
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The major organic product that would result from reaction of iodomethane with soda amide along with the nucleophile, nucleophilic atom the electrophilic atom in the substrate molecule, and leaving group should be identified.
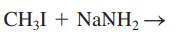
Concept introduction:
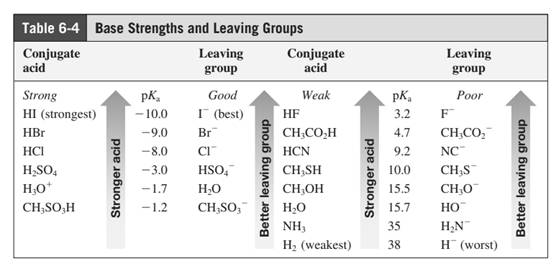
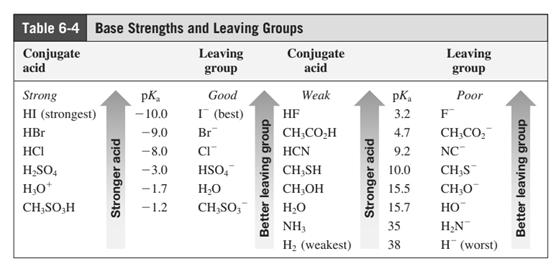
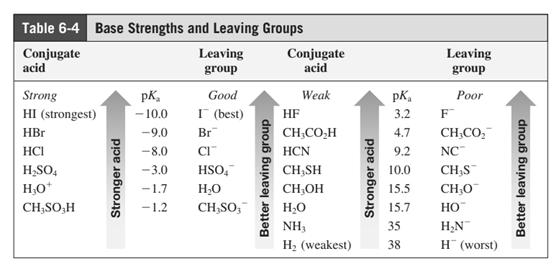
Leaving-group ability is determined by the capacity of leaving group to accommodate the negative charge as it is displaced from the alkyl halide. Among halogens, the iodides are best-leaving groups followed by bromide chloride and fluoride. Besides halides, some sulphonates and sulphate that can easily delocalize the negative charge can also behave as good leaving group. These include tosylate, mesylate and triflate.
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. The table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases is as follows:
(b)
Interpretation: The structure of major organic product that would result from reaction of should be written and nucleophile, nucleophilic atom the electrophilic atom in the substrate molecule, and leaving group should be identified.
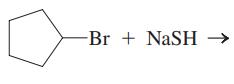
Concept introduction:
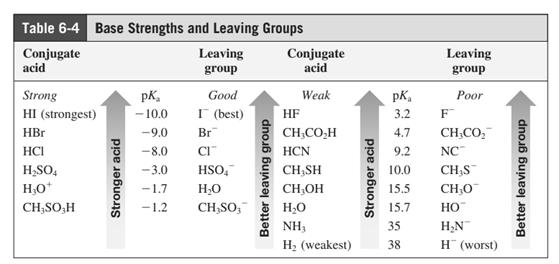
Leaving-group ability is determined by the capacity of leaving group to accommodate the negative charge as it is displaced from the alkyl halide. Among halogens, the iodides are best-leaving groups followed by bromide chloride and fluoride. Besides halides, some sulphonates and sulphate that can easily delocalize the negative charge can also behave as good leaving group. These include tosylate, mesylate and triflate.
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. The table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases is as follows:
(c)
Interpretation: The structure of major organic product that would result from reaction of should be written and nucleophile, nucleophilic atom the electrophilic atom in the substrate molecule, and leaving group should be identified.
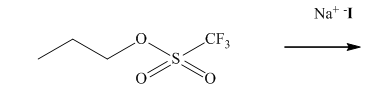
Concept introduction:
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. The table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases is as follows:
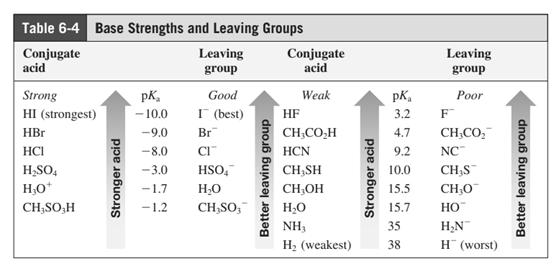
(d)
Interpretation: The structure of major organic product that would result from reaction of should be written and nucleophile, nucleophilic atom the electrophilic atom in the substrate molecule, and leaving group should be identified.
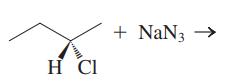
Concept introduction: Leaving-group ability is determined by the capacity of leaving group to accommodate the negative charge as it is displaced from the alkyl halide. Among halogens, the iodides are best-leaving groups followed by bromide chloride and fluoride. Besides halides, some sulphonates and sulphate that can easily delocalize the negative charge can also behave as good leaving group. These include tosylate, mesylate and triflate.
(e)
Interpretation: The structure of major organic product that would result from reaction of should be written and nucleophile, nucleophilic atom the electrophilic atom in the substrate molecule, and leaving group should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Leaving-group ability is determined by the capacity of leaving group to accommodate the negative charge as it is displaced from the alkyl halide. Among halogens, the iodides are best-leaving groups followed by bromide chloride and fluoride. Besides halides, some sulphonates and sulphate that can easily delocalize the negative charge can also behave as good leaving group. These include tosylate, mesylate and triflate.
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. The table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases is as follows:
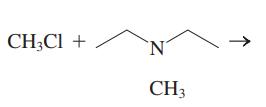
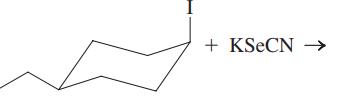
(f)
Interpretation: The structure of major organic product that would result from reaction of should be written and nucleophile, nucleophilic atom the electrophilic atom in the substrate molecule, and leaving group should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Leaving-group ability is determined by the capacity of leaving group to accommodate the negative charge as it is displaced from the alkyl halide. Among halogens, the iodides are best-leaving groups followed by bromide chloride and fluoride. Besides halides, some sulphonates and sulphate that can easily delocalize the negative charge can also behave as good leaving group. These include tosylate, mesylate and triflate.
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. The table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases is as follows:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- What is the slow, rate-determining step, in the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2- butanol? Loss of a b-hydrogen from the carbocation to form an alkene. Protonation of the alcohol to form an oxonium ion. Loss of water from the oxonium ion to form a carbocation. The simultaneous loss of a B-hydrogen and water from the oxonium ion.arrow_forwardDraw the skeletal ("line") structure of the smallest organic molecule that produces sodium hexanoate when reacted with NaOH. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✗ D: ☑ ค 5arrow_forwardConsider the reaction between an alcohol and tosyl chloride, followed by a nucleophile. Write the condensed formula of the expected main organic product. CH3OH −→−−−−−−−−2. CH3S−1. TsCl,pyridinearrow_forward
- Consider the following nucleophilic substitution reaction: R CI Nal R I NaCl acetone Given that the reactants and the products look structurally similar, how can one determine if the substitution reaction took place? O Nal precipitates in acetone. O Nal dissolves in acetone. O NaCl precipitates in acetone. O NaCl dissolves in acetone.arrow_forward4 Why would the chemical equation 1 B2(CO3)3 →1 B2O3+3 CO2 be considered “wrong”?arrow_forward4a. Which type of molecule is this? Label the nonpolar and polar regions of this molecule. Label the ester bonds and phosophodiester bonds. H₂C-0-C HC-0-C CH, CH,−N O CH₂ O CH3 4b. What products would you obtain if you performed an hydrolysis reaction? Draw them. O=C O=0arrow_forward
- Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) is the alcohol found in beverages. It is oxidized in the body to acetaldehyde by the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase. Methanol (CH3OH), also known as wood alcohol, is converted to formaldehyde by the same enzyme. Acetaldehyde is toxic, but formaldehyde is far more toxic to humans, which is why the ingestion of relatively small amounts of methanol can cause blindness or death. One treatment for mild methanol poisoning is the administration of ethanol. Why might a doctor choose this treatment? A. Ethanol likely irreversibly binds to alcohol dehydrogenase which prevents the formation of formaldehyde. B. The doctor has given up on the patient and administers ethanol for sedation. C. Ethanol must act as a competitive inhibitor for the alcohol dehydrogenase and therefore slows the formation of formaldehyde. D. The ethanol is likely an uncompetitive inhibitor and binds to a site other than the active site of the enzyme.arrow_forwardOH 1. NaOH, EtOH 2. n-BuBr A nucleophilic substitution reaction is a frequently used method to convert one functional group into another. A nucleophile is mixed with an electrophile and the nucleophile replaces the leaving group to produce a new compound. In this experiment, a weak nucleophile (2-naphthol) is converted into a strong nucleophile by deprotonation with sodium hydroxide. Then this strong nucleophile, now with a negative charge, reacts with alkyl halide to yield an ether, 2-butoxynaphthalene. 2-butoxynaphthalene is a flavoring agent that has strong fruit smell like raspberry and strawberry.arrow_forwardDistinguish between intermediate products and final products.arrow_forward
- PAP Chemistry-2903012-42100P-1/ Le Chatelier's Principle/ Lesson 128 2. Zinc (Zn) granules react slowly with dilute hydrochloric acid (HCI), but much faster if the acid is concentrated. Zn(s) 2HCI(aq)ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) Zinc + Hydrochloric Acid Zinc Chloride + Hydrogen What causes the reaction to proceed faster with concentrated acid? The concentrated hydrochloric acid causes more hydrogen gas to be produced. The pressure of hydrogen gas molecules increases as concentration increases. The concentrated hydrochloric acid molecules move faster than in dilute acid. There are more collisions between the zinc and concentrated hydrochloric acid. PREVIOUarrow_forwardDraw the structure of the product that forms when the carbonyl compound shown is treated with K,Cr₂O, If no reaction occurs, draw the structure of the organic starting material (reactant). CH,(CH,), (CO)CH(CH,), Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 1 :0 Statover G 0arrow_forwardWhat are the differences between electrophilic reactions and nucleophilic reactions?arrow_forward

 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning



