
Interpretation:Compound that is intended for synthesis by student after aqueous workup should be given and the reason behind the unexpected formation of tertiary alcohol and the manner it is formed should be given.
Concept introduction:Grignard reagents are
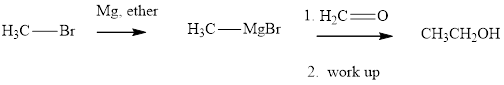
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methylmagnsium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol. The mechanistic pathway for the latter reaction is as follows:
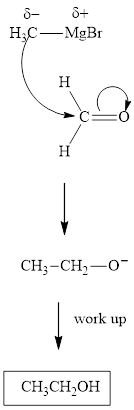
The polar carbonyl bond breaks and the polar Grignard reagent attack at electron-deficient carbon. Finally with the hydrolysis and work up the alcohol is formed.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- 4. Using structures for all species, write the complete esterification reaction begun below: HSO, methanol (CH3OH) + salicylic acidarrow_forwardHO - CH, НО - ОН I CH_ - :0: solute CH ОН - NaCl ОН I CH - CH ОН - :0: || с :0: || - · C — CH2 — CH2 — C — ОН н Which is the better solvent? Н н C | H 1 C C 1 Н CH3- H2O CH₂OH C ||| C CH3(CH2), ОН :0: || S о- CH3 CH₂CH₂OH Н Нarrow_forwardYou have been tasked to assess a new laboratory for safety issues. The lab has a large amount of benzene, hydrochloric acid, phenol, sodium hydroxide and toluene. Describe the (5) potential hazards that can be associated with each chemical above, as well as the methods to control their potential hazards in the lab.arrow_forward
- You have a mixture of an aryl halide and a carboxylic acid that you wish to separate(both are solids). Both are soluble in diethyl ether. Explain ALL the steps you would take to obtain the two compounds in pure form from your sample.arrow_forwardYou have a mixture of an aryl halide and a carboxylic acid that you wish to separate (both are solids). Both are soluble in diethyl ether. Explain ALL the steps you would take to obtain the two compounds in pure form from your sample.arrow_forwardPredict the color change if 1% ferric chloride (yellowish solution) is added to a test tube containing a mixture of ethanol and pure acetyl salicylic acid. purple to yellow yellow to dark blue light blue to pink yellow to purple no color change ————— Which of the following will be easily detected (not using any chemical test or instrument) if acetyl salicylic acid is heated in a flame? acetic anhydride acetic acid ethanol salicylic acid ————— Which of the following is NOT a volatile chemical? acetone hexanes benzoic acid methylene chloride petroleum ether ——— All of the following are corrosive chemicals EXCEPT hydrochloric acid sodium hydroxide benzoic acid sulfuric acid nitric acid potassium hydroxidearrow_forward
- If you are given a mixture of three organic compounds (aspirin, β-naphthol, and naphthalene), Write a flow chart to briefly describe the steps involved.arrow_forwardThe disinfection of drinking water to control microbial contaminants can form chemical disinfection byproducts. These compounds result from the reaction of chlorine with naturally occurring organic matter (the dissolved molecules that give natural water the yellow-greenish color). One class of disinfection byproducts is the malodorous and unpalatable chlorophenols. 2,4-dichlorophenol is one compound of this class. a) Calculate the vapor pressure p*L of 2,4-dichlorophenol at 60 °C using Tb and structural information only OH .CI M, = 163.0 g/mol Tm = 43.7 °C Tp = 213.0°C %3D %3D %3Darrow_forwardTrimethylamine, (CH3)3N, is a common reagent. It interacts readily with diborane gas, B₂H6. The latter dissociates to BH3 and this forms a complex with the amine, (CH3)3N→BH3. The reaction between trimethylamine and borane is shown. CH3 CH3 H CH3-N : + B-H CH3-N B-H CH3 H CH3 H Is the BH3 fragment a Lewis acid or a Lewis base? To decide this, answer the following questions: H a Which of the following is a definition of a Lewis acid? proton donor electron pair acceptor proton acceptor electron pair donorarrow_forward
- Which of the following compounds has a different classification according to their solubility? ac NH₂ НО. HS OH OH OH NH₂ Farrow_forwardBox the functional group/s that contribute to the solubility (hydrophilic and lipophilic) of the given organic molecules then check whether the drug molecule is hydrophilic or lipophilic.arrow_forwardIdentify the characteristics of polar protic solvents and polar aprotic solvents, and complete each sentence below. Select all options that correctly complete each sentence. Polar protic solvents do not dissolve ionic compounds well. have a large dipole moment. have at least one H bonded to an N, O, or F. can be hydrogen-bond acceptors. have an easily accessible δ+ charge. Polar aprotic solvents can be hydrogen-bond acceptors have an easily accessible δ+ charge. have at least one H bonded to an N, O, or F. have a large dipole moment. may not dissolve ionic compounds well.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

