
Machine Elements in Mechanical Design (6th Edition) (What's New in Trades & Technology)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780134441184
Author: Robert L. Mott, Edward M. Vavrek, Jyhwen Wang
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 48P
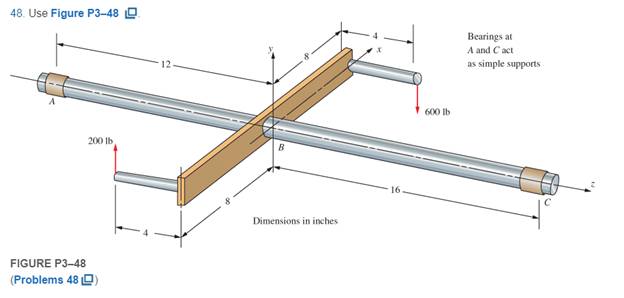
For Problems 48−50, draw the free-body diagram of the main shaft portion, labeled A, B, and C. Include any unbalanced torque on the shaft that tends to rotate it about the z-axis. In each case, the reaction to the unbalanced torque is taken at the right end of the shaft labeled C. Then draw the complete shearing force and bending moment diagrams for loading in the y−z plane. Also prepare a graph of the torque in the shaft as a function of position along the shaft from A to C.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Need help with number 13, please!
5.2 Please help.
Provide Free Body Diagram, labeled with appropriate quantities to better understand. Also solve. Thank you.
4-Determine the rotation angle between A and C, if the torque is
T=0.9 N.m in point C, if G=80 GPa and diameter of all shafts are
D=4 mm. (The radius of small circle are r and the bigger one are
2r)
e are
Coder
40
T=09N.N
Chapter 3 Solutions
Machine Elements in Mechanical Design (6th Edition) (What's New in Trades & Technology)
Ch. 3 - A tensile member in a machine structure is...Ch. 3 - Compute the stress in a round bar having a...Ch. 3 - Compute the stress in a rectangular bar having...Ch. 3 - A link in a packaging machine mechanism has a...Ch. 3 - Two circular rods support the 3800 lb weight of a...Ch. 3 - A tensile load of 5.00 kN is applied to a square...Ch. 3 - An aluminum rod is made in the form of a hollow...Ch. 3 - Compute the stress in the middle portion of rod AC...Ch. 3 - Compute the forces in the two angled rods in...Ch. 3 - If the rods from Problem 9 are circular, determine...
Ch. 3 - Repeat Problems 9 and 10 if the angle is 15 .Ch. 3 - Figure P312 shows a small truss spanning between...Ch. 3 - The truss shown in Figure P313 spans a total space...Ch. 3 - Figure P314 shows a short leg for a machine that...Ch. 3 - Consider the short compression member shown in...Ch. 3 - Refer Figure P38 . Each of the pins at A, B, and C...Ch. 3 - Compute the shear stress in the pins connecting...Ch. 3 - Prob. 18PCh. 3 - Prob. 19PCh. 3 - Prob. 20PCh. 3 - Prob. 21PCh. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress in a circular...Ch. 3 - If the shaft of Problem 22 is 850 mm long and is...Ch. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress due to a torque...Ch. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress in a solid...Ch. 3 - Compute the torsional shear stress in a hollow...Ch. 3 - Compute the angle of twist for the hollow shaft of...Ch. 3 - A square steel bar, 25 mm on a side and 650 mm...Ch. 3 - A 3.00 in-diameter steel bar has a flat milled on...Ch. 3 - A commercial steel supplier lists rectangular...Ch. 3 - A beam is simply supported and carries the load...Ch. 3 - For each beam of Problem 31, compute its weight if...Ch. 3 - For each beam of Problem 31, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For the beam loading of Figure P334, draw the...Ch. 3 - For the beam loading of Figure P334, design the...Ch. 3 - Figure P336 shows a beam made from 4 in schedule...Ch. 3 - Select an aluminum I-beam shape to carry the load...Ch. 3 - Figure P338 represents a wood joist for a...Ch. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - Prob. 40PCh. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - Prob. 42PCh. 3 - Prob. 43PCh. 3 - Prob. 44PCh. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - For Problems 39 through 50, draw the free-body...Ch. 3 - For Problems 4850, draw the free-body diagram of...Ch. 3 - For Problems 4850, draw the free-body diagram of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 50PCh. 3 - Compute the maximum tensile stress in the bracket...Ch. 3 - Compute the maximum tensile and compressive...Ch. 3 - For the lever shown in Figure P353 (a), compute...Ch. 3 - Compute the maximum tensile stress at sections A...Ch. 3 - Prob. 55PCh. 3 - Refer to Figure P38. Compute the maximum tensile...Ch. 3 - Prob. 57PCh. 3 - Refer to P342. Compute the maximum stress in the...Ch. 3 - Refer to P343. Compute the maximum stress in the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 60PCh. 3 - Figure P361 shows a valve stem from an engine...Ch. 3 - The conveyor fixture shown in Figure P362 carries...Ch. 3 - For the flat plate in tension in Figure P363,...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - For Problems 64 through 68, compute the maximum...Ch. 3 - Prob. 68PCh. 3 - Figure P369 shows a horizontal beam supported by a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 70PCh. 3 - Prob. 71PCh. 3 - The beam shown in Figure P372 is a stepped, flat...Ch. 3 - Figure P373 shows a stepped, flat bar having a...Ch. 3 - Figure P374 shows a bracket carrying opposing...Ch. 3 - Prob. 75PCh. 3 - Figure P376 shows a lever made from a rectangular...Ch. 3 - For the lever in P376, determine the maximum...Ch. 3 - Figure P378 shows a shaft that is loaded only in...Ch. 3 - Prob. 79PCh. 3 - Prob. 80PCh. 3 - A hanger is made from ASTM A36 structural steel...Ch. 3 - A coping saw frame shown in Figure P382 is made...Ch. 3 - Prob. 83PCh. 3 - Figure P384 shows a hand garden tool used to break...Ch. 3 - Figure P385 shows a basketball backboard and goal...Ch. 3 - Prob. 86P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Repeat Problem 11.2-3 assuming that R= 10 kN · m/rad and L = 2 m.arrow_forwardPlease I want answer of that question from these choicesarrow_forwardA gear reduction unit uses the countershaft shown in the figure. Gear A receives power from another gear with the transmitted force FA applied at the 20° pressure angle as shown. The power is transmitted through the shaft and delivered through gear B through a transmitted force FB at the pressure angle a = 34º. Determine the bending moment at the critical location assuming the bearings act as simple supports. Put your answer in the lbf.in unit to 4 significant figures. Only enter the numerical value and positive/negative sign. Answer: 1.25-in dia. Gear A 20-in dia. F-300 lbf 16 in 20⁰ 14 in Gear B 8-in dia.arrow_forward
- 4-67. Compute the angle of twist of the free end rela- tive to the fixed end of the steel bar shown in Figure P4-67.arrow_forward4) The 1.5 in diameter shaft below is supported by a thrust bearing at A and a self-aligning bearing at B. The gear weights 100 lbs and supports a 400 lb load in the axial direction (+x-direction), a 2000 lb transmitted load (+y-direction), and 600 lb radial load (-z-direction). The pulley weighs 400 lb and supports loads in the +z-direction. a. Construct the V-M-N-T diagrams for the shaft. b. Determine the location on the shaft with the most severe state of stress. c. Sketch the Mohr's circle and find the principal stresses at that location. 6 in. -12 in. - 8 in. YA 400 lb 600 lb Gear 2000 lb 4 in. 1200 lb 200 lb D 8 in. Pulleyarrow_forwardII kN m 5 kN m 3 kN m 3 kN m 75 mm 85 mm 70 mm 2 m 2m 2 m FIGURE P12-6 The "new" magnitude of the external torque applied at "B" to maintain equilibrium of the shaft is ---_kN-m. The magnitude of the minimum shear stress in the shaft between "A" and "B" is MPа. The magnitude of the maximum shear stress in the shaft between "A" and "B" is _____MPa. The magnitude of the maximum shear stress in the shaft between "B" and "C" is MРа. The magnitude of the maximum shear stress in the shaft between "C" and "D" is _____MPa. The magnitude of the minimum shear stress in the shaft between "C" and "D" is __--_MPa. 10arrow_forward
- The shaft is fixed at ends A and B and has a positive torque T a distance of 4m from A and 8m from end B. If the angle of twist is zero and the reaction torque at A is 334N-m, what is the magnitute of applied torque T?arrow_forwardThe axis ABCD receives a torque of 500Nm from the motor and transmits movement to other devices, by means of belts and pulleys connected at B and C. If it is known that the torques exerted on pulleys B and C are as shown In the figure, determine the minimum radius the shaft must have. You should consider that at point D of the motor there is a bearing that acts as a support for the shaft as at point A. The material of the shaft and its allowable shear stress are indicated in the drawing.Determine:to. Free-Body diagram.b. Shear force diagrams.c. Bending moment diagrams.d. Identification of the critical point of the axis.e. Calculation of the axis radius. tperm=80MPaarrow_forwardHomework helparrow_forward
- The A36 steel shafts as shown in the figure below are made from two segments: solid segment AC with diameter = 1 in and a hollow segment CB with an outside diameter = 2 in and inside diameter = 1 in. The shaft is fixed at both ends. Determine the magnitude of the applied torque T (lb-in) if the reaction at A is 600 lb-in clockwise.arrow_forwardd1(mm)= 40 d2(mm)=30 L1(mm)=300 L2(mm)=150 T1(Nm)=775 T2(Nm)=985 only HANDWRITTEN answer needed ( NOT TYPED)arrow_forwardA shaft ABCD is fixed at end D and has torques acting at points A, B, and C as shown below. The bearing support between A and B allows free rotation. If we know that A = −0.382 rad, A/B = 0.358 rad, and B/C = −0.233 rad, calculate the absolute twist of the shaft at point C(oc) and enter it in rad (radians) correct to 3 significant digits below. Make sure to include the sign if it is negative noting that CCW rotations are positive and CW rotations are negative. 150 N.m 280 N.m B 40 N-m Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Everything About TRANSVERSE SHEAR in 10 Minutes!! - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4x0E9yvzfCM;License: Standard Youtube License