
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:Whether
Concept introduction:There are three classes of major solvents namely non-polar, polar-protic and polar aprotic. The non-polar solvents include cyclohexane,
Polar-protic solvents possess partial positive and negative charges that confer polarity to such molecules. Through their
Polar-aprotic solvents possess partial positive and negative charges also. However, they do not liberate any proton to the substrate unlike water, methanol solvents. Acetone, DMSO, THF or DMF are categorized as polar aprotic solvent.
(b)
Interpretation:Effect on rate of nucleophilic substitution reaction between sodium cyanide and
Concept introduction:Bimolecular substitution or
A general
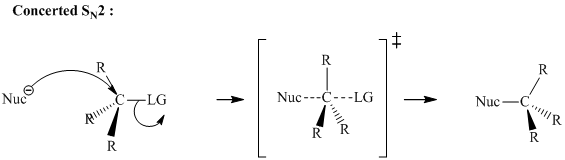
Polar-aprotic solvents accelerate the rate of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Predict the product of the following organic reaction: CH₂ CH O || C–CH2–CH=CH—(CH2)3 CH3 (CH₂)3 CH=CH- - CH₂ CH3 + 4 H₂ Ni CH,−O -C–CH2–CH=CH–CH=CH–CH2–CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below, draw the chemical structure of the product P. If there is no product, because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. × Ś +arrow_forwardAlkoxides R-O- can be used to synthesize alkenes as exemplified by the reaction shov below, where the symbol (et) indicates that the substance is dissolved in ethanol (CH;CH,OH) used as solvent: Br (1) + HO Br(et) (et) + (et) CH,CH,OH t-but-Br Ethoxide Isobutylene 9. The table to the right shows the results for the initial rate of this reaction when performed under different conditions (four different trials) at 25 °C. What is the rate law for this reaction? a) Rate = k [t-but-Br] b) Rate = k [t-but-Br] [ethoxide] c) Rate = k [t-but-Br]? d) Rate = k [ethoxide]? Trial Initial Initial Initial Rate (M/s) [t-but-Br] [Ethoxide] [isobutylene] 1 0.08 M 0.04 M 6.8 x 10-8 13.6 x 10-8 6.8 x 10-8 13.6 х 10-8 2 0.16 M 0.04 M 3 0.08 M 0.08 M 4 0.16 M 0.08 Marrow_forwardIn this lab you are performing your first organic synthesis and safety information on all the materials you are using must be obtained. Companies are required to provide material safety data sheets (MSDS) for chemical compounds they sell. Please examine the MSDS for salicylic acid, available here. You will find GHS pictograms within the sheet that summarize the main hazards of this compound. The pictograms are essentially the same as the symbols on WHMIS labels, available here for reference. Based on the pictograms, whatare the main hazards for salicylic acid? Select as many answers as appropriate Select one or more: Acute oral or inhalation toxicity Flammable material Carcinogen Self-reactive substance Gas under pressure Corrosive Oxidizing materialarrow_forward
- SCH4U Unit 4 Organic Chemistry 19. Name the following (8) H H | | | | н-с-с-с-с-с-H | | | | | H H 0 CH₂CH₂ HH CH₂CH₂CH₂ б OH H c=c CH3 Н Н H CH₂CH3 CH3 H H C Ontario Virtual School H-с-с-с-с=c-C-H H Н Н H-C-H H H CH₂CH₂CH₂-C-CH₂CH₂CH CH3arrow_forwardWhich hydrocarbon (heptane, 1-octadecene) is expected to be more soluble in isopropanol? Why?arrow_forward5. (1) Ethan-1,2-diol is miscible with water. Draw this structure and show all the Hydrogen-bonds that a single ethan-1,2-diol molecule can make with waters (as many as you need).arrow_forward
- Identifying organic functional groups Name the family to which each organiC compound belongs. The first answer has been filled in for you. compound family ester CH,– CH,– -0–C – CH, CH; CH, — о — с —Н CH, NH, – C=O CH, Check Explanation O2021 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms ||arrow_forwardThe following synthetic schemes all have at least one flaw in them. What is wrong with each? CH, „COOH 1. BH, 2. H,0 (a) ÇOOH 1. Mg 2 NaCN 3. H,0* (b) CH,CH,CHBrCH¿CH, CH,CH,CHCH,CH, „CH2COOH „CH,CH 1. LIAIH, 2. H,0* (e)arrow_forwardBenzene is one of the compounds used as octane enhancers in unleaded gasoline. It is manufactured by the catalytic conversion of acetylene to benzene: 3C2H2 (8) C6H6 (8). Which value of Kwould make this reaction most useful commercially? K 0.01, K1, or K 10. Explain your answer.arrow_forward
- With the molecular formula C4H8O , I ask you to draw 3 molecules: an aldehyde, a ketone and an enol.For each molecule, you must: a) Complete detailed Lewis structure;b) Make the 3D structure respecting the connection angles;c) Determine which intermolecular interactions are present if you glue 2 twin molecules together (2 aldehydes together, 2 ketones together, 2 enols together, therefore 3 situations to analyze).arrow_forwardDraw the organic product expected from the reaction. Include all hydrogen atoms. Note that K, Cr, 0, is present in excess. H H H, SO, CH, CH,CH, OH + K,Cr,0,(aq) |arrow_forwardOrganic Chemistry HW: CANNOT BE HAND DRAWN 2,6-dimethyloct-2-ene Hydrogen Bonding with Water use a computer program and illustrate the expanded structure of your molecule. (If the structure already contains any dashed lines, make them solid (non-dashed) covalent bonds for this assignment so that they are not confused with hydrogen bonds) Illustrate all the locations where your molecule could form hydrogen bonds with water either as a hydrogen donor or as a target (receiver) of hydrogen bonds from water. Do this by drawing bent water molecules as necessary and representing hydrogen bonds between water and the molecule using dashed lines. Be sure it is clear exactly which atoms on each molecule are involved in the hydrogen bonds. If your molecule is not capable of forming hydrogen bonds with water explain why not.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
