
Concept explainers
Interpretation: The structures of A and B that should to be determined.
Concept introduction:The alcohols are best synthesized from retrosynthetic analysis with the aid of Grignard reagents.
The carbonyl bond is polar with partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
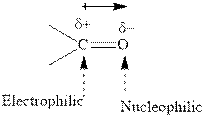
Grignard reagents are
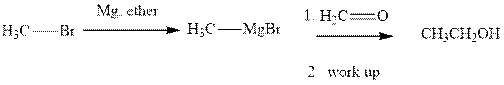
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methylmagnsium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol. The mechanistic pathway for the latter reaction is as follows:
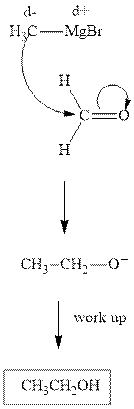
The polar carbonyl bond breaks and the polar Grignard reagent attack at electron deficient carbon. Finally with the hydrolysis and work up the alcohol is formed.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Formaldehyde, H2C=O, is known to all biologists because of its usefulness as a tissue preservative. When pure, formaldehyde trimerizes to give trioxane, C3H6O3, which, surprisingly enough, has no carbonyl groups. Only one monobromo derivative (C3H5BrO3) of trioxane is possible. Propose a structure for trioxane.arrow_forwardOne frequently used method for preparing methyl esters is by reaction of carboxylic acids with diazomethane, CH2N2. The reaction occurs in two steps: (l) protonation of diazomethane by the carboxylic acid to yield methyldiazonium ion, CH3N2+, plus a carboxylate ion; and (2) reaction of the carboxylate ion with CH3N2+. (a) Draw two resonance structures of diazomethane, and account for step 1. (b) What kind of reaction occurs in step 2?arrow_forward5. Compound A, C 10H 18O, undergoes reaction with dilute H 2SO 4 at 50 °C to yield a mixture of two alkenes, C 10H 16. The major alkene B, gives only cyclopentanone after ozone treatment followed by reduction with zinc in acetic acid. Which of the following reactions are correct.arrow_forward
- Hydrocarbon X has the formula C6H12.X reacts with one molar equivalent of hydrogen in the presence of a palladium catalyst to form a product having 12 primary hydrogens.Treatment of X with ozone followed by zinc in aqueous acid gives a mixture two aldehydes.What is the structure of X?arrow_forward4. Compound A has the formula C 8H 8. It reacts rapidly with KMnO 4 to give CO 2 and a carboxylic acid, B (C 7H 6O 2), but reacts with only 1 molar equivalent of H 2 on catalytic hydrogenation over a palladium catalyst. On hydrogenation under conditions that reduce aromatic rings, 4, equivalents of H 2 are taken up and hydrocarbon C (C 8H 16) is produced. What are the structures of A, B, and C.arrow_forwardAn optically active monoterpene (compound A) with molecular formula C10H18O undergoes catalytic hydrogenation to form an optically inactive compound with molecular formula C10H20O (compound B). When compound B is heated with acid, followed by reaction with O3 and then with dimethyl sulfide, one of the products obtained is 4-methylcyclohexanone. Give possible structures for compounds A and B.arrow_forward
- A compound of unknown structure (Compound A) is determined by elemental analysis to have a molecular formula of C10H12. Upon reaction with H2 and Pd/CacO3 the unknown absorbs one mole equivalent of hydrogen gas. Upon reaction with ozone, followed by zinc/acetic acid a product with structure shown is obtained. Four possibilities are given for the structure of Compound A. Select the correct answer. HO,C B A D В Both B and C are correct O o o o oarrow_forwardCompound AA has a molecular formula of C3H6O and gives a positiveresult using Tollen’s reagent. The reaction of compound AA with hotacidified potassium permanganate, KMnO4 gives compound BB. Thecatalytic hydrogenation of compound AA with nickel, Ni producedcompound CC. The reaction of compound BB with ethanamine,CH3CH2NH2 produces compound DD I) Draw the structural formula of compounds AA, BB, CC and DD. 2)Name the type of chemical reaction for the formation of compound CC.arrow_forwardCompound A and compound B both have molecular formula C6H12. Both compounds produce epoxides when treated with a peroxy acid (RCO3H). The epoxide resulting from compound A was treated with aqueous acid (H3O+) and the resulting diol has no chiral centers. Identify the two possible structures for compound A (enter two numbers separated by commas with no spaces, e.g. "1,2") The epoxide resulting from compound B was treated with (H3O*) and the resulting diol was a meso compound. Identify compound B 2 3 potn 7 1 5 6 4 8arrow_forward
- Compound T (C6H6O) reacts with sodium hydroxide to form Compound U. Compound V can be formed when Compound T reacted with sodium. Compound W formed when Compound T reacts with dilute nitric acid at room temperature while Compound X formed when Compound T reacts with concentrated nitric acid at room temperature. Compound T reacts with Br2 in CS2 to produce Compound Y. Identify the possible structural formulae for compound T to Y and give TWO (2) characteristics of compound T.arrow_forward1. The ketone 2-heptanone has been identified as contributing to the odor of a number of dairy products, including condensed milk and cheddar cheese. Describe the synthesis of 2-heptanone from acetylene and any necessary organic and inorganic reagents. 2. Compound A has the molecular formula C14H25Br and was obtained by reaction of sodium acetylide (HC≡CNa) )with 1,12-dibromododecane. On treatment of compound A with sodium amide, it was converted to compound B (C14H24). Ozonolysis of compound B gave the diacid HO2C(CH2)12CO2H. Catalytic hydrogenation of compound B over Lindlar palladium gave compound C (C14H26), while hydrogenation over platinum gave compound D (C14H28). Sodium-ammonia reduction of compound B gave compound E (C14H26). Both C and E yielded O═CH(CH2)12CH═O on ozonolysis. Assign structures to compound A through E so as to be consistent with the observed transformations.arrow_forwardSharpless epoxidation of allylic alcohol X forms compound Y. Treatment of Y with NaOH and C6H5SH in an alcohol–water mixture forms Z. Identify the structure of Y and draw a mechanism for the conversion of Y to Z. Account for the stereochemistry of the stereogenic centers in Z. Z has been used as an intermediate in the synthesis of chiral carbohydrates.arrow_forward
