
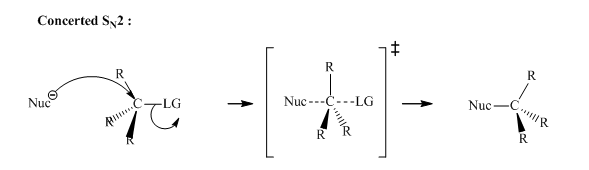
Interpretation:The reason behind slower reaction rates of halocyclopropane and halocyclobutane substrates relative to analogous acyclic secondary
Concept introduction: Bimolecular substitution or
A general
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- ganic 2) Draw the structure of the product/s formed in following reactions. Be sure to pay attention to stereochemistry where appropriate. för i) ii) Br Br OTS EKOH EICH NaBr NASH 1 equivalent + Br-itarrow_forward4-42 For each alkane, 1. Draw all the possible monochlorinated derivatives. 2. Determine whether free-radical chlorination would be a good way to make any of these monochlorinated derivatives. (Will the reaction give mostly one major product?) 3. Which monobrominated derivatives could you form in good yield by free-radical bromination? (a) cyclopentane (c) 2-methylpentane (b) methylcyclopentane (d) 2,2,3,3-tetramethylbutanearrow_forwardIn light of the fact that tertiary alkyl halides undergo spontaneous dissociation to yield a carbocation plus halide ion (see Problem 10-45), propose a mechanism for the following reaction.arrow_forward
- Q1. For each reaction, give the expected substitution product and predict whether the mechanism will be first order (S,1) or second order (S,2): a) 2-chloro-2-methylbutane + CH,COOH b) isobutyl bromide + NaOMe c) 1-iodo-1-methylcyclohexane + CH;CH,OHarrow_forwardwhat is the expected major product of HBr addition to the alkene shown below? Show the mechanismarrow_forwardWhich of the following species has the most stoble anion? Consider the free energy profile for the transformation A to 0 ye on Dut of me overot reoction is endergonic andoemic evergone Refer to the following reaction mechanism slow CH, C-OCH fast CH-C OCH, OH CH,0 OH fast CH,C-O CH,OH The least stoble transition staote has which structure 8- A. CH-C-OCH3 B. CH, C OCH, C. CH, C-OCH, D. CH, C,OCH OH OHarrow_forward
- Chlorine and bromine react in the dark with alkenes. The reaction shown below affords a single major product as a racemic mixture. .CI Cl2 For the mechanism step below, draw curved arrows to show electron reorganization. Consider the formation of just one of the product stereoisomers. Arrow-pushing Instructionsarrow_forwardWhat is the Potential energy diagram for this reaction. Pls draw with as much detail as possible. labels and scale) 2-methylpropan-2-ol ---> 2-methylpropene +H2O Draw the potential energy diagram for the reaction of 2-methylpropan-2-ol ---> 2-methylpropene + H20 (1) Label the structures of the (a) reactants, (b) intermediates, (c) transition states, (d) products, and (e) activation energies (E.) for each step. (2) Which step is the rate-determining step? (3) Identify the electrophile and nucleophile in each step when applicable.arrow_forward4. Draw the mechanism that accounts for the formation of the product under the conditions shown. You may not add any other reagents. Be sure to show: all intermediate structures that occur in the course of the mechanism, any important resonance structures that play a role in the process, what if anything is added or lost in each step, and all formal charges on the structures. CHO H+ HO-C-H HO OH H-C-OH CH,OH НО 1 2 = 3arrow_forward
- ow the mechanism for the following reaction conducted at -5 °C in CC14: cyclohexene + bromine yields a dibromocyclohexane Draw structures - including charges and electrons - and add curved arrows. Details count. Step 1 Add three curved arrows to the first step. Draw the step 1 products: 1 organic species; 1 inorganic species. Step 2 • Reproduce the step 1 products. Add two curved arrows to show the bromide ion reacting with the organic species. Draw the final product. 1L o ↑ Maparrow_forwardSynthesis the followiong reactions Pt 1) Cyclohexyne + 2H,- (850-900)C 3) CH;CH,CCCH3 + H20 2HB. 4) 5) + Zn 6) + HF-arrow_forwardQuestion 2 of 4 Attempt 8 Identify the two diastereomeric hydroboration-oxidation products that can be formed from the alkene by dragging the product pair to the product bin. Then suggest which product should be the major product or whether they will be formed in equal amounts by dragging the appropriate label to the bin under the products. > O Macmillan Learning 1) BH3, THF 2) H2O2, “OH OH ထိုသို့ ထိုသို့ + OH OH OH ထူးထူ OH ОН minor product and major product Answer Bank ထို OH ОН OH ထို OH ОН H major product and minor product approximately equal amounts ОН ||Tarrow_forward
