
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:The geometry of indicated atom in the given molecule with the help of hybridization needs to be determined.
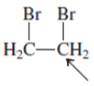
Concept Introduction: Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure. The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(b)
Interpretation:The geometry of indicated atom in the given molecule with the help of hybridization needs to be determined.
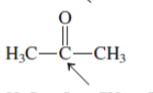
Concept Introduction: Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure. The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(c)
Interpretation:The geometry of indicated atom in the given molecule with the help of hybridization needs to be determined.
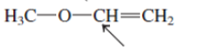
Concept Introduction: Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure. The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(d)
Interpretation:The geometry of indicated atom in the given molecule with the help of hybridization needs to be drawn.
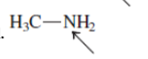
Concept Introduction: Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure. The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(e)
Interpretation:The geometry of indicated atom in the given molecule with the help of hybridization needs to be determined.
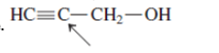
Concept Introduction: Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure. The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
(f)
Interpretation:The geometry of indicated atom in the given molecule with the help of hybridization needs to be drawn.
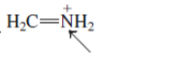
Concept Introduction: Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure. The bond formation between the atoms takes place due to the sharing of valence electrons of bonded atoms while the remaining electrons present in outer shell represented as lone pair of electrons.
The hybridization gives idea about the geometry of each atom. It can be checked with the below formula:
Hybridization = Number of sigma bonds + Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Choose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. i H A B 1. CH3CH2Na 2. H3O+ 1. CH3CH2MgBr 2. H3O+ 1. CH3MgBr Q C 2. H3O+ 1. H3O+ D 2. CH3MgBr 00 OH Q E CH³MgBrarrow_forwardThe kinetics of a gas phase reaction of the form A → Products results in a rate constant of 0.00781 M/min. For this reaction, the initial concentration of A is 0.501 M. What is the half-life for this reaction?arrow_forwardChoose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. 1. PhNa A 2. H3O+ 1. PhCH2MgBr B 2. H3O+ хё 1. PhMgBr C 2. H3O+ 00 HO Q E D 1. H3O+ 2. PhMgBr PhMgBrarrow_forward
- Please answer all of the questions and provide detailed explanations and include a drawing to show the different signals on the molecule and include which ones should be highlighted.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 1 attempt remaining 1. LiAlH4 2. H3O+ Q OH ☑ Select to Drawarrow_forwardHow should I graph my data for the Absorbance of Pb and Fe for each mushroom? I want to compare the results to the known standard curve. Software: Excel Spreadsheets Link: https://mnscu-my.sharepoint.com/:x:/g/personal/vi2163ss_go_minnstate_edu/Eb2PfHdfEtBJiWh0ipHZ_kkBW4idWWwvpLPPtqoq2WkgbQ?rtime=HxrF0_tR3Ugarrow_forward
- Provide the proper IUPAC name only for the following compound. Dashes, commas, and spaces must be used correctly, but do not use italics in Canvas.arrow_forwardThe kinetics of a gas phase reaction of the form A → Products results in a rate constant of 0.00781 M/min. For this reaction, the initial concentration of A is 0.501 M. How many minutes will it take for the concentration of A to reach 0.144 Marrow_forwardWhat is the rate for the second order reaction A → Products when [A] = 0.256 M? (k = 0.761 M⁻¹s⁻¹)arrow_forward
- For reaction N2(g) + O2(g) --> 2NO(g) Write the rate of the reaction in terms of change of NO.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardThe reaction of 2-oxacyclopentanone with hydrochloric acid in water (i.e., "excess") produces which of the following carboxylic acids?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





