
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: Thepossible synthetic route for synthesis of menthol from first
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
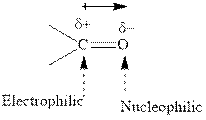
Grignard reagents are
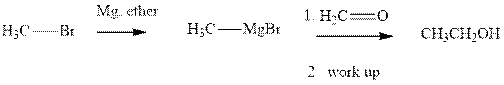
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol. The mechanistic pathway for the latter reaction is as follows:

The polar carbonyl bond breaks and the polar Grignard reagent attack at electron-deficient carbon. Finally with the hydrolysis and work up the alcohol is formed.
(b)
Interpretation: The possible synthetic route for synthesis of ethanol from first aldehyde and second a ketone should be suggested.
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
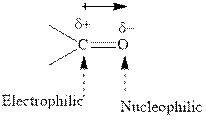
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. These reagents are useful precursors for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
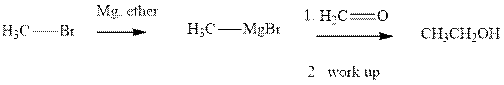
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol. The mechanistic pathway for the latter reaction is as follows:

The polar carbonyl bond breaks and the polar Grignard reagent attack at electron-deficient carbon. Finally with the hydrolysis and work up the alcohol is formed.
(c)
Interpretation: The possible synthetic route for synthesis of
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
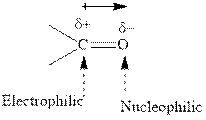
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. These reagents are useful precursors for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
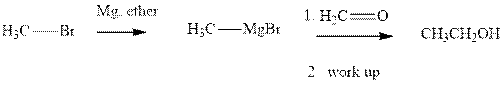
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol. The mechanistic pathway for the latter reaction is as follows:

The polar carbonyl bond breaks and the polar Grignard reagent attack at electron-deficient carbon. Finally with the hydrolysis and work up the alcohol is formed.
(d)
Interpretation: The possible synthetic route for synthesis of
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
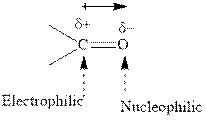
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. These reagents are useful precursors for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
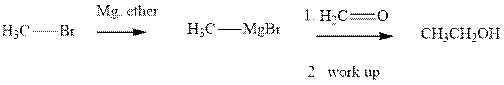
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol. The mechanistic pathway for the latter reaction is as follows:

The polar carbonyl bond breaks and the polar Grignard reagent attack at electron-deficient carbon. Finally with the hydrolysis and work up the alcohol is formed.
(e)
Interpretation: The possible synthetic route for synthesis of
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
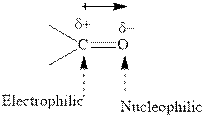
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. These reagents are useful precursors for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
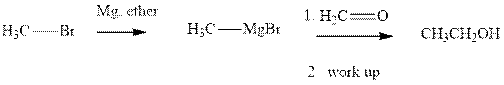
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol. The mechanistic pathway for the latter reaction is as follows:

The polar carbonyl bond breaks and the polar Grignard reagent attack at electron-deficient carbon. Finally with the hydrolysis and work up the alcohol is formed.
(f)
Interpretation: The possible synthetic route for synthesis of
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
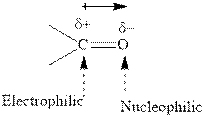
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. These reagents are useful precursors for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
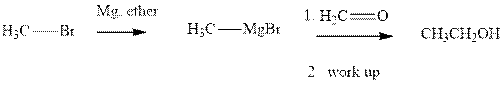
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol. The mechanistic pathway for the latter reaction is as follows:

The polar carbonyl bond breaks and the polar Grignard reagent attack at electron-deficient carbon. Finally with the hydrolysis and work up the alcohol is formed.
(g)
Interpretation: The possible synthetic route for synthesis of
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
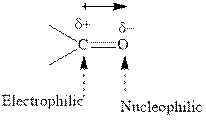
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. These reagents are useful precursors for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
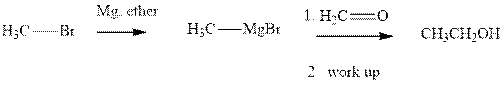
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol. The mechanistic pathway for the latter reaction is as follows:

The polar carbonyl bond breaks and the polar Grignard reagent attack at electron-deficient carbon. Finally with the hydrolysis and work up the alcohol is formed.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- 2. Provide the reagents required to complete the following multi-step synthesis. Write the structure of the product after each synthetic step.arrow_forward1. Determine the structure of Grignard reagent and carbonyl compound as the starting materials to produce the following alcohols. он b) CH,OH LOH d) Lon онarrow_forwardGIVE THE COMPLETE PRODUCT OF THE FOLLOWING REAGENTS.arrow_forward
- 8) Show how the following conversions might be accomplished, including all reagents and intermediates. Br Y. OHarrow_forward5. Synthesize the following compounds by using cyclohexanone and propene as your only sources of carbon. Any other needed reagents are available.arrow_forwardStep 3: If excess alcohol is present in the hemiacetal, the hemiacetal can be further converted to an acetal product, but only in the presence of acid. R₁ R₂ R3OH, H+ HO OR3 R3OH, H+ R3Q OR 3 + H2O R₁ R₁ R₂ hemiacetal acetal Why is acid required? The alkoxy group in the hemiacetal must first be converted into a good leaving group. Acid stabilizes the product. Acid stabilizes the hemiacetal, making it more reactive. The hydroxy group in the hemiacetal must first be converted into a good leaving group.arrow_forward
- b) The Wolf-Kishner reduction is a reaction used in Organic Chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene group. The reaction was used to convert an aldehyde or ketone to an alkane using hydrazine, base and thermal conditions. The mechanism begins with the attack of hydrazine of the aldehyde or ketone. Stage 1: The reaction of aldehyde/ketone with hydrazine to produce hydrazine Stage 2: Reaction with the base and heat to convert hydrozone to alkane Write the mechanism of the reaction.arrow_forwardFill in the blanks with the MAJOR organic product in the following reactions.arrow_forwardFrom benzaldehyde, compunds of 2 carbons or less, and any inorganic reagent you want synthesize the following compound.arrow_forward
- Which reagent(s), if any, may be used to carry out the following reactionarrow_forwardProvide the missing reagent(s) to complete the reaction below, more than one step may be required. Be sure to indicate the amount needed of any reagents, if necessary.arrow_forwardProvide the necessary reagents to complete the following reaction in multiple steps. You may only use alcohols as the starting precursors whose carbon atoms are incorporated into the final product. ОНarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


