
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: Whether the given reaction works well, poorly or not at all needs to be determined. Also, the alternative products formed needs to be formulated.
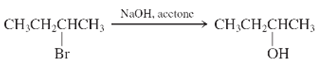
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an
(b)
Interpretation: Whether the given reaction works well, poorly or not at all needs to be determined. Also, the alternative products formed needs to be formulated.
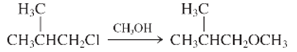
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(c)
Interpretation: Whether the given reaction works well, poorly or not at all needs to be determined. Also, the alternative products formed needs to be formulated.
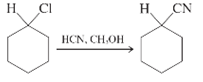
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(d)
Interpretation: Whether the given reaction works well, poorly or not at all needs to be determined. Also, the alternative products formed needs to be formulated.
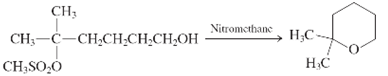
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(e)
Interpretation: Whether the given reaction works well, poorly or not at all needs to be determined. Also, the alternative products formed needs to be formulated.
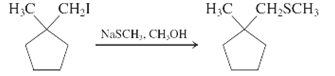
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(f)
Interpretation: Whether the given reaction works well, poorly or not at all needs to be determined. Also, the alternative products formed needs to be formulated.
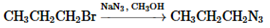
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(g)
Interpretation: Whether the given reaction works well, poorly or not at all needs to be determined. Also, the alternative products formed needs to be formulated.

Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(h)
Interpretation: Whether the given reaction works well, poorly or not at all needs to be determined. Also, the alternative products formed needs to be formulated.
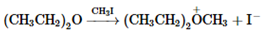
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(i)
Interpretation: Whether the given reaction works well, poorly or not at all needs to be determined. Also, the alternative products formed needs to be formulated.
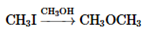
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(j)
Interpretation: Whether the given reaction works well, poorly or not at all needs to be determined. Also, the alternative products formed needs to be formulated.
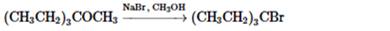
Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(k)
Interpretation: Whether the given reaction works well, poorly or not at all needs to be determined. Also, the alternative products formed needs to be formulated.

Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
(l)
Interpretation: Whether the given reaction works well, poorly or not at all needs to be determined. Also, the alternative products formed needs to be formulated.

Concept Introduction: Nucleophillic substitution and elimination reactions are two types of the reactions, playing important role in organic chemistry. In the nucleophillic substitution reaction, a leaving group is replaced with a nucleophile and in the elimination reaction rearrangement takes place resulting formation of an alkene.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Which of the following is/are the best major product for this reaction? HBr, A Br OH Br Br HO Br D Br HO Farrow_forwardWhat is a major product of this reaction? HBr Br Br Br Brarrow_forwardWhich is the major product of the following reaction? NH2 + H,N 2 NH2 NH но || OH но HO, но II IV ZI IZarrow_forward
- How many steps are in a reaction using an organometallic reagent? O 4 0 3 O 2 O 1arrow_forwardNBS ·Br Mg, ether> CO2 9. Determine whether the following reactions are flawed. Put "Yes" on the line for flawed reactions and for reactions that are not flawed (3 points). MeO COME LIAIH4 HgSO4 H3O EtOH H₂O 7 O EtQ OEt 667 MeOarrow_forwardWhat is the final product (B) of the following reaction? CH3 Br2 1. KCN light → B 2. H30*, heat CH3 CO2H CO,H CH3 CH2CO2H (a) (d) `CO2Harrow_forward
- Which of the following statements is correct about the reaction below? HBr CH₂Cl2 1 Br + Product 1 is the major product Product 2 is the major product Product 1 and 2 are formed in equal amounts 2 Br None of the products listed are the major product.arrow_forwardMethamphetamine can exist in two possible forms, shown below: He is trying to convert structure A into structure B, but he forgot what Nora told him to do. Which of the reagents below can he add to A to get the desired B? CHOICES: H2 NaCl NaOH HClarrow_forwardWhat type of reaction is shown below? H-Br (gas) CH CH + H20 Ether CH,CH CH,CH, O An addition O A substitution O An elimination O Arearrangementarrow_forward
- What is the major product to the following reaction? C2 (excess) NAOH CI CI- CI Cl HO CIarrow_forwardGive the major organic product of the following reaction. NO2 HBr CH3OH NO, OMe NON Br OMe NO2 NO, Br There is no reaction under these conditions or the correct product is not listed.arrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? OH CrO3 H,SO, CH,OH CHO COOH COOH сосн COOH COOH COOHarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





