
(a)
Interpretation:The product formed in indicated reaction should be formulated and whether it is chiral and shows any optical activity or not should be determined.
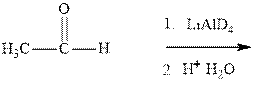
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
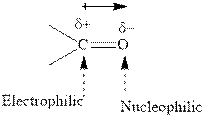
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include
Optical activity refers to ability to rotate the plane polarized light. For example, if the light is passed through a substance and the light that emerges has radiations are confined to one plane only the substance is said to be optically active.
The earliest criteria for optical activity were presence of a chiral center. The chiral refer to species attached to four different substituents. Chiral center leads to existence of organic compounds as two enantiomeric forms. However chiral center alone is not sufficient condition for determination of optical activity.
The criteria to identify the optical activity are to look for absence of any symmetry element. The symmetry elements make any molecule optically inactive.
(b)
Interpretation: The product formed in indicated reaction should be formulated and whether it is chiral and shows any optical activity or not should be determined.

Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
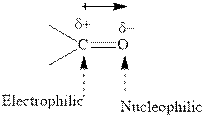
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include
Optical activity refers to ability to rotate the plane polarized light. For example, if the light is passed through a substance and the light that emerges has radiations are confined to one plane only the substance is said to be optically active.
The earliest criteria for optical activity were presence of a chiral center. The chiral refer to species attached to four different substituents. Chiral center leads to exists of organic compounds as two enantiomeric forms. However chiral center alone is not sufficient condition for determination of optical activity.
The criteria to identify the optical activity are to look for absence of any symmetry element. The symmetry elements make any molecule optically inactive.
(c)
Interpretation: The product formed in indicated reaction should be formulated and whether it is chiral and shows any optical activity or not should be determined.
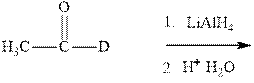
Concept introduction:The carbonyl bond is polar with partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
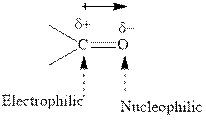
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include
Optical activity refers to ability to rotate the plane polarized light. For example, if the light is passed through a substance and the light that emerges has radiations are confined to one plane only the substance is said to be optically active.
The earliest criteria for optical activity were presence of a chiral center. The chiral refer to species attached to four different substituents. Chiral center leads to exists of organic compounds as two enantiomeric forms. However chiral center alone is not sufficient condition for determination of optical activity.
The criteria to identify the optical activity are to look for absence of any symmetry element. The symmetry elements make any molecule optically inactive.
(d)
Interpretation: The product formed in indicated reaction should be formulated and whether it is chiral and shows any optical activity or not should be determined.

Concept introduction:The carbonyl bond is polar with partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
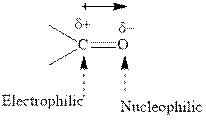
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include
Optical activity refers to ability to rotate the plane polarized light. For example, if the light is passed through a substance and the light that emerges has radiations are confined to one plane only the substance is said to be optically active.
The earliest criteria for optical activity were presence of a chiral center. The chiral refer to species attached to four different substituents. Chiral center leads to exists of organic compounds as two enantiomeric forms. However chiral center alone is not sufficient condition for determination of optical activity.
The criteria to identify the optical activity are to look for absence of any symmetry element. The symmetry elements make any molecule optically inactive.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- For each of the following compounds,determine whether each is optically active. For optically active compounds, identify the chiral carbon: ethane, 2-chloro-2-methylbutane, CH3CH(NH2)COOH, CH3CH2CHClCH3and CH3CH2CH2CH3. And for non-optical active compounds, just provide the structure of the compoundarrow_forwardHow many different organic products are possible when pentan-2-ol is heated in the presence of acid? Ignore any stereoisomers (cis/trans isomers).arrow_forwardProvide the name of the following hydrocarbon. CI 0 D Br 0 0 Provide the name of the following structure. xx : 0 0 0 For the structure below, provide (type): The number of chiral centers; The total number of primary H-atoms: The total number of secondary H-atoms: The total number of tertiary H-atoms: The maximum number of stereoisomers: 0 + • 0 0 0 0 How many different primary chlorides can be obtained as possible radical chlorination products? Please answer all parts of the questionarrow_forward
- In the following structure I have abbreviated the long carbon chain as an R group. Provide the two major products of the following reaction (Hint: Must consider stereochemistry!). HO H R H Br₂ What is the isomeric relationship of the two products?arrow_forwardThere are four isomers with the molecular formula C4H9Cl. Only one of these isomers (compound A) has a chiral center. When compound A is treated with sodium ethoxide, three products are formed: compounds B, C, and D. Compounds B and C are diastereomers, with compound B being the less stable diastereomer. Provide structures for compounds A, B, C, and D. Do you expect compound D to exhibit a signal at approximately 1650 cm−1 in its IR spectrum? Explain.arrow_forwardIn addition to more highly fluorinated products, fluorination of 2-methylbutane yields a mixture of compounds with the formula C5H10F2. Draw the structures of all the isomers with the formula C5H10F2 that would be produced and label with a star all the chiral centers present in their structures.arrow_forward
- Cr(VI) compounds are common reagents for the oxidation of alcohols. Primary alcohols are oxidized to carboxylic acids and secondary alcohols are oxidized to ketones. The mechanism involves a reaction similar to the E2 elimination, whereby a C=O double bond is formed with a reduced Cr(IV) compound as the leaving group.Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism.arrow_forwardWrite the structure of the compound that will be produced in the following reaction? CH3 –C ≡ C–CH2– CH2 – CH3 + 2HBr→arrow_forward-Tetrahedral representation of the enantiomers of the structure below -tetrahedral representations of both R and S enantiomers of the structure below -what functional groups does the given structure posses?arrow_forward
- A compound with formula C7H12O is treated with sodium borohydride in methanol to yield 2,2-dimethylcylopentanol. Write a reaction scheme showing the structures of the reactant, the reagents, and the product. Will the product be optically active? Explain.arrow_forwardThe stereochemistry of the products of reduction depends on the reagent used, as you learned in Sections 20.5 and 20.6. With this in mind, how would you convert 3,3-dimethylbutan-2-one [CH3COC(CH3)3] to: (a) racemic 3,3-dimethylbutan-2- ol [CH3CH(OH)C(CH3)3]; (b) only (R)-3,3-dimethylbutan-2-ol; (c) only (S)-3,3-dimethylbutan-2-ol?arrow_forwardThe following chemical reaction is used to synthesize a flavouring agent that has an aroma similar to bananas. H₂SO4(aq) CH3COOH(1) + CH₂(CH₂)₂OH(1) I || Identify the type of reaction that is represented by this synthesis. Select one: O hydrogenation O esterification O addition O substitution O elimination Identify the functional group and the IUPAC name for each of the three compounds in the reaction below: H₂SO4(aq) I Compound Functional Group IUPAC Name II CH₂COOH(1) + CH₂(CH₂)₂OH(1) I || III CH3COO(CH₂)₂CH₂(1) + H₂O(1) III IV ◆ → ◆ CH3COO(CH₂)₂CH₂(1) + H₂O(1) IV ||| ◆ ◆arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

