
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:The resonance structures of bicarbonate ion needs to be drawn with the use of electron pushing arrows and the form that will be the major contributor to the real structure of bicarbonate ion needs to be determined.
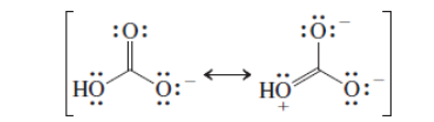
Concept Introduction:VSEPR theory stands as Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory. It helps to predict the molecular shape or geometry of the molecule with the help of the number of bond pair or lone pair present in it. According to VSEPR theory, the presence of lone pair on the central atom of molecule causes deviation from standard molecular geometry.
The resonance is the phenomenon in which if all the properties cannot explain by one structure, it can be shown in two or more structures by the shifting of pi bonds or lone pair but there is no change in sigma bond and position of atoms.
(b)
Interpretation:The resonance structures of
Concept Introduction:VSEPR theory stands as Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory. It helps to predict the molecular shape or geometry of the molecule with the help of the number of bond pair or lone pair present in it. According to VSEPR theory, the presence of lone pair on the central atom of molecule causes deviation from standard molecular geometry.
The resonance is the phenomenon in which if all the properties cannot explain by one structure, it can be shown in two or more structures by the shifting of pi bonds or lone pair but there is no change in sigma bond and position of atoms.
(c)
Interpretation:The resonance structures of
Concept Introduction:VSEPR theory stands as Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory. It helps to predict the molecular shape or geometry of the molecule with the help of the number of bond pair or lone pair present in it. According to VSEPR theory, the presence of lone pair on the central atom of molecule causes deviation from standard molecular geometry.
The resonance is the phenomenon in which if all the properties cannot explain by one structure, it can be shown in two or more structures by the shifting of pi bonds or lone pair but there is no change in sigma bond and position of atoms.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- 3. a) The most plausible Lewis structure of azide ion, N3 could be determined using formal charge. (Proton number N=7) i. Draw all possible Lewis structures for azide ion.ii. Select the most plausible Lewis structure of the ion. Explain.arrow_forward(b) The Murchison meteorite that landed in Australia in 1969 contained 92 different amino acids, including 21 found in Earth organism A skeleton structure (single bond only) of one of these extraterrestrial amino acids is shown below. Draw a Lewis structure, and identify any atoms having a nonzero formal charge. H3N. C ČH2 ČH3 (c) Draw the orbital diagrams and Lewis symbols to depict the formation of Na* and CI ions from the atoms. Give the formula of the compound formed. (d) The predicted bond length for HF is 109 pm (the sum of the covalent radii of H, 37 pm and F, 72 pm), however the actual bond length for HF is shorter (92 pm). It was observed that the difference between predicted and actual bond lengths becomes smaller going down the halogen group from HF to HI Describe these observationsarrow_forward2. Below are drawn four possible isomers (partial Lewis structures with different atomic connectivity) for an anion with the molecular formula C₂H4NO. 10 A B D "TOTT" raptor H H -0- (a) First, add enough electrons as either lone pairs or r bonds to give an overall negative charge. Show all lone pairs in each completed Lewis structure, and show any atomic formal charges that result. (b) Then, for each isomer, consider if other resonance structures can contribute. Since this is an anion, look for a strong electron donor with an adjacent electron acceptor. For each additional resonance structure you draw (some isomers may have more than one additional RS, some may have none), circle the electron pairs in the original Lewis structure which have moved, and draw a curved arrow depicting the motion required to create the new RS. If you have colored pens, color coding your electrons pairs is nice (but not required).arrow_forward
- II. Please expand each of the following bond-line formulas to the corresponding standard Lewis structure, be sure to show all the bonds and unshared electron pairs as well as formal charges, if it applies. 0: (a) (c) O Br | Br-B-Br -N- (b) HO: NO₂ 0: blos ohsup?arrow_forward19. :O: || :0-N- O: Which of the following statements, if true, would support the claim that the NO3 ion, represented above, has three resonance structures? (A) The NO3 ion is not a polar species. (B) The oxygen-to-nitrogen-to-oxygen bond angles are 90°. (C) One of the bonds in NO3 is longer than the other two. (D) One of the bonds in NO3¯ is shorter than the other two.arrow_forward2. A. Acetoin has the structure shown below. Carbon atoms exist at the corners of the sharp bends, such as where arrow C points (there are four carbon atoms in the structure). A CH3 H3C B (i) add lone pairs of electrons where appropriate to the diagram. (ii) Give bond angle values for the points marked A, B, and C. Bond Angle A = Bond Angle B =, Bond Angle C = (iii) Give the hybridization of the atoms marked A, B, and C. Hybridization A = Hybridization B = Hybridization C = (iv) Give the total number of sigma and pi bonds in the molecule. Number of sigma bonds = Number of pi bonds = (v) How many atoms in this molecule lie in the same plane?arrow_forward
- There are two main types of covalent bond breakage. In ho-molytic breakage , each atom in the bond gets one of the shared electrons. In some cases, the electronega-tivity of adjacent atoms affects the bond energy. In heterolytic breakage, one atom gets both electrons and the other gets none;thus, a cation and an anion form. (a) Why is the C−C bond in H₃C−CF₃(423 kJ/mol) strongerthan that in H₃C−CH₃(376 kJ/mol)?(b) Use bond energy and any other data to calculate the heat ofreaction for the heterolytic cleavage of O₂.arrow_forwardWrite resonance forms that describe the distribution of electrons in each of these molecules or ions. (a) sulfur dioxide, SO2 (b) carbonate ion, CO3²- (c) hydrogen carbonate ion, HCO3- (C is bonded to an OH group and two O atoms) (d) pyridine: H. H. (e) the allyl ion: H H H H-C-C-c-Harrow_forwardThe structural formulas for ethanol, CH3CH2OH, and propene, CH;CH=CH,2, are нн H Н—С—С—0—н H-C-C=C-H нн H H H Ethanol Propene (a) Complete the Lewis structure for each molecule showing all valence electrons. (b) Using the VSEPR model, predict all bond angles in each molecule.arrow_forward
- 9a.) Let's put some pieces together. We can also apply energy diagrams to resonance structures. Explain what is happening in the following energy diagram AND draw curved arrows to show the "movement" of electrons from A, to A2.arrow_forward1. What is the formal charge on each atom in PH4 and the Lewis structure for it?arrow_forward1. Write Lewis symbols for the following atoms. (1pt each) (a) Kr (b) Ge (c) N (d) Ga (e) As (f) Rb 2. Write plausible Lewis structures for the following molecules that contain only single covalent bonds. (2 pts each) (а) FCI (b) I2 (c) SF2 (d) NF3 (е) Н-Те 3. By means of Lewis structures, represent bonding between the following pairs of elements (Your structures should show whether the bonding is essentially ionic or covalent): (2 pts each) (a) Cs and Br (b) H and Sb (c) B and Cl (d) Cs and Cl (e) Li and O (f) Cl and I 4. Assign formal charges to each of the atoms in the following structures. (3 pts each) (a) [H–C=C:]¯ (c) [CH3–CH-CH3]* (b) |2– :0: :0: 5. What is the formal charge of the indicated atom in each of the following structures? (2 pts each) (a) the central O atom in 03 (b) Al in AIH4- (c) Cl in Cl03 (d) Si in SiF62- (e) Cl in CIF3 6. Arrange the following elements in the order of decreasing electronegativity: fluorine, bromine, lithium, francium, silicon. (1 pt each per…arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





