
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: Primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogen in below structure along with IUPAC name should be labeled.
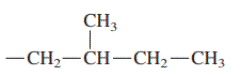
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
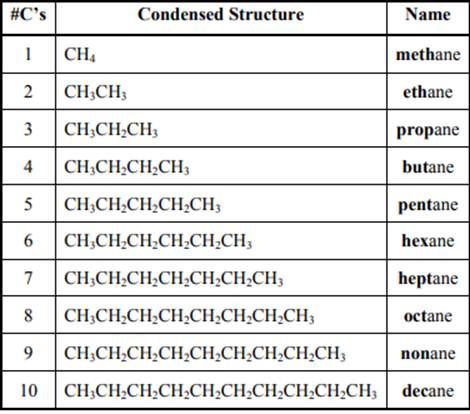
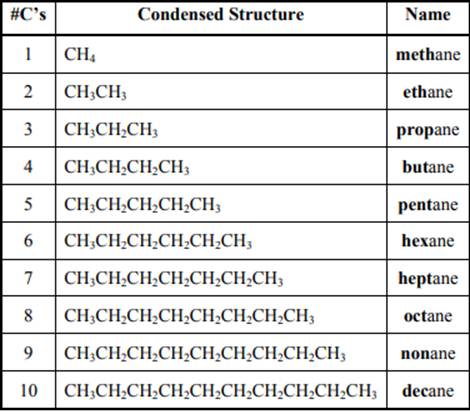
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
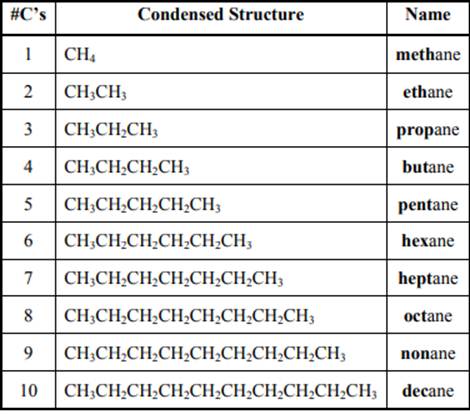
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes include prefixes “iso-” and “neo-”. For example, isobutane is common name used popularly for
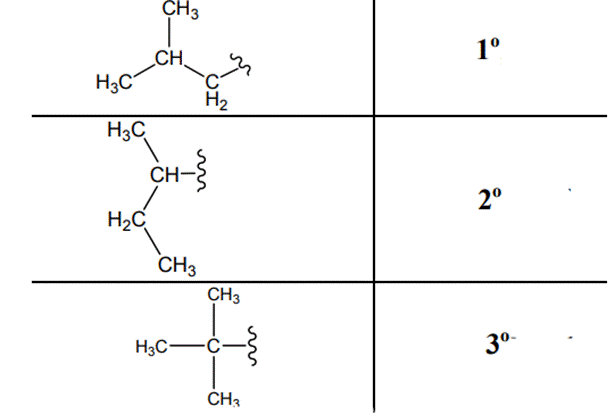
The carbon linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
(b)
Interpretation: Primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogen in below structure along with IUPAC name should be labeled.
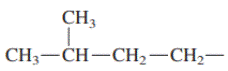
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes include prefixes “iso-” and “neo-”. For example, isobutane is common name used popularly for
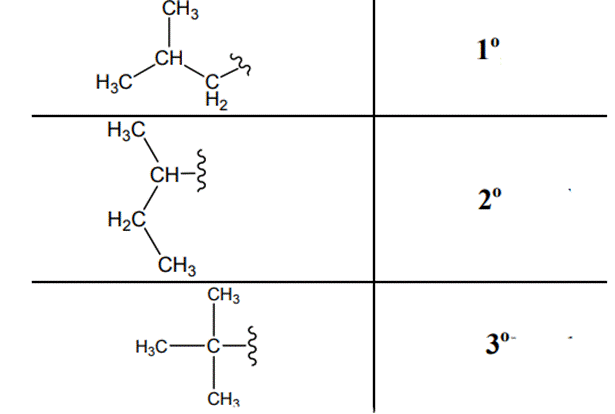
The carbon linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
(c)
Interpretation: Primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogen in below structure along with IUPAC name should be labeled.
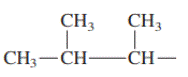
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
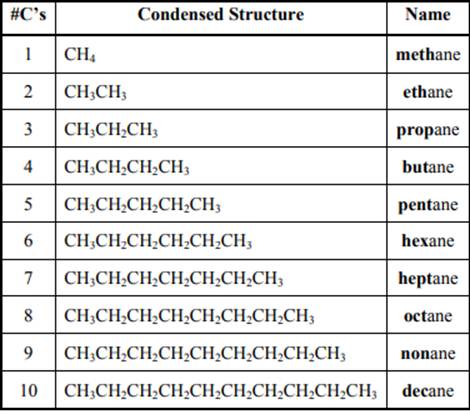
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes” iso-“ and “neo-“ .For example isobutane is common name used popularly for
The carbon linked to one alkyl / carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
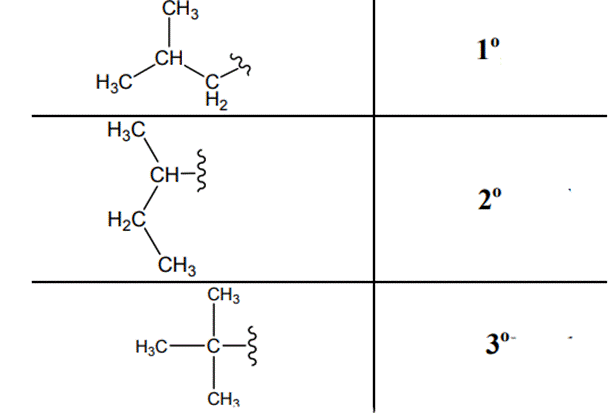
(d)
Interpretation: Primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogen in below structure along with IUPAC name should be labeled.
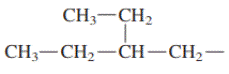
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
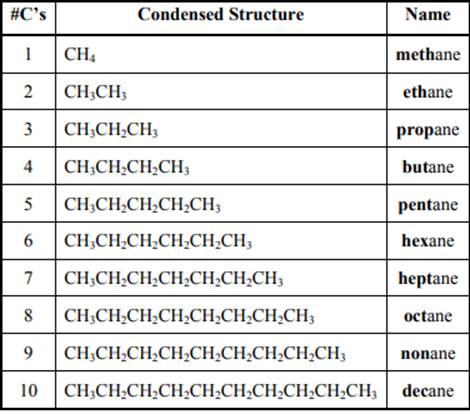
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes” iso-“ and “neo-“ .For example isobutane is common name used popularly for
The carbon linked to one alkyl / carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
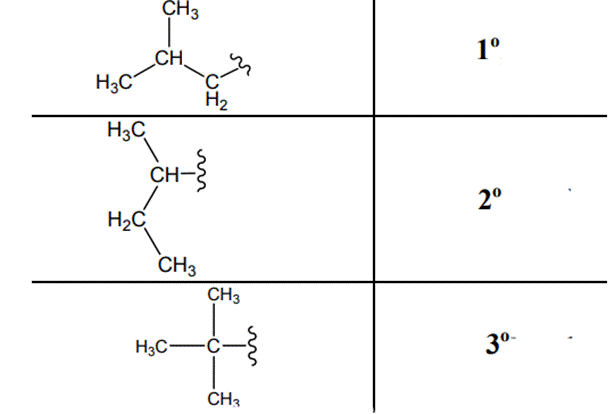
(e)
Interpretation: Primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogen in below structure along with IUPAC name should be labeled.
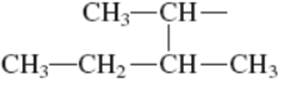
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
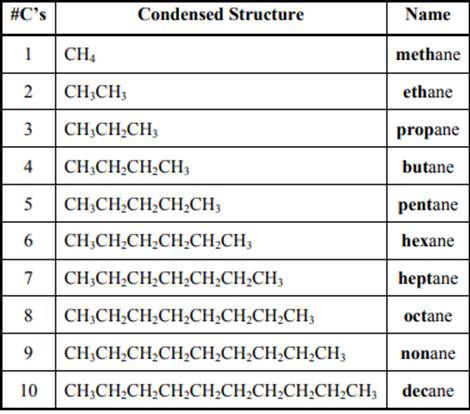
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes” iso-“ and “neo-“ .For example isobutane is common name used popularly for
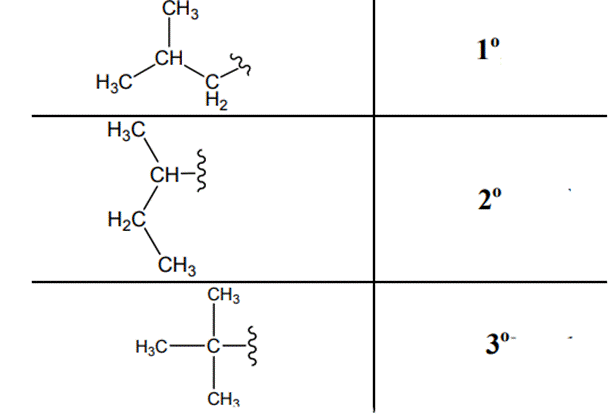
The carbon linked to one alkyl / carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
(f)
Interpretation: Primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogen in below structure along with IUPAC name should be labeled.
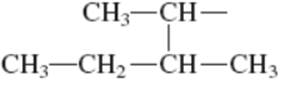
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
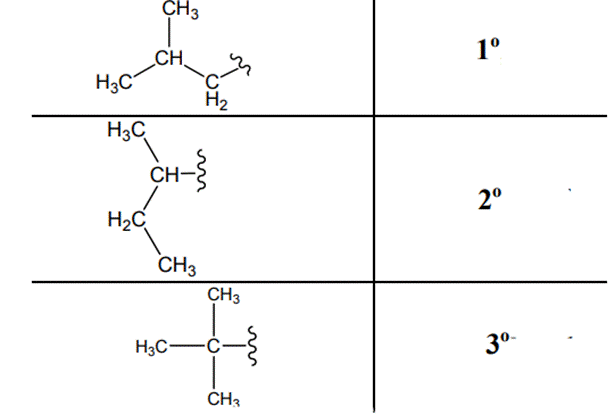
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes” iso-“ and “neo-“ .For example isobutane is common name used popularly for
The carbon linked to one alkyl / carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Give the complete IUPAC name (with E/Z designation) of the following alkynes and aromatic compounds.arrow_forwardGive the structural formula (condensed or skeletal) of the given IUPAC names of saturated hydrocarbons. 1) 2-methyl-3-oxohept-4-enoic acid 2) 4-chloro-2-oxohexanoyl chloride 3) 4-nitro-4-propoxybut-1-ene 4) 1-hydroxyhex-5-yn-2-one 5) 1-methylpropyl 3-amino-3-(1-methylpropoxy)propanoate 6) 1-ethoxy-3-mercaptohexane-2-thionearrow_forward(a) Alkenes are relatively stable compounds but are more reactive than alkanes and serve as a feedstock for the petrochemical industry because they can participate in a wide variety of reactions. Predict the products obtained from following reaction. Write the chemical reaction and name the products according to IUPAC system. (i) the reaction of 3-ethyl-3-methyl-1-pentene with hydrogen bromide (ii) the reaction of 3-ethyl-2-pentene with hydrogen bromidearrow_forward
- Given each of the IUPAC names provided, draw the corresponding structure. (a) 1-ethoxypropane; (b) 2-ethoxypropane;(c) 1,2,3-trimethoxybutanearrow_forwardGive the IUPAC name for the organic compound shown here: C-C-O-C-C-Carrow_forwardAll about Alkene, Alkyne and Alkyl halides Write a complete chemical equation showing reactants, products, and catalysts needed (if any) for the following reaction and Draw and name the organic compound found in every reaction (A) Reaction of 3,4-Dimethylcyclodecyne with sodium amidearrow_forward
- Give the IUPAC and common name of the following hydrocarbons just like how it was shown in the example belowarrow_forwardClassify alkyl halides as primary, secondary, tertiary, aliphatic, or benzenearrow_forwardProvide the appropriate IUPAC name for the following organic molecules 0 CH₂CH₂C=CCHCH₂CH₂ L CH₂ CH₂ CH3CH₂CH=C-CH3 Br OH -Farrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,

