
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:The hybridization and geometry of each C atom in the given molecule needs to be determined.
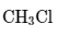
Concept Introduction:Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure. The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons.
Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(b)
Interpretation:The hybridization and geometry of each C atom in the given molecule needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure. The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons.
Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(c)
Interpretation:The hybridization and geometry of each C atom in the given moleculeneeds to be determined.
Concept Introduction: Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure. The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons.
Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(d)
Interpretation:The hybridization and geometry of each C atom in the given molecule needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure. The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons.
Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(e)
Interpretation:The hybridization and geometry of each C atom in the given molecule needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure. The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons.
Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(f)
Interpretation:The hybridization and geometry of each C atom in the given molecule needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure. The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons.
Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
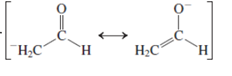
(g)
Interpretation:The hybridization and geometry of each C atom in the given molecule needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure. The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons.
Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form same number of hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals overlap with atomic orbital of other atoms to form covalent bond. These hybrid orbitals are of same energy and share therefore overlap effectively to form covalent bond.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Use the VSEPR model to predict the bond angles around each central atom in the following Lewis structures (benzene rings are frequently pictured as hexagons, without the letter for the carbon atom at each vertex). Note that the drawings do not necessarily depict the bond angles correctly.arrow_forwardThe hybridization of the two carbon atoms differs in an acetic acid, CH3COOH, molecule. (a) Designate the correct hybridization for each carbon atom in this molecule. (b) What is the approximate bond angle around each carbon?arrow_forwardGamma hydroxybutyric acid, GHB, infamous as a date rape drug, is used illicitly because of its effects on the nervous system. The condensed molecular formula for GHB is HO(CH2)3COOH. (a) Write the Lewis structure for GHB. (b) Identify the hybridization of the carbon atom in the CH2 groups and of the terminal carbon. (c) Is hydrogen bonding possible in GHB? If so, write Lewis structures to illustrate the hydrogen bonding. (d) Which carbon atoms are involved in sigma bonds? In pi bonds? (e) Which oxygen atom is involved in sigma bonds? In pi bonds?arrow_forward
- Two compounds have the molecular formula N3H3. One of the compounds, triazene, contains an NN bond; the other compound, triaziridene, does not. (a) Write the correct Lewis structures for each compound. (b) Approximate the bond angle between the three nitrogen atoms in each compound.arrow_forwardDraw the geometric structures of all the molecules. Write all bond angles and write the kind of geometry observed (linear/trigonal planar/tetrahedral) CH₃CH₃ = CH₃COH = CH₃OH = CH₂CH₂ =arrow_forwardA student investigates the physical and chemical properties of various carbon-containing compounds. The complete Lewis electron-dot diagrams and boiling points for two compounds, Q and X are shown in the following table. Identify the hybridization of the valence orbitals of the carbon atom in compound X that is indicated by the arrow in the diagram. The C-H bonds in compound Q are shorter than the C-C bonds in compound X. Explain the reason for this difference using principles of atomic structure. For each compound, list all intermolecular forces present. Q = X =arrow_forward
- Ion E Lewis structure Hybridization [H;O]* Number of valence Number of o and n electrons bonds O: Number of bonded atoms Molecular shape on central atom Number of lone pairs on central atom Bonded-atom lone- Polarity pair arrangement Central atom Bond angles Bond order steric number O-H: Molecule F Lewis structure Hybridization BRNS Number of valence Number of o and n electrons bonds 0: Number of bonded atoms Molecular shape on central atom Bonded-atom lone- Number of lone pairs on central atom Polarity pair arrangement Central atom Bond angles Bond order steric number N-Br: N-S:arrow_forwardYeni Metin Belgesi - Not Defteri Dosya Düzen Biçim Görünüm Yardım For acetaldehyde (CH3CHO) write the Lewis structure. Write the hybridization and geometry of each carbon. Draw its 3D structure and write the bond angles (approximately).arrow_forwardMolecule G Lewis structure Hybridization PFs Number of o and n bonds Number of valence electrons Number of bonded atoms Molecular shape on central atom Number of lone pairs on central atom Bonded-atom lone- Polarity pair arrangement Central atom Bond angles Bond order steric number P-F: Molecule H Lewis structure Hybridization TeF6 Number of valence Number of o and n electrons bonds 0: Number of bonded atoms Molecular shape on central atom Number of lone pairs Bonded-atom lone- Polarity on central atom pair arrangement Central atom Bond angles Bond order steric number Тe-F:arrow_forward
- Draw a line-bond structure for propene, CH3CH=CH2. Indicate the hybridization of the orbitals on each carbon, and predict the value of each bond angle.arrow_forwardPredict the hybridization, geometry, and bond angles for the carbon and oxygen atoms in acetaldehyde (CH3CHO)arrow_forwardAcrylic fibers are polymers made from a starting material called acrylonitrile, H2C(CH)CN. In acrylonitrile, a - CN group replaces a hydrogen atom on ethene. Draw the Lewis diagram for this molecule, give the hybridization of each carbon atom, and describe the \pi orbitals and the number of electrons that occupy each one. Draw the three-dimensional structure of the molecule, showing all angles.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

