
(a)
Interpretation: Bond-line structures for reaction 1 and 2 should be formulated.
Concept introduction: Bimolecular substitution or SN2 proceeds via single-step mechanism. Thus it is well known as concerted mechanism. Nucleophile approaches carbon while the leaving group still departs from the rear side (opposite to leaving group). The transition state only illustrates the geometric orientation of the substrates and reagents as they pass through the maxima in the single-step mechanism.
SN2 pathway as it is a stereospecific reaction. This essentially means the R stereoisomer can only lead to inverted S stereoisomer and vice versa. Thus the outcome is the rear side displacement of leaving group.
(b)
Interpretation: The nature of carbon at reactive site of the starting haloalkane should be identified.
Concept introduction:The carbon linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two H are termed primary carbon. Thus hydrogen linked to such carbon is referred as primary.
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one H is termed secondary carbon. Thus hydrogen linked to such carbon is referred as secondary.
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no H is termed tertiary carbon. Thus hydrogen linked to such carbon is referred as tertiary.
(c)
Interpretation:The manner in that different species would react and possible pathway that describes difference in rate between the reactions should be determined.
Concept introduction: Bimolecular substitution or SN2 proceeds via single -step mechanism. Thus it is well known as concerted mechanism. Nucleophile approaches carbon while the leaving group still departs from the rear side (opposite to leaving group). The transition state only illustrates the geometric orientation of the substrates and reagents as they pass through the maxima in the single-step mechanism.
SN2 pathway as it is a stereospecific reaction. This essentially means the R stereoisomer can only lead to inverted S stereoisomer and vice versa. Thus the outcome is the rear side displacement of leaving group.
(d)
Interpretation: Hashed-wedged line structures to make a three-dimensional pathway to describe the trajectory should be drawn.
Concept introduction: Bimolecular substitution or SN2 proceeds via single -step mechanism. Thus it is well known as concerted mechanism. Nucleophile approaches carbon while the leaving group still departs from the rear side (opposite to leaving group). The transition state only illustrates the geometric orientation of the substrates and reagents as they pass through the maxima in the single-step mechanism.
A general SN2reaction mechanistic pathway is illustrated below:
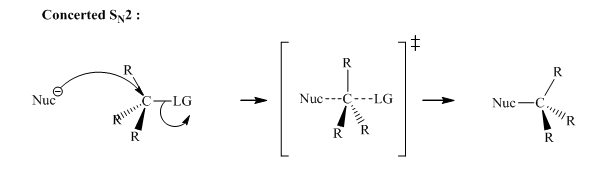
SN2 pathway as it is a stereospecific reaction. This essentially means the R stereoisomer can only lead to inverted S stereoisomer and vice versa. Thus the outcome is the rear side displacement of leaving group.
Polar-aprotic solvents accelerate the rate of SN2 reactions. These solvents possess partial positive and negative charges also. However, they do not liberate any proton to the substrate unlike water, methanol solvents. Acetone, DMSO, THF or DMF are categorized as
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Which of the m/z values corresponds to the base peak in the mass spectrum shown? 100 80 A. 45 B. 44 C. 29 D. 15 Intensity 20 0 10 20 30 40 B- m/z -8 50 E. 30 Which of the m/z values correspond to the molecular ion for the compound shown? A. 18 B. 82 OH C. 100 D. 102 E. 103arrow_forwardCan someone help me with drawing my arrows.arrow_forwardCan I get help drawing my arrows #2arrow_forward
- Can I get some help with my arrows? I have included what the final outcome needs to look like. #3arrow_forwardPlease explain how to calculate the pH.arrow_forwardI'm having trouble with converting lewis diagrams into VSEPR diagrams. I currently have this example of C2BrCl3 which I want to turn into a lewis structure, but I'm not sure what steps I need to do in order to do so. I have the table written down, however, there's two central atoms so what would I do? There seems to be 4 electron domains on the carbon atom and no lone pairs so it would seem like this shape would be tetrahedral. Here's what I have now. Thanks!arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
