
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:The major product of indicated reaction should be identified.
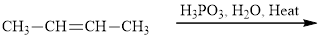
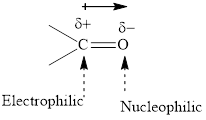
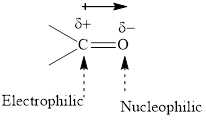
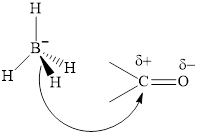
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial postive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
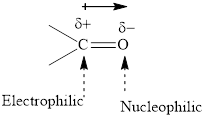
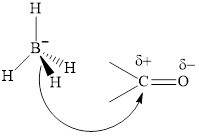
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride. The boron and lithium in these reagents tend to push the electron of
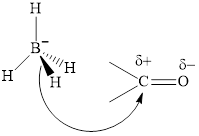
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be chiral or optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
(b)
Interpretation:The major product of indicated reaction should be identified.
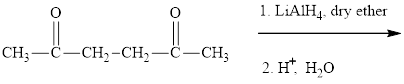
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial postive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
The aluminum and lithium in these reagents such as
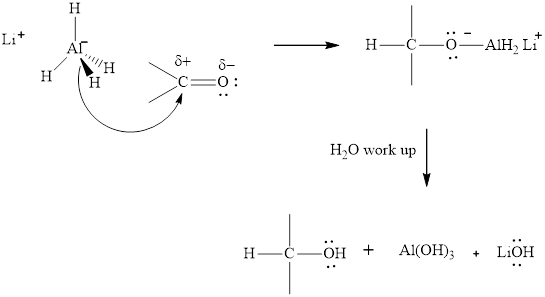
(c)
Interpretation: The major product of indicated reaction should be identified.
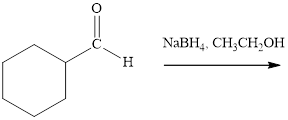
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial postive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride. The boron and lithium in these reagents tend to push the electron of
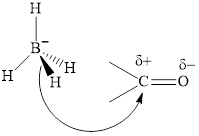
(d)
Interpretation: The major product of indicated reaction should be identified.

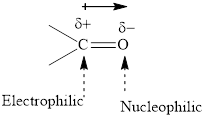
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial postive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
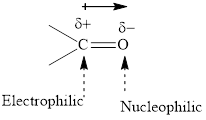
The aluminum and lithium in these reagents such as
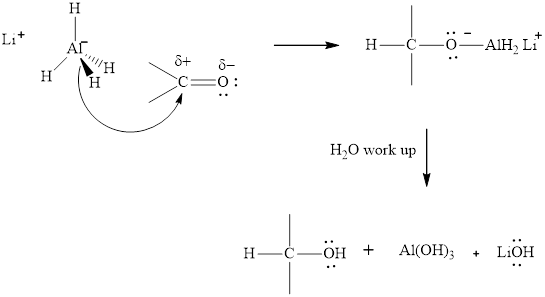
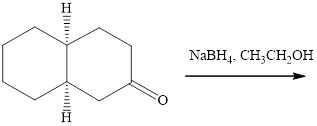
(e)
Interpretation: The major product of indicated reaction should be identified.
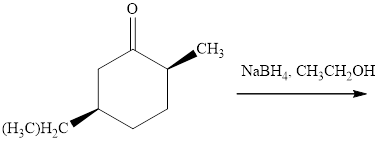
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial postive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride. The boron and lithium in these reagents tend to push the electron of
(f)
Interpretation: The major product of indicated reaction should be identified.
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial postive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
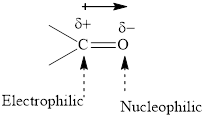
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride. The boron and lithium in these reagents tend to push the electron of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- 4. Write a mechanism to account for the product formed in each of the following reactions. Use arrows to show electron flow and include the structure of all reaction intermediates CHCH.CCH₂ B₂ CH,COOH 9 CH,CHCCH Br 00/th HBarrow_forwardGive the minor product of the following reaction. CO,Me heat CO,Me CO,Me cO, Me cO, Me co, Me H. Meo, co,Me There is no reaction under these conditions or the correct product is not listed here.arrow_forwardCH3 CH3 Br- Br2 .CH3 CH2Cl2 CH3 H3C H3C Br Electrophilic addition of bromine, Brɔ, to alkenes yields a 1,2-dibromoalkane. The reaction proceeds through a cyclic intermediate known as a bromonium ion. The reaction occurs in an anhydrous solvent such as CH,Cl,. In the second step of the reaction, bromide is the nucleophile and attacks at one of the carbons of the bromonium ion to yield the product. Due to steric clashes, the bromide ion always attacks the carbon from the opposite face of the bromonium ion so that a product with anti stereochemistry is formed. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow-pushing Instructions CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 H3C H3C :Br: :Br:arrow_forward
- Write the MAJOR product(s) for each of the following reactions. (Write only one product UNLESS the reaction has both a 1,2 and a 1,4 product). You can either write the structure(s) of the product(s)arrow_forwardPredict the product of the following organic reaction: CH₂ CH O || C–CH2–CH=CH—(CH2)3 CH3 (CH₂)3 CH=CH- - CH₂ CH3 + 4 H₂ Ni CH,−O -C–CH2–CH=CH–CH=CH–CH2–CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below, draw the chemical structure of the product P. If there is no product, because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. × Ś +arrow_forward2) What is the product of the following reaction? HBr Br₂ H₂O 3) Write the product of the following reaction. CH₂OHarrow_forward
- You are trying to determine whether the following organic reaction can be done in a single synthesis step. If so, add any missing reagents or conditions in the drawing area below. If it isn't possible to do this reaction in a single synthesis step, check the box below the drawing area instead. 口 OH : + T X Clarrow_forwardWhat is the final product (B) of the following reaction? CH3 Br2 1. KCN light → B 2. H30*, heat CH3 CO2H CO,H CH3 CH2CO2H (a) (d) `CO2Harrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: CH3 O I || CH3−O−CH -C OH + NaOH A No reaction ? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. Xarrow_forward
- Draw the organic product you would expect to isolate from the nucleophilic substitution reaction between the molecules shown. Note: You do not need to draw any of the side products of the reaction, only the substitution product. H × 5 Br + HO + 1 Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardGive the major product(s) of the following reaction. ? HBr (1 mole) Br Br 1 Br Br Br Br There is no reaction under these conditions or the correct product is not listed here.arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: + 2 H₂ No reaction. Pt ? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal structure of each product. If there's more than one product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. If there is no reaction, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X :0 Śarrow_forward
