answer – calculations are unnecessary.arrow_forward6. Which of the following alcohol/s would give a positive triiodomethane reaction? Indicate YES or NO on the boxes provided below the structure OH OH CH3(CH,);-CH,OH CH, —С—н (a) (b) (c)arrow_forward
- Paragraph Styles Edi 7. Answer ALL parts of the question (a) Predict the organic products formed when 3-methoxybenzaldehyde is heated with formaldehyde in the presence of concentrated sodium hydroxide (after final acidification with HCI) (Scheme Q7a): 1. NaOH, heat MeO, H. H. 2. HCI Aromatic (Scheme Q7a) (b) Give the full name of this reaction. (c) (1) Identify the electrophile in the hydride transfer step to form the aromatic product. (ii) Draw a mechanism for the reduction of this electrophile.arrow_forwardUse bond-dissociation enthalpies (Table 4-2, p. 167) to calculate values of ∆H° for the following reactions. (a) CH3¬CH3 + I2 ¡ CH3CH2I + HI(b) CH3CH2Cl + HI ¡ CH3CH2I + HCl(c) (CH3)3C¬OH + HCl ¡ (CH3)3C¬Cl + H2O (d) CH3CH2CH3 + H2 ¡ CH3CH3 + CH4 (e) CH3CH2OH + HBr ¡ CH3CH2¬Br + H2Oarrow_forwardChemistry 3. Provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the following syntheses. Several steps are required in some cases. (c) (d) H2N. NH2 но H. NH2 ноarrow_forward
