
(a)
Interpretation: The reason behind hydrogen abstraction by chlorine rather than bromine atoms even when equimolar amount of each is present should be explained.
Concept introduction: The monochlorination performed with ultraviolet light proceeds via radical chain mechanism. Chlorine transforms
The fundamental radical chain mechanism is summarized in the illustration below:
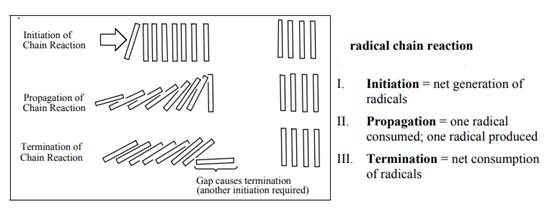
(b)
Interpretation: The bond enthalpies involved in radical halogenation carried out with
Concept introduction: The monochlorination performed with ultraviolet light proceeds via radical chain mechanism. Chlorine transforms
The formula to calculate
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- (a) What is the standard enthalpy of reaction for the reaction of 1.00 mol of propene with 1.00 mol of hydrogen to yield 1.00 mol of propane. (All gas phase) (b) What is the standard entropy change for the reaction? (c) What is the standard free energy change for the reaction carried out at 400 K? (You cannot use ∆Gfo data from the appendix). (d) Is the reaction spontaneous? (a) (b) (c) (d)arrow_forward1: In the sweetening MEROX process for kerosene the mercaptans are converted into (a) Sulpher (b) Disulphide (c) Hydrogen sulphide (d) None of these 2: Which of the following products contain maximum sulphur? (a) Diesel fuel (b) Fuel oil (c) Jet fuel (d) LPG 3: Which of the following petroleum product has a maximum C/H ratio (by weight)? (a) Light diesel oil (b) Fuel oil (c) Naphtha (d) Heating oil 4: Which of the following hydrocarbon are most desirable in gasoline? (a) Paraffins (b) Isoparaffins (c) Naphthenes (d) Aromatic 5: Octane no. of paraffins: (a) Remain constant with change in the number of carbon atoms (b) Increases with increase in the number of carbon atoms (c)Decreases with increase in the number of carbon atoms (d)None of the above 6: Which of the following hydrocarbons has a maximum octane number? (a) Benzene (b) Cyclohexane (c) Hexane (d) Iso-hexane 7: Which of the following petroleum products has a minimum flashpoint? (a)Gasoline (b) Kerosene (c) Fuel oil (d) Heating…arrow_forwardThe pentadienyl radical, H2C“CH¬CH“CH¬CH2#, has its unpaired electron delocalized over three carbon atoms.(a) Use resonance forms to show which three carbon atoms bear the unpaired electron.(b) How many MOs are there in the molecular orbital picture of the pentadienyl radical?arrow_forward
- Using a table of average bond enthalpies. Table 6.2 ( Sec. 6-6b), estimate the enthalpy change for the industrial synthesis of methanol by the catalyzed reaction of carbon monoxide with hydrogen.arrow_forward(b) (1-chloromethyl)cyclopentane, CeH11CI reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide, NaOH to produce a primary alcohol AA. When CeH11Cl is added with magnesium, Mg in ether, an organometallic compound BB is formed. When compound BB reacts with ethanal, CH3CHO, a secondary alcohol cCis formed. The molecular structure of CeH11Cl is given below. (1-klorometil)siklopentana, CoH1,CI bertindak balas dengan akues natrium hidroksida, NaOH bagi menghasilkan satu alkohol primer AA. Apabila CeH11CI ditambah dengan magnesium, Mg dalam eter, sebatian organologam BB terbentuk. Apabila sebatian BB bertindak balas dengan etanal, CH;CHO, satu alkohol sekunder CC dihasilkan. Struktur molekul bagi CsH11CI diberikan di bawah. .CI (1-chloromethyl)cyclopentane (i) Draw the structural formula for compound AA through Cc. Lukiskan formula struktur bagi sebatian AA sehingga C. (ii) What is the type of reaction to produce compound AA? Apakah jenis tindak balas untuk menghasilkan sebatian AA?arrow_forwardWrite the contributing resonance structures and resonance hybrid for each of the following: (a) CH;CH=CH-CH=OH (f) CH3 (b) CH2=CH-CH-CH=CH2 (g) CH3-S-CH, (h) CH3-NO, (d) CH2=CH-Br CH, (e)arrow_forward
- (b) (1-chloromethyl)cyclopentane, C6H11CI reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide, NaOH to produce a primary alcohol AA. When CsH11Cl is added with magnesium, Mg in ether, an organometallic compound BB is formed. When compound BB reacts with ethanal, CH3CHO, a secondary alcohol cC is formed. The molecular structure of C6H11CI is given below. (1-klorometil)siklopentana, C6H11CI bertindak balas dengan akues natrium hidroksida, NaOH bagi menghasilkan satu alkohol primer AA. Apabila C6H11CI ditambah dengan magnesium, Mg dalam eter, sebatian organologam BB terbentuk. Apabila sebatian BB bertindak balas dengan etanal, CH3CHO, satu alkohol sekunder CC dihasilkan. Struktur molekul bagi C6H11CI diberikan di bawah. (1-chloromethyl)cyclopentanearrow_forwardThe bond length of the indicated C-C single bond in hexa-1,3,5-triene is about 146 pm, which is considerably shorter than that in ethane, H3C-CH3. (a) How much shorter is it? Hint: See Figure 14-2, page 685. (b) Which occupied T MOS (obtained in Problem 14.32) help decrease this bond length? (c) If an electron were promoted from the HOMO to the LUMO, would the length of the C-C single bond increase, decrease, or stay roughly the same? Explain. 146 pmarrow_forward(b) Compare combustion of Anthracene and Xylene in sufficient supply of air. Which one will produce more carbon rich sooty flame and why?arrow_forward
- Carbon–carbon bond dissociation enthalpies have been measured for many alkanes. Identify the alkane in each of the following pairs that has the lower carbon–carbon bond-dissociation enthalpy, and explain the reason for your choice. (a) Ethane or propane (b) Propane or 2-methylpropane (c) 2-Methylpropane or 2,2-dimethylpropane (d) Cyclobutane or cyclopentanearrow_forwardUse bond-dissociation enthalpies (Table 4-2, p. 167) to calculate values of ∆H° for the following reactions. (a) CH3¬CH3 + I2 ¡ CH3CH2I + HI(b) CH3CH2Cl + HI ¡ CH3CH2I + HCl(c) (CH3)3C¬OH + HCl ¡ (CH3)3C¬Cl + H2O (d) CH3CH2CH3 + H2 ¡ CH3CH3 + CH4 (e) CH3CH2OH + HBr ¡ CH3CH2¬Br + H2Oarrow_forward(a) (i) 3-Methyl-2-butanol will react with sulphuric acid to give two isomeric alkenes in 3:1 proportions.(i) Write down the structures for these alkenes and assign appropriate systematic names to them. (ii) Name the most abundant isomer. (iii) Write down detailed mechanism for the formation of a minor product.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
