
(a)
Interpretation:The expected product of
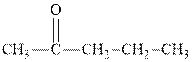
Concept introduction:The carbonyl bond is polar with partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
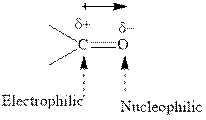
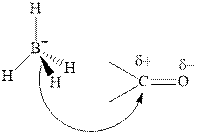
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride. The boron and lithium in these reagents tend to push the electron of
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be chiral or optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
(b)
Interpretation: The expected product of
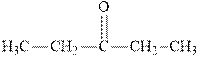
Concept introduction:The carbonyl bond is polar with partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
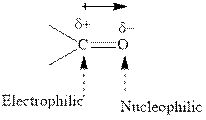
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride. The boron and lithium in these reagents tend to push the electron of
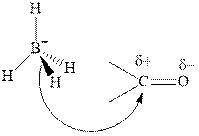
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be chiral or optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
(c)
Interpretation: The expected product of
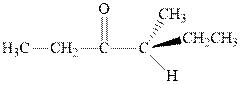
Concept introduction:The carbonyl bond is polar with partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
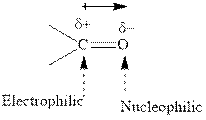
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride. The boron and lithium in these reagents tend to push the electron of
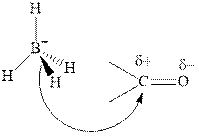
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be chiral or optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
(d)
Interpretation: The expected product of
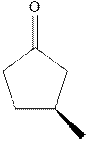
Concept introduction:The carbonyl bond is polar with partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
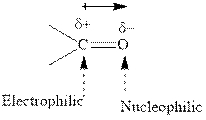
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride. The boron and lithium in these reagents tend to push the electron of
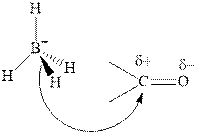
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be chiral or optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
(e)
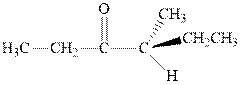
Interpretation: The expected product of
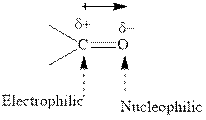
Concept introduction:The carbonyl bond is polar with partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
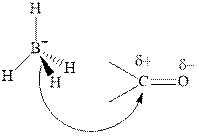
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride. The boron and lithium in these reagents tend to push the electron of
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be chiral or optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





