
(a)
Interpretation: The species
Concept introduction:
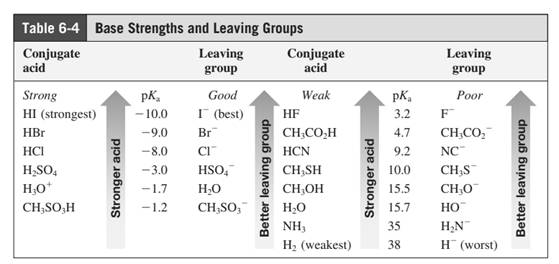
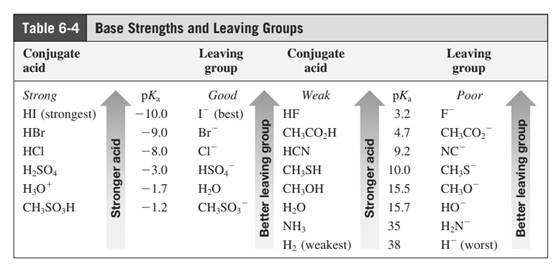
Leaving-group ability is determined by the capacity of leaving group to accommodate the negative charge as it is displaced from the alkyl halide. Among halogens, the iodides are best leaving groups followed by bromide chloride and fluoride. Besides halides, some sulphonates and sulphate that can easily delocalize the negative charge can also behave as good leaving group. These include tosylate, mesylate and triflate.
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. Table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases are as follows:
(b)
Interpretation: The species
Concept introduction:
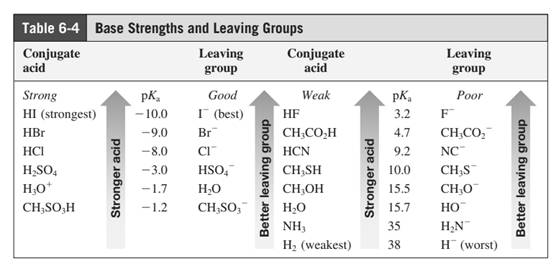
Leaving-group ability is determined by the capacity of leaving group to accommodate the negative charge as it is displaced from the alkyl halide. Among halogens, the iodides are best leaving groups followed by bromide chloride and fluoride. Besides halides, some sulphonates and sulphate that can easily delocalize the negative charge can also behave as good leaving group. These include tosylate, mesylate and triflate.
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. Table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases are as follows:
(c)
Interpretation: The species
Concept introduction:
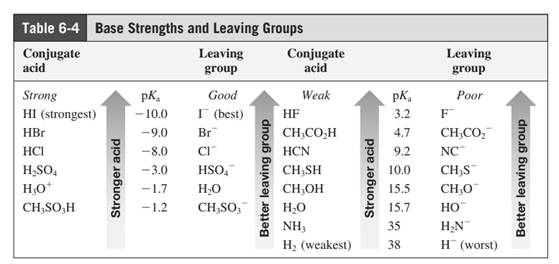
Leaving-group ability is determined by the capacity of leaving group to accommodate the negative charge as it is displaced from the alkyl halide. Among halogens the iodides are best leaving groups followed by bromide chloride and fluoride. Besides halides some sulphonates and sulphate that can easily delocalize the negative charge can also behave as good leaving group. These include tosylate, mesylate and triflate.
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. Table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases are as follows:
(d)
Interpretation: The species
Concept introduction:
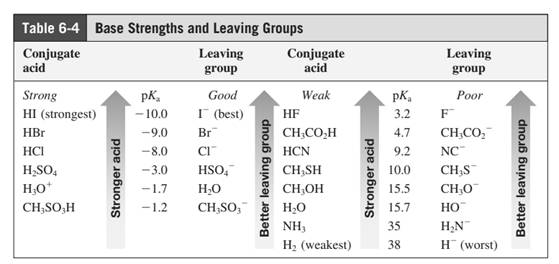
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. Table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases are as follows:
(e)
Interpretation: The species
Concept introduction:
Leaving-group ability is determined by the capacity of leaving group to accommodate the negative charge as it is displaced from the alkyl halide. Among halogens, the iodides are best leaving groups followed by bromide chloride and fluoride. Besides halides, some sulphonates and sulphate that can easily delocalize the negative charge can also behave as good leaving group. These include tosylate, mesylate and triflate.
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups.
Nucleophillicity varies directly with negative charge, and also for elements that lie far left and bottom of the periodic table. It also increases with
(f)
Interpretation: The species
Concept introduction:
Leaving-group ability is determined by the capacity of leaving group to accommodate the negative charge as it is displaced from the alkyl halide. Among halogens, the iodides are best leaving groups followed by bromide chloride and fluoride. Besides halides, some sulphonates and sulphate that can easily delocalize the negative charge can also behave as good leaving group. These include tosylate, mesylate and triflate.
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. Table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases are as follows:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- How is nucleophilicity (nucleophile strength) related to basicity?arrow_forwardRank the hydrogens shown in bold in order of increasing acidity. .H A)I < || < |II H. B)I< III < || II C) I| < |II < | H D) III < I<|| H. E) I| < |< III IIarrow_forward51. Which is NOT a valid resonance structure for the conjugate base of this molecule? (A) (C) OEt (C) :0: : OEt (+) HBr ROOR ü (B) OCH 3 (D) 52. What is the major product of this reaction sequence? o Mg ether (A) (B) :0: (D) H OEt OEt H OEt X CH31 LOH LOCH₁arrow_forward
- What is the correct arrangement in increasing basicity of the given compounds? III < I < II III < II < I I < II < IIIarrow_forwardDraw an energy diagram for the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base reaction of CH3CO2H with -OC(CH3)3 to form CH3CO2-and (CH3)3COH. Label the axes, starting materials, products, ?H°, and Ea. Draw the structure of the transition state.arrow_forward4a.. Rank the following in order of increasing acidity: О F3C ОН F3C OH A OH B ОН 4b. Rank the following in order of increasing basicity: Ө OCH 3 NH₂ CH3CH₂CH₂CH2 с D ОН Barrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in their correct order of acidity. 1=Most acidic and 4=least acidic.arrow_forward(a) Explain how NaBH, in CH;OH can reduce hemiacetal A to 1,4-butanediol (HOCH,CH,CH,CH,OH). (b) What product is formed when A is treated with Ph;P=CHCH,CH(CH),? (c) The drug isotretinoin is formed by reaction of X and Y. What is the structure of isotretinoin? Although isotretinoin (trade name Accutane or Roaccutane) is used for the treatment of severe acne, it is dispensed under strict controls because it also causes birth defects. PPha NaOCH,CH3 HO- isotretinoin HO A Br X Yarrow_forwardWhat is the increasing order of basicity among the following compounds ? I NH OH | < | < III < IV OIV < III < II < 1 I < III < II < IV OII < | < ||| < |V || < ||| < | < IV II NH III NH OH IV OH NHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of increasing acidity (1 = least acidic, 3 = most acidic) and in the space provided use resonance (of the conjugate base) to explain why the compound you have labelled “3” is the most acidic.arrow_forward4. Rank the following compounds in terms of increasing basicity: oto oo, oa Brarrow_forwardhydrogens on a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl group are far more acidic than those not adjacent to a carbonyl group. The anion derived from acetone, for example, is more stable than is the anion derived from ethane. Account for the greater stability of the anion from acetone. CH,ČCH, H CH,CH, H Acetone Ethane pK, 20.2 pK, 51arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

