
Interpretation:Bromoalkanes that most closely resemble
Concept introduction: Bimolecular substitution or
A general
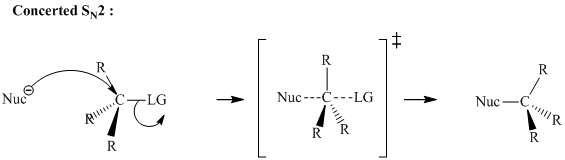
The three-dimensional orbital description of
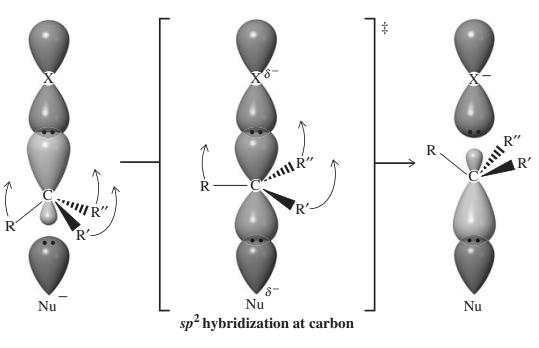
The
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Please predict the outcome of the addition of HBr to (a) trans-2-pentene, (b) 2-methyl-2-butene, and (c) 4-methylcyclohexene. Also please list how many isomers can be formed in each case? Thank youarrow_forwardDraw the structures for each of the following molecules. (a) 2-fluorotoluene; (b) 4-ethoxytoluene; (c) 2-ethoxyanisole;(d) 1,3-diphenylheptane; (e) 4,4-diphenyl-1-octene; (f) benzylbenzenearrow_forwardPlease tell the outcome of the addition of HBr to (a) trans-2-pentene, (b) 2-methyl-2-butene, and (c) 4-methylcyclohexene. Also please list how many isomers can be formed in each case.arrow_forward
- Draw the structures for these molecules. (a) 2-chloropropene; (b) 3-methylbut-1-ene; (c) 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene;(d) 2-ethoxy-3,3-dimethylcyclohexene; (e) 3,4,5-trimethoxycycloheptene; (f) 3-bromo-2-methyl-4-nitrocyclopentene;(g) 3,3-dibromo-4-methylcyclopentene; (h) 4-methyl-2-pentynearrow_forwardAll the structures shown here have the molecular formula CH18. Which structures are the same molecule? (Hint: One way to answer this ques+ion is to determine the chemical name for each structure.) ÇH3 CHз ҫHз (a) CH-CCH-CHСH; (b) CH;CHснСН, СHз CHз CH2 ČH3 CHз CHCНCH3 (с) CH,CHCHCНЗ (d) CH;CHĊHCH3 СНCH3 ČH3 ČH3arrow_forwardA certain hydrocarbon had the molecular formula C18H30 and contained two triple bonds. Ozonolysis gave CH₂(CH₂)CO₂H and HO₂CCH₂CH₂CO₂H as the only products. Draw a reasonable structure for this hydrocarbon. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- How does the addition of NaNH2 to an alkane lead to the synthesis of a terminal alkyne? Doesn't the starting material have to be an alkene?arrow_forwardDraw structural formulas for the major organic product(s) of the reaction shown below. CN AICI3 + (CH3)2CHCI • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. If no reaction occurs, draw the organic starting material. Remember to include all of the formal charges on the atoms of any nitro groups.arrow_forwardBr ||| Br Rank these alkyl halides in order of increasing reactivity in an SN1 reaction. Br A) III < | < || B) || < ||| < | C) ||| < || < | D) || < | < III E) | < ||| < ||arrow_forward
- C=CH H20, H2SO4 H9SO4 CH3 Alkynes do not react directly with aqueous acid as do alkenes, but will do so in the presence of mercury(II) sulfate as a Lewis acid catalyst. The reaction occurs with Markovnikov regiochemistry, so the OH group adds to the more highly substituted carbon and the H adds to the less highly substituted carbon. The initial product of the reaction is a vinyl alcohol, also called an enol. The enol immediately rearranges to a more stable ketone via tautomerization. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow-pushing Instructions H-OH HO: Hjö: C=CH c=CH Hö Hg Hgarrow_forward5B In the following reactions, mixtures of alkenes and ethyl ethers are formed. Draw their structures. Explain which is or are likely to be the main product(s) in each reaction. In case of formation of two isomers of alkenes, explain which is formed in greater proportion CH3 CH3 H3C-C H -Br CH3 EtOHarrow_forwardProvide your answers in the Text Submission box below. The following names are incorrect. Write the correct form. (a) 3,5-dibromobenzene; (b) o-aminophenyl fluoride; (c) p-fluorochlorobenzene.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





