
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: Primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogen in structure of ethane should be labeled.
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
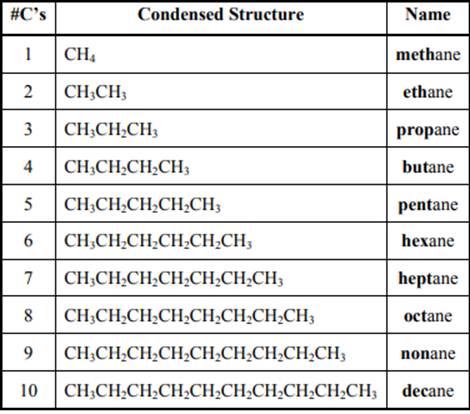
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
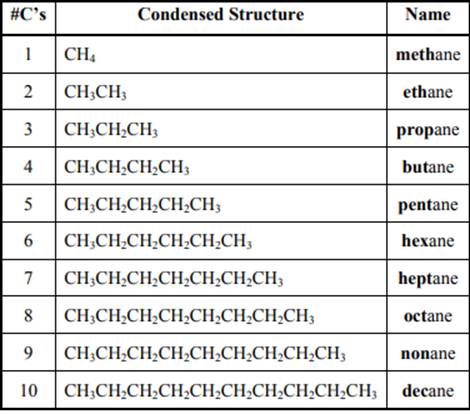
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes “iso-” and “neo-”.For example, isobutane is common name used popularly for
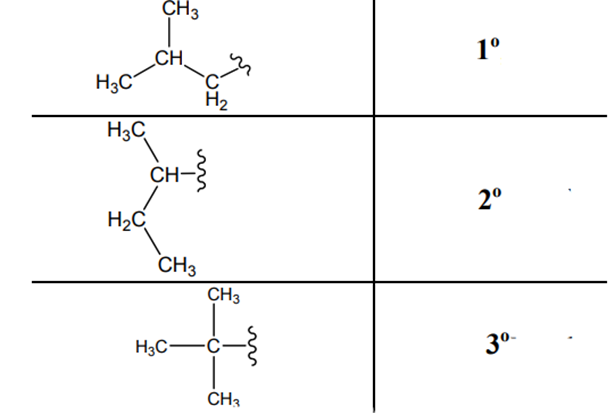
The carbon linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
(b)
Interpretation: Primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogen in structure of pentane should be labeled.
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
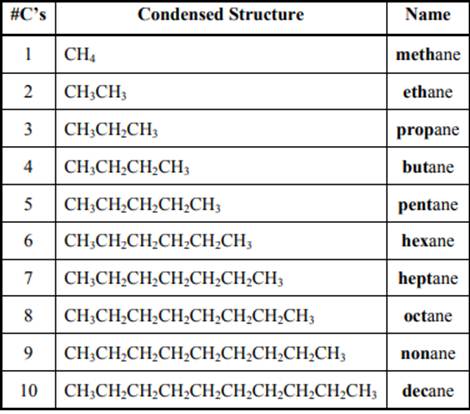
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes “iso-” and “neo-”.For example, isobutane is common name used popularly for
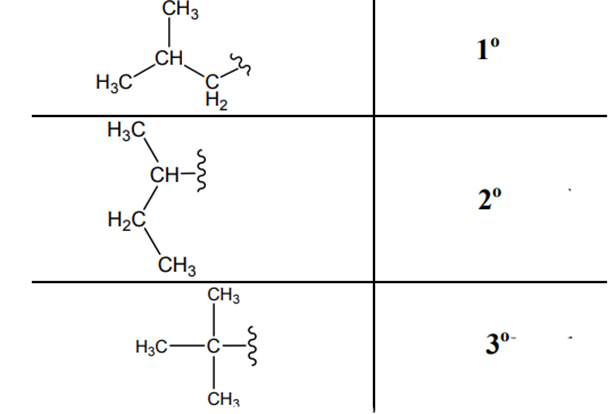
The carbon linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
(c)
Interpretation: Primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogen in structure of
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
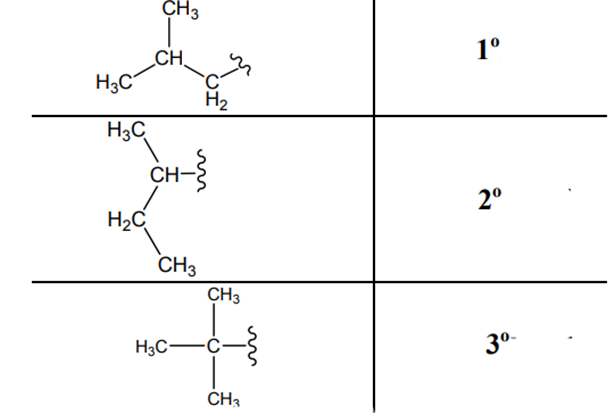
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes “iso-” and “neo-”. For example, isobutane is common name used popularly for
The carbon linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
(d)
Interpretation: Primary, secondary and tertiary carbons in structure of
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
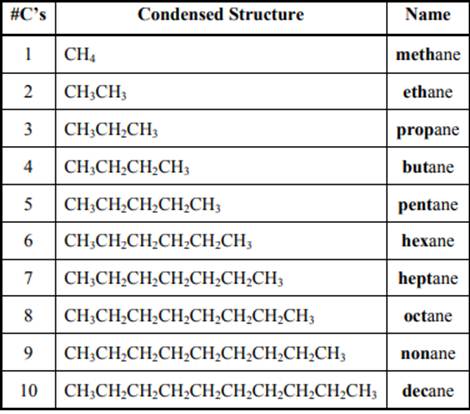
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes “iso-” and “neo-”. For example, isobutane is common name used popularly for
The carbon linked to one alkyl/carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Name these organic compounds: structure name CH3 3-methyl-1-butyne CH; - CH –C= CH CH, CH, — сн, — с. CH; - CH; CH,-C= CH – CH,arrow_forwardName the family to which each organic compound belongs. The first answer has been filled in for you. compound CH,—NH, CH3-C- CH3 || O CH₂=CH-OH CH,=0=CH=CH, family aminearrow_forwardWhich chemical formulas represent organic compounds and which represent inorganic compounds: (a) H 2SO 4; (b) Br 2; (c) C 5H 12?arrow_forward
- For each of the following hydrocarbons, state how manycarbon atoms are in each molecule:(a) methane(b) decane(c) 2-methylhexane(d) neopentane(e) acetylenearrow_forward(a) What is meant by the term isomer ? (b) Among the four alkanes, ethane, propane, butane, and pentane, which is capable of existing in isomeric forms?arrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure O || H-C—CH-CH3 OH H—C–CH2–CH2–CH3 || HỌ—CH,—CH,—CH–CH OH name Ú 0 0arrow_forward
- Name these organic compounds: structure name CH3 CH; - CH — С CH CH, Cн — сн,— с — сн, - CH, CH,: C- CH;arrow_forwardB. Molecular Models of Hydrocarbon Derivatives 1. Organic Halides (a) "methyl chloride," CH3-CI (b) "ethyl iodide," CH3CH2-I 2. Alcohols (a) methanol, CH3-OH ("methyl alcohol") (b) ethanol, CH3CHz-OH ("ethyl alcohol") (c) 1-propanol, CH3CH;CH2 OH ("propyl alcohol") (d) 2-propanol, CH;CH(OH)CH3 ("isopropyl alcohol") 3. Phenols (a) phenol, CHs-OH (b) ortho-methyl phenol, C&H4(CH3)-OH 4. Ethers (a) "dimethyl ether," CH3-O-CH3 (b) "diethyl ether," CH;CH2 O-CH2CH3 5. Amines (a) "methyl amine," CH3-NH2 (b) "ethyl amine," CH3CH2-NH2 280 Experiment 23 Copyright ©2019 Pearson Education, Inc.arrow_forwardFor each of the following hydrocarbons, state how many carbon atoms are in each molecule: (a) 2-methylhexane (b) neopentane (c) acetylenearrow_forward
- (a) Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the combustion of 1 mol of benzene, C6H61l2, to CO21g2 and H2O1l2.(b) Compare the quantity of heat produced by combustion of 1.00 g propane with that produced by 1.00 g benzene.arrow_forwardName or write the condensed structural formula for the fol- lowing compounds: (a) trans-2-pentene (b) 2,5-dimethyl-4-octene (c) CH3 CH;CHCH,CH3 C=C `H. CH;CH2, H СООН H CH3 CH CH3 CH3 `CH2 (d)arrow_forwardMTBE, Methyl tert-butyl ether, CH3OC(CH3)3, is used as an oxygen source in oxygenated gasolines. MTBE is manufactured by reacting 2-methylpropene with methanol.(a) Using Lewis structures, write the chemical equation representing the reaction.(b) What volume of methanol, density 0.7915 g/mL, is required to produce exactly 1000 kg of MTBE, assuming a 100% yield?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





