
Interpretation:The reason behind racemic mixture of iodoheptane products formed rather than pure
Concept introduction:Bimolecular substitution or
A general
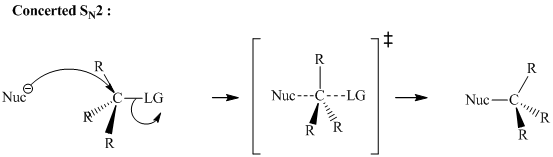
Polar-aprotic solvents accelerate the rate of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Tautomerization is a process in which an enol yields a ketone Give one examplefor a keto to enol tautomerization. Which form is more stable. Also, which ismore stable the E isomer or the Z isomer of 2-Chloro, 2-Butenearrow_forwardProvide the major product of each of the following reactions: What do all these reactions have in common? How do all reactions differ?arrow_forwardThe high reactivity of alkyl halides can be explained in terms of nature of C-X bond which is highly polarized covalent bond due to large difference in the electronegativities of carbon and halogen atom. This polarity is responsible for the nucleophilic substitution reactions of alkyl halides which mostly occur by Swa and Swa mechanisms. Sy reaction is a two-step process and in the first step, R-X ionizes to give carbocation (slow process). In the second step, the nucleophile attacks the carbocation from either side to form the product (fast process). In Swi reaction, there can be racemization and inversion. Swi reaction is favored by heavy (bulky) groups on the carbon atom attached to halogens. i.e., R,C-X>R;CH-X>R-CH,X>CH,X. In Sna reaction, the strong nucleophile OH attacks from the opposite side of the chlorine atom to give an intermediate (transition state) which breaks to yield the product (alcohol) and leaving (X) group. The alcohol has a configuration opposite to that of the…arrow_forward
- Give step-by-step mechanism for the following reactionarrow_forwardprovide appropriate reagents or product for the following example if you can show work I'd appreciate it!!! OMe OMearrow_forwardChoose which compound is more reactive when reacted with N2OH in water solvent and he reason clearly. vs OH HO,arrow_forward
- Provide the missing reagents to complete the reactions below, if there is more than one step required, be sure to indicate appropriately.arrow_forwardCurrent Attempt in Progress When toluene is sulfonated (concentrated H₂SO4) at room temperature, predominantly (about 95% of the total) ortho and para substitution occurs. If elevated temperatures (150-200°C) and longer reaction times are employed, meta (chiefly) and para substitution account for some 95% of the products. Account for these differences in terms of kinetic and thermodynamic pathways. At the lower temperature, the reaction is observed. At higher temperatures, the reaction is be reached, the most stable isomer, controlled, and the usual o/p directive effects of the -CH3 group are ✓ controlled. At reaction times long enough for equilibrium to , is the principal product.arrow_forwardPredict the main reaction product(s) under the following reaction conditionsarrow_forward
- Give the mechanistic Symbols CE1, E₂, SN, SN²) that are Con Sistent with Statemenst! most each of the following O Methyl halides react with Sodium ethoxide in eth and only by this mechanism In ethanol that contains Sodiumn ethoxide, tert-butyl bromide reacts mainly by this mechanism c) these reaction Con certed DJ these involve are mechanisms infere processes reactions mechanisms carbc cation intermedites E) Reactions proceeding by mechanisms are these Sterospecificarrow_forwardWhich of the following best describes a key step in the mechanism for the reaction below? HO, ... -CH3 -CH3 + en dihydroxylation H3C- H3C- OH (A) free-radical substitution at the carbonyl carbon B elimination reaction by abstraction of a beta-hydrogen nucleophilic attack by an alkene to form a cyclic (epoxide) intermediate electrophilic addition reaction to form a carbocation intermediatearrow_forwardWhat is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction? Hint: Be mindful of the stereochemistry which is reflective in selecting the answer. O only 1 O only 2 O only 3 CH3CO3H 2 ས། swowu ' 1 ·!,v:,、 O both 2 and 3 A 3 Harrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

