
(a)
Interpretation: Each functional group in the compound should be circled and identified.
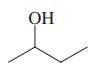
Concept introduction: A functional group is defined as an atom or group of certain atoms that confer reactivity to the overall organic compound. They undergo specific reactions. majority of
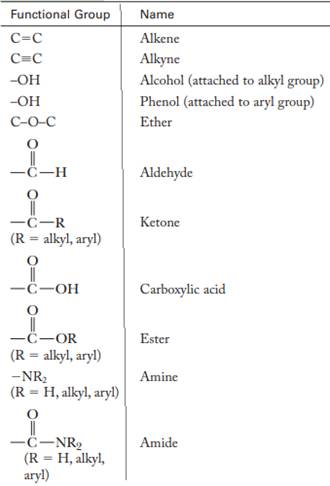
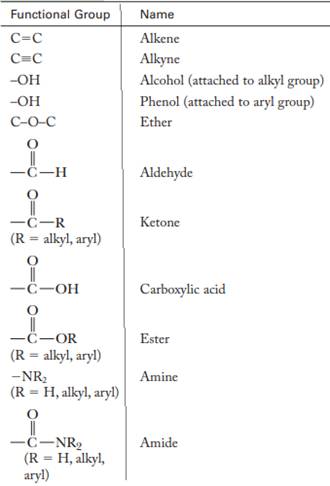
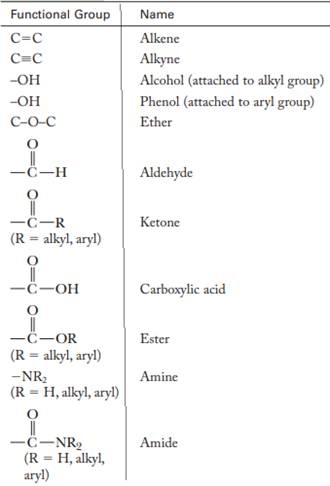
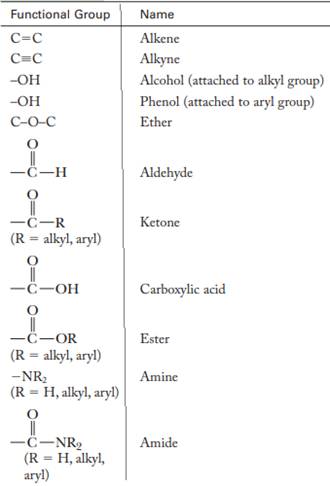
The major functional groups are given as follows:
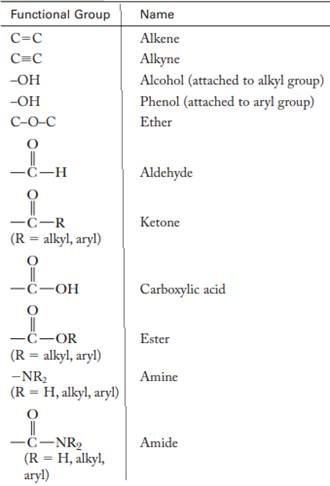
(b)
Interpretation: Each functional group in the compound should be circled and identified.
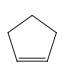
Concept introduction: A functional group is defined as an atom or group of certain atoms that confer reactivity to the overall organic compound. They undergo specific reactions. majority of functional groups are polarized in nature. The presence of functional groups controls the reactivity of organic moiety as a whole.
The major functional groups are given as follows:
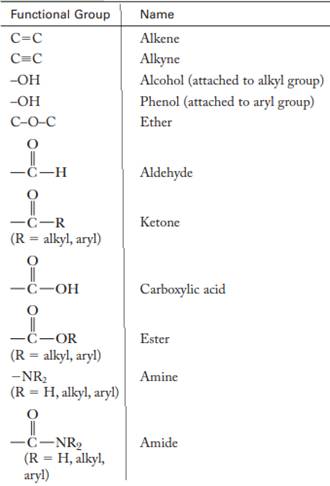
(c)
Interpretation: Each functional group in the compound should be circled and identified.
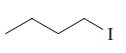
Concept introduction: A functional group is defined as an atom or group of certain atoms that confer reactivity to the overall organic compound. They undergo specific reactions. majority of functional groups are polarized in nature. The presence of functional groups controls the reactivity of organic moiety as a whole.
The major functional groups are given as follows:
(d)
Interpretation: Each functional group in the compound should be circled and identified.
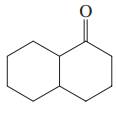
Concept introduction: A functional group is defined as an atom or group of certain atoms that confer reactivity to the overall organic compound. They undergo specific reactions. majority of functional groups are polarized in nature. The presence of functional groups controls the reactivity of organic moiety as a whole.
The major functional groups are given as follows:
(e)
Interpretation: Each functional group in the compound should be circled and identified.
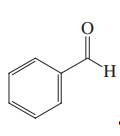
Concept introduction: A functional group is defined as an atom or group of certain atoms that confer reactivity to the overall organic compound. They undergo specific reactions. majority of functional groups are polarized in nature. The presence of functional groups controls the reactivity of organic moiety as a whole.
The major functional groups are given as follows:
(f)
Interpretation: Each functional group in the compound should be circled and identified.
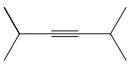
Concept introduction: A functional group is defined as an atom or group of certain atoms that confer reactivity to the overall organic compound. They undergo specific reactions. majority of functional groups are polarized in nature. The presence of functional groups controls the reactivity of organic moiety as a whole.
The major functional groups are given as follows:
(g)
Interpretation: Each functional group in the compound should be circled and identified.
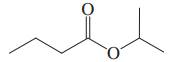
Concept introduction: A functional group is defined as an atom or group of certain atoms that confer reactivity to the overall organic compound. They undergo specific reactions. majority of functional groups are polarized in nature. The presence of functional groups controls the reactivity of organic moiety as a whole.
The major functional groups are given as follows:
(h)
Interpretation: Each functional group in the compound should be circled and identified.
Concept introduction: A functional group is defined as an atom or group of certain atoms that confer reactivity to the overall organic compound. They undergo specific reactions. majority of functional groups are polarized in nature. The presence of functional groups controls the reactivity of organic moiety as a whole.
The major functional groups are given as follows:
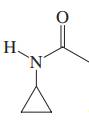
(i)
Interpretation: Each functional group in the compound should be circled and identified.
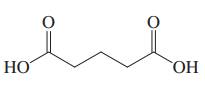
Concept introduction: A functional group is defined as an atom or group of certain atoms that confer reactivity to the overall organic compound. They undergo specific reactions. majority of functional groups are polarized in nature. The presence of functional groups controls the reactivity of organic moiety as a whole.
The major functional groups are given as follows:
(j)
Interpretation: Each functional group in the compound should be circled and identified.
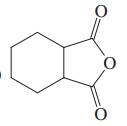
Concept introduction: A functional group is defined as an atom or group of certain atoms that confer reactivity to the overall organic compound. They undergo specific reactions. majority of functional groups are polarized in nature. The presence of functional groups controls the reactivity of organic moiety as a whole.
The major functional groups are given as follows:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
 Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
