
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:The orbital that are used to form every bond with indicated atom in the given molecule needs be determined.
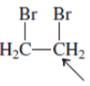
Concept Introduction:Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlapeffectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(b)
Interpretation:The orbital that are used to form every bond with indicated atom in the given molecule needs to be determined.
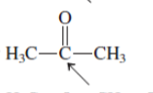
Concept Introduction:Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(c)
Interpretation:The orbital that are used to form every bond with indicated atom in the given molecule needs to be determined.
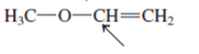
Concept Introduction:Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(d)
Interpretation:The orbital that are used to form every bond with indicated atom in the given molecule needs to be determined.
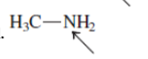
Concept Introduction:Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(e)
Interpretation: The orbital that are used to form every bond with indicated atom in the given molecule needs to be determined.
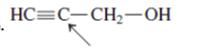
Concept Introduction:Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(f)
Interpretation: The orbital that are used to form every bond with indicated atom in the given molecule needs to be determined.
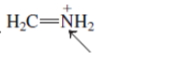
Concept Introduction:Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Borax has the molecular formula Na2B4O5(OH)4. The structure of the anion in this compound is shown below. What is the electron pair geometry and molecular geometry surrounding each of the boron atoms in this anion? What hybridization can be assigned to each of the boron atoms? What is the formal charge of each boron atom?arrow_forwardTwo compounds have the molecular formula N3H3. One of the compounds, triazene, contains an NN bond; the other compound, triaziridene, does not. (a) Write the correct Lewis structures for each compound. (b) Approximate the bond angle between the three nitrogen atoms in each compound.arrow_forwardSuppose you carry out the following reaction of ammonia and boron trifluoride in the laboratory. (a) What is the geometry of the boron atom in BF3? In H3NBF3? (b) What is the hybridization of the boron atom in the two compounds? (c) Considering the structures and bonding of NH3 and BF3, why do you expect the nitrogen on NH3 to donate an electron pair to the B atom of BF3? (d) BF3 also reacts readily with water. Based on the ammonia reaction above, speculate on how water can interact with BF3.arrow_forward
- The sulfamate ion, H2NSO3, can be thought of as having been formed from the amide ion, NH2, and sulphur trioxide, SO3. (a) What are the electron-pair and molecular geometries or the amide ion and or SO3? What are the hybridizations of the N and S atoms, respectively? (b) Sketch a structure for the sulfamate ion, and estimate the bond angles. (c) What changes in hybridization do you expect for N and S in the course of the reaction NH2 + SO3 H2NSO3? (d) Is SO3 the donor of an electron pair or the acceptor of an electron pair in the reaction with amide ion? Does the electrostatic potential map shown below confirm your prediction?arrow_forwarda Nitrogen trifluoride, NF3, is a relatively unreactive, colorless gas. How would you describe the bonding in the NF3 molecule in terms of valence bond theory? Use hybrid orbitals. b Silicon tetrafluoride, SiF4, is a colorless gas formed when hydrofluoric acid attacks silica (SiO2) or glass. Describe the bonding in the SiF4 molecule, using valence bond theory.arrow_forwardCarbon dioxide (CO2), dinitrogen monoxide (N2O), the azide ion (N3), and the cyanate ion (OCN) have the same geometry and the same number of valence shell electrons. However, there are significant differences in their electronic structures. (a) What hybridization is assigned to the central atom in each species? Which orbitals overlap to form the bonds between atoms in each structure. (b) Evaluate the resonance structures of these four species. Which most closely describe the bonding in these species? Comment on the differences in bond lengths and bond orders that you expect to see based on the resonance structures.arrow_forward
- Sketch the resonance structures for the N2O molecule. Is the hybridization of the N atoms the same or different in each structure? Describe the orbitals involved in bond formation by the central N atom.arrow_forwardCompare the atomic and molecular orbital diagrams to identify the member of each of the following pairs that has the highest firs ionization energy (the most tightly bound electron) in the gas phase: (a) H and H2 (b) N and N2 (c) O and O2 (d) C and C2 (e) B and B2arrow_forwardThe structure of amphetamine, a stimulant, is shown below. (Replacing one H atom on the NH2, or amino, group with CH3 gives methamphetamine a particularly dangerous drug commonly known as speed.) (a) What are the hybrid orbitals used by the C atoms of the C6 ring. by the C atoms of the side chain, and by the N atom? (b) Give approximate values for the bond angles A, B, and C. (c) How many bonds and bonds are in the molerule? (d) Is the molecule polar or nonpolar? (e) Amphetamine reacts readily with a proton (H+) in aqueous solution. Where does this proton attach to the molecule? Explain how the electrostatic potential map predicts this site of protonation.arrow_forward
- C2H6 and HI State the type of hybridization (sp, sp", etc) for the central atom in each molecule. Show how the various single, double and/or triple bonds form in each of the molecules. Make use of orbital diagrams, labels, and/or written sentences in your explanation.arrow_forwardWhat atomic or hybrid orbitals make up the bond between C and O in carbon dioxide, CO2 ?arrow_forwardDraw a Lewis diagram(s) for the ozone molecule (O3). Determine the steric number and hybridization of the central oxygen atom, and identify the molecular geometry. Describe the nature of the p bonds and give the bondorder of the O-O bonds in ozone.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





