
Interpretation: The reason behind specific product formed in below reaction should be written.
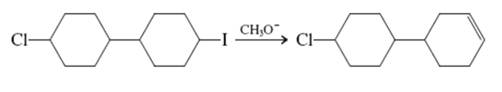
Concept introduction: Carbocation formation is relatively slower than acid-base reactions. Carbocations generated from
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- provide the reactants in the given products below to complete the reaction.arrow_forwardComplete the following reactions by identifying the majority product(s) or the reaction conditions that are missing. No mechanism is neededarrow_forwardConsider the reaction scheme shown below. HCI [1] ОН (a) Provide a detailed mechanism for reaction [1].arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
