
Concept explainers
(a)
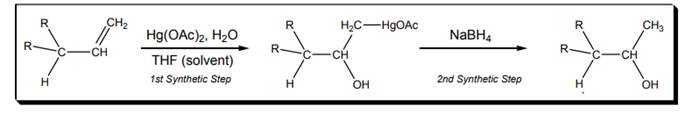
Interpretation: Mechanism for the first synthetic step of oxymercuration-demercuration reaction shown below should be drawn.
Concept introduction:
(b)
Interpretation: A Lewis structure of
Concept introduction: Lewis structures depict covalent bonds and describe valence electrons are present in the molecule. The sequence that leads to the Lewis structure of the molecule is as follows:
- Identify the central atom and arrange various other atoms around it. This atom so chosen is the least electronegative one.
- Estimate the total valence electrons.
- First, place a single bond between each pair.
- The remaining electrons can be allocated as lone pairs to satisfy the octet rule for each atom.
(c)
Interpretation: Particular characteristics of oxymercuration reaction shown below should be explained.
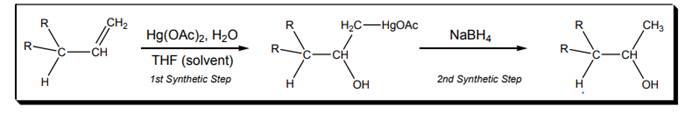
Concept introduction: Oxymercuration takes place in the presence of
(d)
Interpretation: Mechanism for acid-catalyzed hydration of below alkene substrate should be drawn.
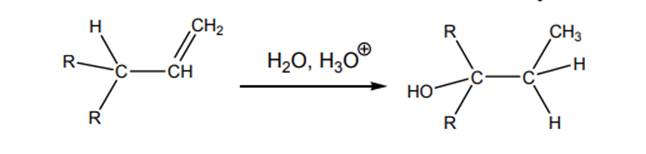
Concept introduction: Acid-catalyzed hydration is the electrophilic addition of water. The reactive species that act as a catalyst are
.In the second stage water, itself acts as a nucleophile and abstracts a proton to hydration product. The carbocation rearrangement can also be found in such reactions.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- OH SYNTHESIS 1. POCI3 2. HBr, ROOR 3. Mg, ether 4. benzaldehyde 5. H3O+ workup 6. PCC 7. CH3MgBr 8. H3O+ workup Br Tarrow_forwardB. Supply the missing reagent, product or starting material of the following reactions. 1. NACN 2. H2SO4, H2O 1. Zn(Hg), H3O* 2. NH-NH>, КОН H. 3. I НО, 4. Reagent I:arrow_forwardWhat is the major product of this reaction? heat + IV. I. I. V. II.arrow_forward
- 1. OH ??? Br + B ОН For the above reaction identify the catalyst and reagents and also show the catalytic cycle.arrow_forwardSelect the correct product of the following reaction series. 1. NaOEt, EtOH 2. Br EtO NHAC OEt 3. H3O+, 100°C ? H₂N. CO₂H HẠN_CO,H HẠN_CO,H Br I II IIIarrow_forward4. Consider the reaction shown below. Which term best describes this reaction? a. Addition b. Elimination c. Rearrangement d. Substitution + Br₂ Br Brarrow_forward
- 7. The reaction of methoxide anion with bromoethane to yield the ether ethyl methyl ether and the bromide anon (Br-) is an excellent example of a general reaction type called Sy2 (substitution nucleophilic bimolecular): CH,0+ CH,СH-Br a CH3-0-CH,СH; + Br- a. Change in enthalpy is -103 kJ/mol; the change in entropy is + 0.025 kJ/mol-K. Calculate DG at 300K. b. Is the reaction endergonic or exergonic? c. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? d. Use curved arrows to show the complete mechanism. Reaction of 2-methyl-1-butene with H-Cl could yield TWO alkyl chloride products. Draw and name 8. them.arrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. 1. RCO3H 2. H3O+ Drawing Q Version: 1.177.0+ productionarrow_forwardNBS heat Draw the molecule(s) on the canvas by choosing buttons from the Tools (for bonds and charges), A toolbars. H± 12D EXP. CONT. H C N O S F CI Br Br P F × Incorrect; Try Again; 2 attempts remaining Note that, in the second propagation step, bromine is attacked by the least sterically hindered carbon ra Δ A. Submit Previous Answers Request Answerarrow_forward
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. O 1. KMnO4, H₂O, heat 2. H* (workup) Drawing ✔arrow_forwardFigure 9-5 Alkenes лекув halides 1 A а Br B 3 с Br Brarrow_forwardfor this question. Draw a structural formula for the missing product in the following reaction. 0. NaHCO3 H20 ? + CO2 + H20 + CH3C-OH • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • Include cationic counter-ions, e.g., Na+ in your answer, but draw them in their own sketcher. C P. opy aste [F **** C - Visited CH4 ChemDoodle Retry Entire Group 5 more group attempts remaining Submit Answerarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
