
(a)
Interpretation:The equation to show the manner
Concept introduction: In accordance with Bronsted definition an acid can act as a proton donor and a base can act as a proton acceptor. Thus in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similar curved arrows are used to show the movement of electrons. After deprotonation, the species left with a negative charge is referred as the conjugate base of acid while the other with a positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example;
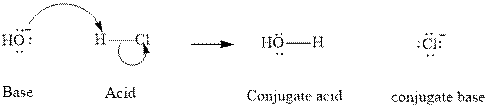
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has a weak conjugate base and the strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa. Smaller the
The order of acidic strength of various alcohols is as follows:
For tertiary alcohols, the steric bulk is maximum that leads to inhibition in solvation of
(b)
Interpretation: The equation to show the manner
Concept introduction: In accordance with Bronsted definition an acid can act as a proton donor and a base can act as a proton acceptor. Thus in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similar curved arrows are used to show the movement of electrons. After deprotonation, the species left with a negative charge is referred as the conjugate base of acid while the other with a positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example;
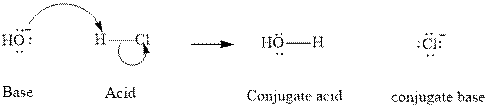
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has a weak conjugate base and the strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.Smaller the
The order of acidic strength of various alcohols is as follows:
For tertiary alcohols, the steric bulk is maximum that leads to inhibition in solvation of
(c)
Interpretation: The equation to show the manner
Concept introduction: In accordance with Bronsted definition an acid can act as a proton donor and a base can act as a proton acceptor. Thus in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similar curved arrows are used to show the movement of electrons. After deprotonation, the species left with a negative charge is referred as the conjugate base of acid while the other with a positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example;
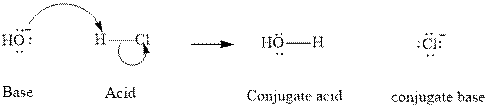
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has a weak conjugate base and the strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.Smaller the
The order of acidic strength of various alcohols is as follows:
For tertiary alcohols, the steric bulk is maximum that leads to inhibition in solvation of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- An alcohol is oxidized to a carboxylic acid, and 0.2003 g of the acid is titrated with 45.25 mL of 0.03811 M NaOH.(a) What is the molar mass of the acid? (b) What are the molarmass and molecular formula of the alcohol?arrow_forward1. (a) Draw the structures of the eight isomeric pentyl alcohols, C3H11OH. (b) Name each by the IUPAC system and by the carbinol system. (c) Label each as primary, secondary, or tertiary, (d) Which one is isopentyl alcohol? tert-Pentyl alcohol? (e) Give the structure of a primary, a secondary, and a tertiary alcohol of the formula C,H13OH.arrow_forwardMTBE, Methyl tert-butyl ether, CH3OC(CH3)3, is used as an oxygen source in oxygenated gasolines. MTBE is manufactured by reacting 2-methylpropene with methanol.(a) Using Lewis structures, write the chemical equation representing the reaction.(b) What volume of methanol, density 0.7915 g/mL, is required to produce exactly 1000 kg of MTBE, assuming a 100% yield?arrow_forward
- (b) Differentiate between bioethanol and biodiesel.arrow_forwardAlcohols A, B, and C all have the composition C4H10O. Molecules of alcohol A contain a branched carbon chain and can be oxidized to an aldehyde; molecules of alcohol B contain a linear carbon chain and can be oxidizedto a ketone; and molecules of alcohol C can be oxidized to neither an aldehyde nor a ketone. Write the Lewis structures of these molecules.arrow_forward(a) When a compound containing C, H, and O is completelycombusted in air, what reactant besides the hydrocarbonis involved in the reaction? (b) What products form in thisreaction? (c) What is the sum of the coefficients in the balancedchemical equation for the combustion of one mole ofacetone, C3H6O1l2, in air?arrow_forward
- Propane, C3H8, is a hydrocarbon that is commonly used as a fuel.(a) Write a balanced equation for the complete combustion of propane gas.(b) Calculate the volume of air at 25 °C and 1.00 atmosphere that is needed to completely combust 25.0 grams of propane. Assume that air is 21.0 percent O2 by volume. (Hint:use the information that 1.00 L of air at 25 °C and 1.00 atm contains 0.275 g of O2 per liter.)(c) The heat of combustion of propane is −2,219.2 kJ/mol. Calculate the heat of formation, ΔH°f of propane given that ΔH°f of H2O(l) = −285.8 kJ/mol and ΔH°f of CO2(g) = −393.5 kJ/mol. (d) Assuming that all of the heat released in burning 25.0 grams of propane is transferred to 4.00 kilograms of water, calculate the increase in temperature of the water.arrow_forwardWrite the structural formula for propylene glycol, 1,2-propanediol. Why is it classified as an alcohol? Is it a polar molecule? Should it be miscible with water?arrow_forwardWrite two complete, balanced equations for each of the following reactions, one using condensed formulas and one using Lewis structures:(a) ethanol reacts with propionic acid(b) benzoic acid, C6H5CO2H, is added to a solution of sodium hydroxidearrow_forward
- Glucose, C6H12O6, contains an aldehyde group but exist predominantly in the form of the cyclic hemiacetal show below. A cyclic hemiacetal is formed when the —OH group of one carbon bonds to the carbonyl group of another carbon. Identify which carbon provides the —OH group and which provides the —CHO? Give a functional isomer of glucose and draw its structure.arrow_forward5) Provide complete and balanced chemical reactions for the following. Write the formula and the name of the alcohol that when dehydrated, gives rise to the following alkenes. Give complete reactions. (а) СH-CH,CH-CH-CHCH-CHa (b) • 3-ethyl-1-hexanol is a primary alcohol. Give the two complete oxidation reactions using potassium permanganate.arrow_forward5.Write the structural formula of the ester that, when hydrolyzed, would yield the following:(a) methanol and propanoic acid(b) 1-octanol and acetic acid (c) ethanol and butanoic acidarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
