
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:Compound
Concept introduction:In accordance with Bronsted definition an acid can act as a proton donor and a base can act as a proton acceptor. Thus in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similar curved arrows are used to show the movement of electrons. After deprotonation, the species left with a negative charge is referred as the conjugate base of acid while the other with a positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example;
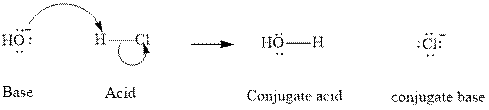
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has a weak conjugate base and the strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.
The order of acidic strength of various alcohols is as follows:
For tertiary alcohols, the steric bulk is maximum that leads to inhibition in solvation of
(b)
Interpretation:Compounds
Concept introduction: In accordance with Bronsted definition an acid can act as a proton donor and a base can act as a proton acceptor. Thus in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similar curved arrows are used to show the movement of electrons. After deprotonation, the species left with a negative charge is referred as the conjugate base of acid while the other with a positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example;
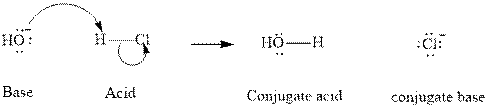
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has a weak conjugate base and the strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.
The order of acidic strength of various alcohols is as follows:
For tertiary alcohols, the steric bulk is maximum that leads to inhibition in solvation of
(c)
Interpretation:Compounds
Concept introduction: In accordance with Bronsted definition an acid can act as a proton donor and a base can act as a proton acceptor. Thus in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similar curved arrows are used to show the movement of electrons. After deprotonation, the species left with a negative charge is referred as the conjugate base of acid while the other with a positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example;
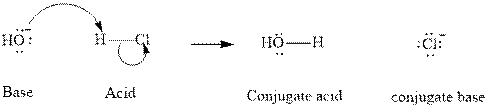
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has a weak conjugate base and the strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.
The order of acidic strength of various alcohols is as follows:
For tertiary alcohols, the steric bulk is maximum that leads to inhibition in solvation of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Rank the following substances in order of increasing acidity: (a) (CH3)2CHOH, HC≡CH, (CF3)2CHOH, CH3OH (b) Phenol, p-methylphenol, p-[trifluoromethyl) phenol (c) Benzyl alcohol, phenol, p-hydroxybenzonic acidarrow_forwardComplete each acid-base reaction and predict whether the position of equilibrium lies toward the left or toward the right. (a) CH3CCH+CH3CH2ONa+CH3CH3OH (b) CH3CCCH2CH2OH+Na+NH2NH3(l)arrow_forwardIn each equilibrium, label the stronger acid, the stronger base, the weaker acid, and the weaker base. Also estimate the position of each equilibrium. (a) CH3CH2O + CH3CCH CH3CH2OH + CH3CC (b) CH3CH2O + HCl CH3CH2OH + Cl (c) CH3COOH + CH3CH2O CH3COO + CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Give the products of the föllówing twó áčid-bášé réáčtións ánd for eách indicate whether reactants or products are favored at equilibrium. CHCH,ОH + CH;NH3* CH;CH,OH CH;NHNAarrow_forwardWhich compound engages in an acid-base reaction with water? = HC HU HC C H A A NH₂ CH B Both A and B Neither A nor B CH 11 HC=CH CH H HC=C HC <=C UH B CH₂ CH HC=CH CHarrow_forwardWhy is H3C-O-SİH3 ether a weaker base than (CH3)3O?arrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds from the least acidic to most acidic, provide a brief explanation. он он `OH `OH O2N II IVarrow_forward1. Which compound is more soulable in water : CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 OR CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 COOH 2. Which compound is more soulable in organic solvent : CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 OR CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 COOHarrow_forwardh) Which is a weaker base and why? Pyridine Pyrrole i) Name the following compounds. H2N A B NH2arrow_forward
- Rank the following in order of increasing basicity. The first in your list should be the least basic. HO 1 0 3 2 < 1 O2 3<1 01 2<3 01 3<2 3 1< 2 3. 2.arrow_forwardGive a systematic (IUPAC) name for each diol.(a) CH3CH(OH)(CH2)4CH(OH)C(CH3)3 (b) HO¬(CH2)8¬OHarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of increasing acidity, putting the least acidic first. CH3COOH CICH₂COOH CICH₂CH₂OH I O IIIarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


