
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The following molecule should be named according to the IUPAC system of nomenclature:
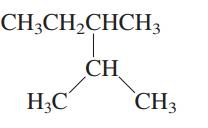
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes” iso-“ and “neo-“ .For example isobutane is common name used popularly for
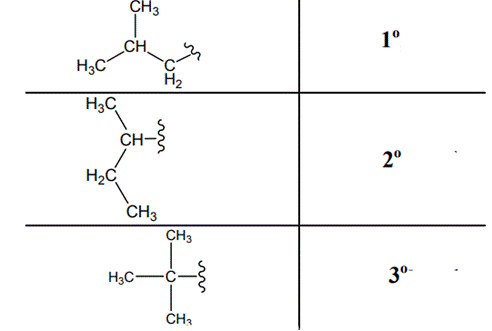
The carbon linked to one alkyl / carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
(b)
Interpretation: The following molecule should be named according to the IUPAC system of nomenclature:
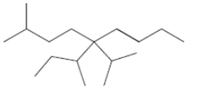
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes” iso-“ and “neo-“ .For example isobutane is common name used popularly for
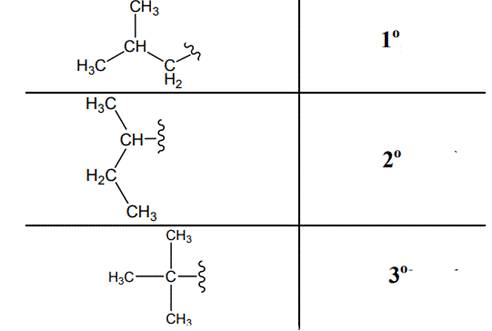
The carbon linked to one alkyl / carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
(c)
Interpretation: The following molecule should be named according to the IUPAC system of nomenclature:
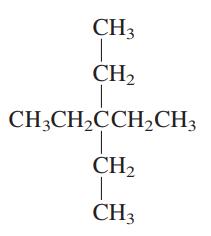
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes” iso-“ and “neo-“ .For example isobutane is common name used popularly for
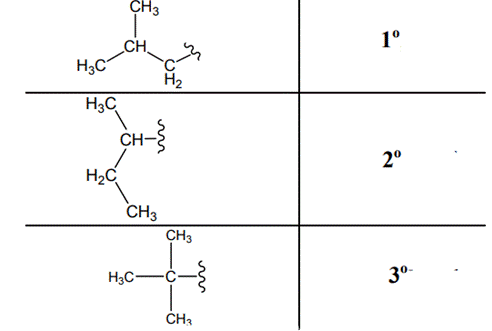
The carbon linked to one alkyl / carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
(d)
Interpretation: The following molecule should be named according to the IUPAC system of nomenclature:
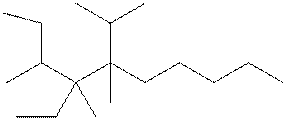
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes” iso-“and “neo-“.For example isobutane is common name used popularly for
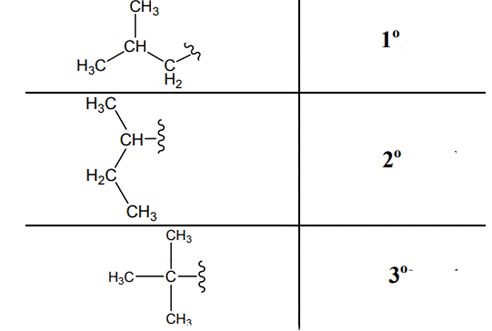
The carbon linked to one alkyl / carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
(e)
Interpretation: The following molecule should be named according to the IUPAC system of nomenclature:
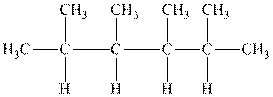
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes” iso-“and “neo-“.For example isobutane is common name used popularly for
The carbon linked to one alkyl / carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
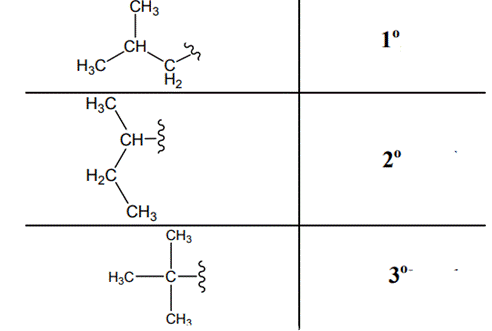
(f)
Interpretation: The following molecule should be named according to the IUPAC system of nomenclature:
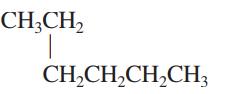
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes” iso-“and “neo-“.For example isobutane is common name used popularly for
The carbon linked to one alkyl / carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
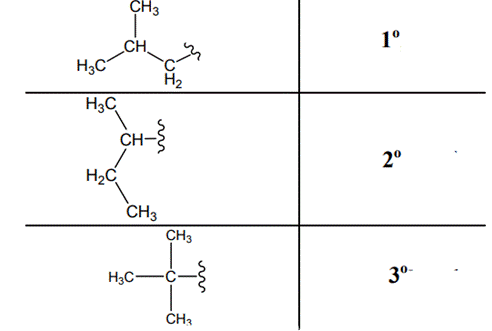
(g)
Interpretation: The following molecule should be named according to the IUPAC system of nomenclature:
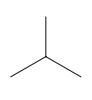
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes” iso-“and “neo-“.For example isobutane is common name used popularly for
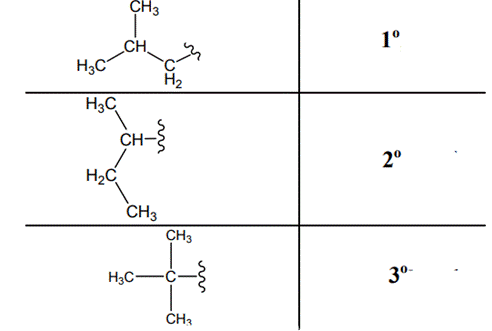
The carbon linked to one alkyl / carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
(h)
Interpretation: The following molecule should be named according to the IUPAC system of nomenclature:
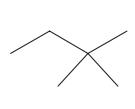
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes” iso-“and “neo-“.For example isobutane is common name used popularly for
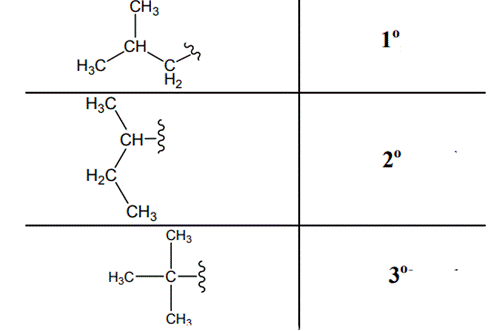
The carbon linked to one alkyl / carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
(i)
Interpretation: The following molecule should be named according to the IUPAC system of nomenclature:
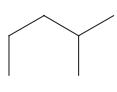
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes” iso-“and “neo-“.For example isobutane is common name used popularly for
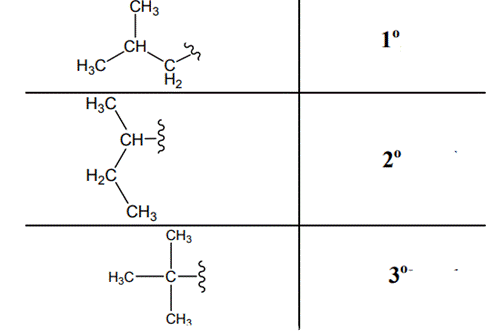
The carbon linked to one alkyl / carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated below:
(j)
Interpretation: The following molecule should be named according to the IUPAC system of nomenclature:
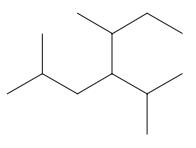
Concept introduction: In accordance with IUPAC convention longest chain can be found from either direction provided it is longest and digits indicate the position of carbon or the position of branched alkyl chain in cases of branched hydrocarbons. All the side chains are named in alphabetical order.
The IUPAC system for nomenclature of straight hydrocarbon makes use of table given as follows:
Beside the IUPAC names there are certain common names. The common prefixes used include prefixes” iso-“and “neo-“.For example isobutane is common name used popularly for
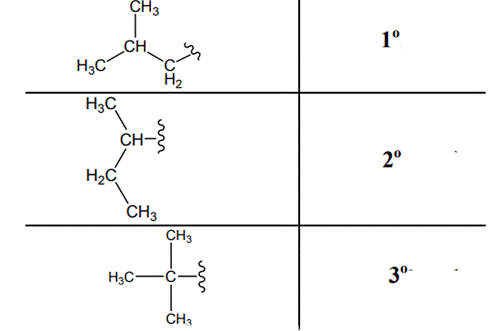
The carbon linked to one alkyl / carbon while other two
The carbon linked to two alkyl /carbons and one
The carbon linked to three alkyl groups/carbons and no
These are indicated as follows:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Arrange these compounds in order of increasing boiling point (values in C are 42, 24, 78, and 118). (a) CH3CH2OH (b) CH3OCH3 (c) CH3CH2CH3 (d) CH3COOHarrow_forwardThe following names are incorrect by IUPAC rules. Determine the correct IUPAC name for each compound. a. 2-Methyl-4-pentene b. 3-Methyl-2,4-pentadiene c. 3-Methyl-3-cyclopentene d. 1,2-Dimethyl-3-cyclohexenearrow_forwardGive the systematic (IUPAC) name for each molecule. This molecule has the condensed formula CH 3 COCH 3. The oxygen atom has a double bond to the center carbon. systematic (IUPAC) name: CH3CH₂CH₂CCH3 systematic (IUPAC) name:arrow_forward
- What is the IUPAC name of this compound? Br O 4-Bromo-3-ethyl-2,2,5,6-tetramethylheptane O 4-Bromo-5-ethyl-2,2,3,6-tetramethylheptane O 3-Bromo-5-ethyl-2,4,6-trimethylheptane O 3-Bromo-5-isoprpyl-2,4-dimethylheptane O 3-Bromo-5-ethyl-2,3,6-trimethylhexanearrow_forward1. Give the IUPAC names for the following organic compounds. a) CH3CH2CH(CH3)COOH e) CH3CH(CH3)CHBRCOOH ) HOOCCH2CH(CH3)CH2COOH OH h) СООН СООН i) NO2 СООН j) O2N 9 ÇH2CH3 ÇH3 ? HOČCH,CHCH,CH,CHCH,COH k) CH;CH2CHCH,CH;CH3 1) ČO2Harrow_forwardwhat is the IUPAC name of the following H3C(CH2)3(CH3)2arrow_forward
- CH3 HC =C —CH2 — CH2 — CH; H₂C Spell out the IUPAC name of the compound.arrow_forwardSelect the IUPAC name for the following structure: CH, CH-CH, ҪН,СH, CH,CH, CH—СH—СH—CH,—СH—СН, -CH—СH—CH, -CH-CH, CH—С—СH, CH, 3. O 4 isopropyl-2,2,3,6-tetramethyloctane O 2-ethyl-4-isopropyl-5,6,6-trimethylheptane O 4-isopropyl-2,2,3,6-tetramethyldecane . O 2-ethyl-4-isopropyl-5,6,6-trimethyloctane O 2-ethyl-4-isopropyl-5-isopropylhexanearrow_forwardGive the IUPAC name for this compound. (Hint: Pay attention to the longest continuous chain in this molecule. You may first want to redraw the formula to have the longest carbon chain on a horizontal plane to facilitate naming.) O 3-methyl-1-hexene O 3-propyl-1-butene O 4-methyl-5-hexene O 2-propyl-3-butenearrow_forward
- Draw the condensed structural formula or skeletal formula, if yclic, for the alkene that is the major product from each of the following dehydration reactions: H+ а. CHз— CH—— СH — СH —ОН - Heat ОН ОН b. H+ с. H+ Heat Heat ОН d. CH3— CH — CH,— СH— СH, Нeat Draw the condensed structural formula for the ether produced y each of the following reactions: H+ а. 2СH3 — ОН Heat H+ b. 2CH3 — СH>— CH-— ОН Heatarrow_forwardDraw the open structures of the molecules named below according to the IUPAC naming system. 1-chloro-3-ethyl benzene 4- (tert-butyl) -5-ethyl octane 3-Methylpentanal (1E, 3Z, 5E) -5-chloro-6-phenyl hexa-1,3,5-trien-1-olarrow_forwardWhat is the structure of the IUPAC name? Draw the structure and give how many carbons are on the parent chain. 2-(4-methylcyclohex-3-enyl)propane-2-thiolarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning



