
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The R and S should be designated to below substrates as well as products of the bimolecular reaction and products with optical activity should be identified.
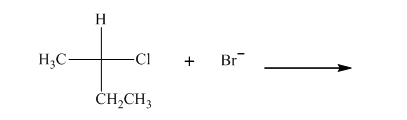
Concept introduction: In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order with the
The Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority. If the groups are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter, if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
(b)
Interpretation: The R and S should be designated to belowsubstrates as well as products of the bimolecular reaction and products that are optically active should be identified.
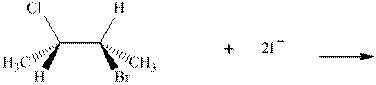
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order with the atomic number as the fundamental property. The one with the highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as “a” and so on.
The Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority. If the groups are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter, if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
(c)
Interpretation: The R and S should be designated to below substrates as well as products of the bimolecular reaction and products that are optically active should be identified.
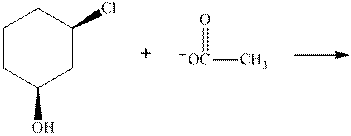
Concept introduction: In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of the atomic number. The one with the highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as “a” and so on.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion the R is assigned to the stereocenter, provided the hydrogen is present below the plane. If hydrogen or least priority group is not below the plane the same molecule is designated as S.
If the rotation is anticlockwise the S is assigned at the configuration provided the hydrogen is present below the plane. If hydrogen or least priority group is not below the plane the same molecule is designated as R.
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
(d)
Interpretation: The R and S should be designated to below substrates as well as products of the bimolecular reaction and products that are optically active should be identified.
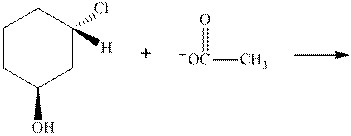
Concept introduction: In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of the atomic number. The one with the highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as “a” and so on.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion the R is assigned to the stereocenter, provided the hydrogen is present below the plane. If hydrogen or least priority group is not below the plane the same molecule is designated as S.
If the rotation is anticlockwise the S is assigned at the configuration provided the hydrogen is present below the plane. If hydrogen or least priority group is not below the plane the same molecule is designated as R.
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- What is the product of the following sequence of reactions? Сно NaCN H,Ot, heat HCI OH OH CO2H CN Co,H CN OH OH II II IVarrow_forwardWhich species is a catalyst in the mechanism in #12?arrow_forward8. Draw a reaction coordinate diagram depicting the thermodynamics of the following reaction. Indicate the locations of any starting materials, intermediates, products, transition states, free energy of reaction and activation energy present in the diagram. Draw the transition state structure, complete with charge information, for the following transformation. Br H₂CCH₂H 20 CA CH3 H3CCH2OH + H CH3 CH3 + BI-arrow_forward
- Draw all products, including stereoisomers, in the following reaction. CH3 CH,COO Part 1: Identify which mechanism(s) the reaction will undergo. Syl D Sy2 SN2 El O E2 Part 2: The number of S1 product(s): 1 The number of El product(s): 2 Part 3 out of 3 The Syl product: draw structure ... CH: The major El product: edit structure #33 The minor El product: edit structurearrow_forwardDetermine the reagent and the intermediates (see choices below) of the reaction to complete the mechanism. но H .CH3 CH3 Intermediate Intermediate 2 1 H Br H HO H CH3 HO OH2* H CH3 H „CH3 CH3 CH3 H Br H Br H Br* H Br H A B D E I-O:arrow_forwardLabel each product in the following reaction as a 1,2-product or a 1,4-product, and decide which is the kinetic product and which is the thermodynamic product.arrow_forward
- What is the rate determining step for the reaction below? 0046 - 00905 + Hoy H IB کار تلوی 0 '애 + ation A B C D دو Acylium lon 0 COH + Multiple Choice: Only one answer is correct, and only one answer can be selected.arrow_forwardIn cationic rearrangements like the pinacol reaction, migrating hydrogens and alkyl groups are shown moving in one step from carbon to carbon as pictured below. This reaction is also classified as a [1,2]-sigmatropic rearrangement. R R R -C+-R R .C+ -R OH R OH R But for migration of phenyl groups (benzene rings), the rearrangement proceeds by a two step process as pictured below: R C+ -R R OH R он R H -R R-C+ OH R -R Relative the to benzene ring and considering the center intermediate, phenyl migration is a(n) a. acyl substitution b. SN2 c. nucleophilic aromatic d. benzyne e. free radical f. electrophilic aromatic g. carbonyl h. SN1 Clear my choice substitution?arrow_forward8. Draw a reaction coordinate diagram depicting the thermodynamics of the following reaction. Indicate the locations of any starting materials, intermediates, products, transition states, free energy of reaction and activation energy present in the diagram. Draw the transition state structure, complete with charge information, for the following transformation. H CH3 Br CH3 + BI- H3CCH ₂0H CA5¹3 H3CCH₂OH + Harrow_forward
- 6. Predict the reactant (starting material) for the reaction and propose a mechanism. NaCN SN2 NaOH E2 CN a Ph Pharrow_forwardDraw the missing reactants/ intermediates in this E1 mechanism. Include all lone pairs. Ignore byproducts.Ignore stereochemistry. I H3O+ : OH H+ Select to I Draw I I Intermediate heat dissociation Select to Draw Intermediate elimination Q Q 1,2-hydride shift I I I I I I I I Iarrow_forwardCH3 CH3 Br- Br2 CH2CI2 CH3 CH3 H3C H3C Br Electrophilic addition of bromine, Br2, to alkenes yields a 1,2-dibromoalkane. The reaction proceeds through a cyclic intermediate known as a bromonium ion. The reaction occurs in an anhydrous solvent such as CH2C12. In the second step of the reaction, bromide is the nucleophile and attacks at one of the carbons of the bromonium ion to yield the product. Due to steric clashes, the bromide ion always attacks the carbon from the opposite face of the bromonium ion so that a product with anti stereochemistry is formed. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow-pushing Instructions CH3 CH3 Br- .CH3 .CH3 H3C H3C :Br :Br:arrow_forward
