
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:The reaction schemes with proper usage of curved arrows in below reaction should be indicated and corrected for the cases that are inappropriate.
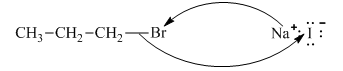
Concept introduction:The fundamental electrostatics suggests that electrons have more affinity for electron-deficient sites in an organic compound. or positive charge. The curved arrow is appropriate mechanism to depict electron movement that occurs from electron rich species to electron deficient species.
Bimolecular substitution or
A general
(b)
Interpretation: The reaction schemes with proper usage of curved arrowsin below reaction should be indicated and corrected for the cases that are inappropriate.
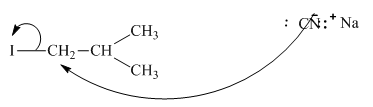
Concept introduction: The fundamental electrostatics suggests that electrons have more affinity for electron deficient sites in an organic compound. or positive charge. The curved arrow is appropriate mechanism to depict electron movement that occurs from electron rich species to electron deficient species.
Bimolecular substitution or
(b)
Interpretation: The reaction schemes with proper usage of curved arrows in below reactionshould be indicated and corrected for the cases that are inappropriate.
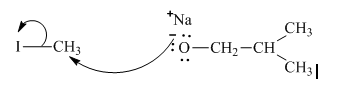
Concept introduction: The fundamental electrostatics suggests that electrons have more affinity for electron deficient sites in an organic compound. or positive charge. The curved arrow is appropriate mechanism to depict electron movement that occurs from electron rich species to electron deficient species.
Bimolecular substitution or
(d)
Interpretation: The reaction schemes with proper usage of curved arrows in below reactionshould be indicated and corrected for the cases that are inappropriate.
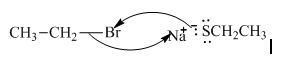
Concept introduction: The fundamental electrostatics suggests that electrons have more affinity for electron deficient sites in an organic compound. or positive charge. The curved arrow is appropriate mechanism to depict electron movement that occurs from electron rich species to electron deficient species.
Bimolecular substitution or
(e)
Interpretation: The reaction schemes with proper usage of curved arrows in below reactionshould be indicated and corrected for the cases that are inappropriate.
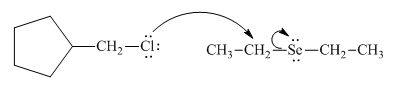
Concept introduction: The fundamental electrostatics suggests that electrons have more affinity for electron deficient sites in an organic compound or positive charge. The curved arrow is appropriate mechanism to depict electron movement that occurs from electron rich species to electron deficient species.
Bimolecular substitution or
(e)
Interpretation: The reaction schemes with proper usage of curved arrowsin below reaction should be indicated and corrected for the cases that are inappropriate.
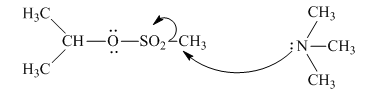
Concept introduction: The fundamental electrostatics suggests that electrons have more affinity for electron deficient sites in an organic compound. or positive charge. The curved arrow is appropriate mechanism to depict electron movement that occurs from electron rich species to electron deficient species.
Bimolecular substitution or
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- For the mechanism, draw the curved arrows as needed. Include lone pairs and charges in your answer. Do not draw out any hydrogen explicitly in your products. Do not use abbreviations such as Me or Ph. x Xa 1) xs EtMgBr 2) conc. H₂SO4, heatarrow_forwardPart A 1. Explain why 1-bromo-2,2-dimethylpropane has difficulty undergoing both SN2 and SN1 reactions. 2. Can it undergo E2 and E1 reactions? Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right. Make certain each sentence is co Submit can SN1 SN2 secondary tertiary primary E2 hydrogen cannot E1 carbon Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining Reset Help 1. The bulky tert-butyl substituent blocks the back side of the carbon bonded to the bromine to nucleophilic attack, making an SN2 reaction difficult. An SN1 reaction cannot occur because it would require the formation of an unstable primary carbocation. 2. It cannot undergo an E2 reaction, because the B-carbon is not bonded to a hydrogen. It cannot undergo an E1 reaction, because that would require the formation of a tertiary carbocation.arrow_forward9. For hydroboration-oxidation, add the H and OH to the appropriate positions, with both regio and stereo considerations. A template is being provided, just add all groups to the appropriate positions – the Cl, Me groups, and Et group. Check your notes or pg. 2 above on whether hydroboration is a syn addition or anti addition. There is no one and only correct way to do this, but there is only one correct answer. Also, the enantiomer of each product you draw will also form. I'm only asking you to draw one of them. Et 1. ВН;, THF 1. ВНз, ТHF 2. Н2О2, NaOН -Me Н 2. H2O2, NaOH Me Me Me CI ....... The enantiomer will also form.arrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the curved arrows to draw the product of the E2 reaction shown below. + Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore byproducts. H₂C H O:O: :0-tBu tBuOH heat Qarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the curved arrows to draw the products of the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H3C. H3C CH3 CH3 H H₂O.arrow_forwardI need help finding the products for each individual portion of these reactions... thanksarrow_forward
- Draw the products of the reaction shown. Electron flow is indicated with curved arrows. • Include all valence lone pairs in your answer. . Include counter-lons, e.g., Na*, F, in your submission, but draw them in their own separate sketcher. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. Separate multiple products using the + sign from the drop-down menu. +98) 24 Y SIF Nextarrow_forwardDraw the structure of the azo compound produced by the reaction below. • Do not include any -SO,Na groups that may be present in either reactant. • Do not include counter-ions, e.g., Na", I, in your answer. NEN HO HO,arrow_forwardXVI. Which of the two nitrogens (a or b) would be more basic (stronger base)? CONCISELY explain why. H ·N· of aarrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Follow the curved arrows and draw the product of the E2 reaction shown below. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore byproducts. :Br: CH3OH heat 0:0: > -CH3 Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges and Lone Pairs Draw or tap a new bond to see suggestions. og f Undo Remove Reset Done Drag To Pan +1arrow_forwardFor each of the following, write the major product(s) and then draw out each step in the mechanism using curved arrows. Show ALL lone pair electrons and formal charges. Redraw ALL molecules as to show explicitly ALL bonds being broken or formed. Identify the molecular orbital (HOMO) of the nucleophile and the molecular orbital (LUMO) of electrophile involved in the nucleophilic attack. MO diagrams are not necessary..arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the curved arrows to draw the products of the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H3C. H3C CH3 H₂O Drawing .CH3arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
