
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The reagent and condition has to be proposed for step 1,2,3 and 5.
Concept introduction:
Hydrogenolysis:
Nitration: The formation of nitro group in a
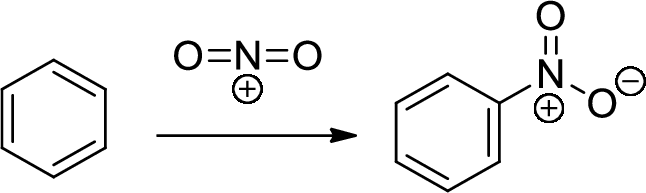
(b)
Interpretation:
The mechanism is to be proposed for iodination of 3-aminobenzoic acid.
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic
Halogenations on benzene:
Halogenation is one of the electrophilic substitution reactions. Halogens reaction with benzene (or electron donating group present in the benzene ring) which gives the corresponding halogenated compound.
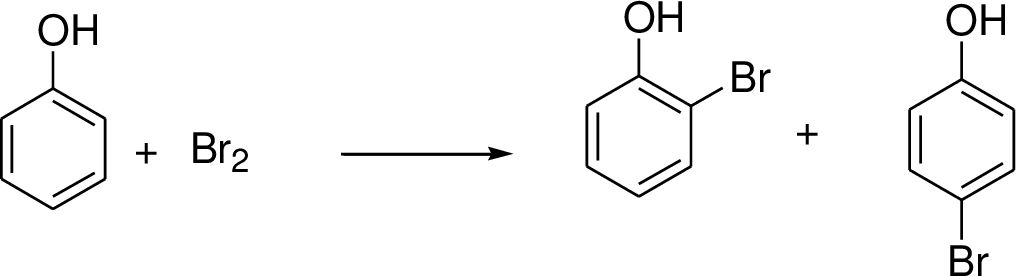
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- The Ksp for lead iodide ( Pbl₂) is 1.4 × 10-8. Calculate the solubility of lead iodide in each of the following. a. water Solubility = mol/L b. 0.17 M Pb(NO3)2 Solubility = c. 0.017 M NaI mol/L Solubility = mol/Larrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forward
- Only 100% sure experts solve it correct complete solutions need to get full marks it's my quiz okkkk.take your time but solve full accurate okkk chemistry expert solve itarrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- Show work. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardPart A Give the IUPAC name and a common name for the following ether: CH3-CH2-O-CH2-CH2-CH3 Spell out the full names of the compound in the indicated order separated by a comma. Submit My Answers Give Up Part B Give the IUPAC name and a common name for the following ether: Spell out the full names of the compound in the indicated order separated by a comma. Submit My Answers Give Uparrow_forwardFrenkel and Schottky are intrinsic or extrinsic defects, point or linear defects.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole




