
Concept explainers
(i)
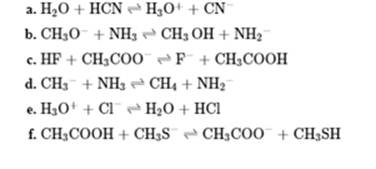
Interpretation: The Bronsted acid or base present in the below reaction should be identified.
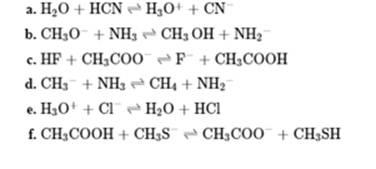
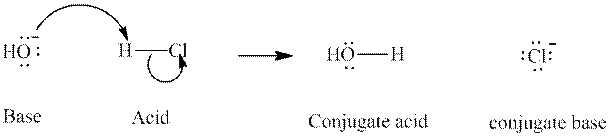
Concept introduction: In accordance with Bronsted definition an acid act as proton donor and a base can act as proton acceptor. Thus in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similarly, curved arrows are used for departing conjugate base. After deprotonation, the species left with negative charge is refers as conjugate base of acid while the other with positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example,
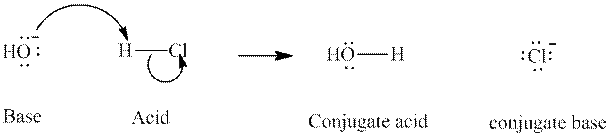
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has a weak conjugate base and the strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.
(ii)
Interpretation: Whether the equilibrium is favored to left or right should be identified in below reactions.
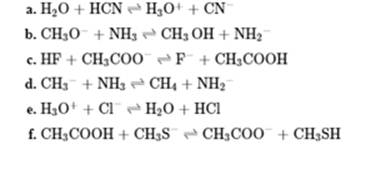
Concept introduction: In accordance with Bronsted definition an acid act as proton donor and a base can act as proton acceptor. Thus in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similarly, curved arrows are used for departing conjugate base. After deprotonation, the species left with negative charge is refers as conjugate base of acid while the other with positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example,
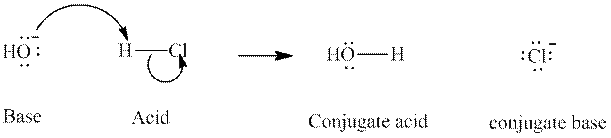
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has a weak conjugate base and the strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.
Smaller the magnitude of
(iii)
Interpretation: The value of
Concept introduction: In accordance with Bronsted definition an acid act as proton donor and a base can act as proton acceptor. Thus in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similarly, curved arrows are used for departing conjugate base. After deprotonation, the species left with negative charge is refers as conjugate base of acid while the other with positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example,
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has a weak conjugate base and strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.
Smaller the magnitude of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- In each of the following acid-base reactions, identify the Brnsted acid and base on the left and their conjugate partners on the right. (a) C2H5N(aq) + CH3CO2H(aq) C5H5NH+(aq) + CH3CO2(aq) (b) N2H4(aq) + HSO4(aq) N2H5+(aq) + SO42(aq) (c) [Al(H2O)6]3+ (aq) + OH(aq) [Al(H2O)5OH]2+ (aq) + H2O+()arrow_forwardUse Table 13-3 to help answer the following questions. a. Which is the stronger base, ClO4 or C6H5NH2? b. Which is the stronger base, H2O or C6H5NH2? c. Which is the stronger base, OH or C6H5NH2? d. Which is the stronger base, C6H5NH2 or CH3NH2?arrow_forwardUsing the diagrams shown in Problem 10-37, which of the four acids is the weakest acid?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





