
Interpretation: Potential-energy versus reaction-coordinate diagrams for the two propagation steps for monobromination of methane should be sketched.
Concept introduction: The mechanism for monobromination comprises of three stages illustrated as follows:
Step1: Initiation via homolytic cleavage of
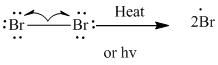
Step2: Propagation: In first of the propagation step bromine radical from step 1 abstracts hydrogen radical from methane as follows:
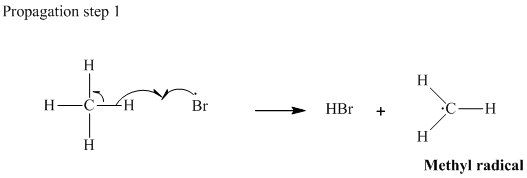
In subsequent propagation step methyl radical abstracts
Step3: Termination: Radicals generated in propagation steps get quenched upon combination with one another. Thus termination steps are essentially the radical− radical combination illustrated as follows:
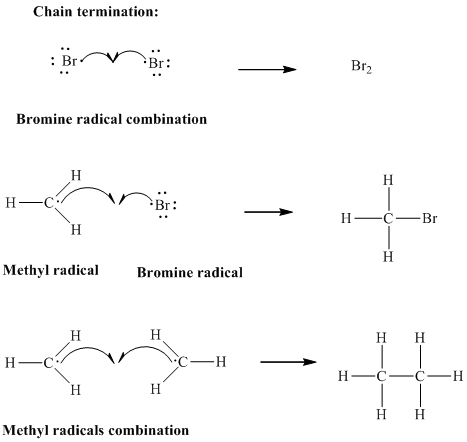
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Two substitution products result from the reaction between 3-chloro-3-methyl-1- butene with sodium acetate (CH3COO – Na +) in acetic acid under SN1. Identify the products.arrow_forward2-chloropropane is a major product of the reaction of chlorine with propane under ultraviolet light. Write the mechanism for this reaction including the initiation step and the two propagation steps.arrow_forwardwrite the free radical monosubtitution mechanism for the bromination of ethane to produce bromoethanearrow_forward
- Ethane reacts with chlorine (Cl2) in the presence of ultra-violet (UV) light, to produce 1-chloropropane (CH3CH2Cl) and hydrogen bromide (HCl). As shown in the equation below.CH3CH3+ Cl2→ CH3CH2Cl+ HClDescribe the reaction mechanism of the reaction between ethane and chlorine to produce 1-chloroethane. The description should be detailed and must include the type of bond fission that takes place. You may sketch and insert suitable diagrams to aid your description if you wish.arrow_forwardThe rate of hydration of 2-butene and 2-methylpropene differ by several orders of magnitude. Please state which alkene is more rapidly hydrated and why.arrow_forwardWrite the propagation steps leading to the formation of dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) from chloromethanearrow_forward
- Describe the reaction to form the catalyst L-prolinamide. (reaction is added below) .arrow_forward7. The following scheme shows the intermediates in the mechanism for the synthesis of isoamyl acetate, an ester with a characteristic banana flavor. Classify steps 1, 2, 3, and 4 as addition, elimination, substitution, or acid base reactions. lo ОН gor H2SO4 2 HO HO QH₂ H2SO4 1 .H ОН له عليه ملا 4 HO 3 لیڈ جل OH HO OH + H2O Harrow_forwardPleasearrow_forward
- didentify the Allowry reactions, as substitution, elimination, or addition DrawWelection arrows to show how the in each reactors Circle and identify any reactive bands break & form intermediates of carbon. Ħ Br Br → AH-Br →→ → XB²arrow_forwardThe chlorination of ethane produces many by-products. One by-product that forms in small amounts is 2-chlorobutane. Suggest a mechanism for the formation of 2-chlorobutane from the radical chlorination of ethane. (NOTES: intermediates can only have one radical, 2-chlorobutane should be the product of your termination step, any intermediate radical formed during the propagation phase can be used in the termination step)arrow_forwardIndustrial chemistry: Provide a mechanism for the hydrocracking of n-Heptane in the presence of hydrogen gas to isopentane and ethane.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
