
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The conjugate base of acetic acid with its two important resonance structuresshould be determined.
Concept introduction: According to Bronsted-Lowry concept, substance that donates proton is termed as acid while that accepts or gains protons is called base. Species formed after loss of protons from acids are known as their respective conjugate bases whereas conjugate acid is produced by addition of protons to base.
(b)
Interpretation: The rank of below bases from highest to lowest potential energy on the basis of their pKa data should be determined.
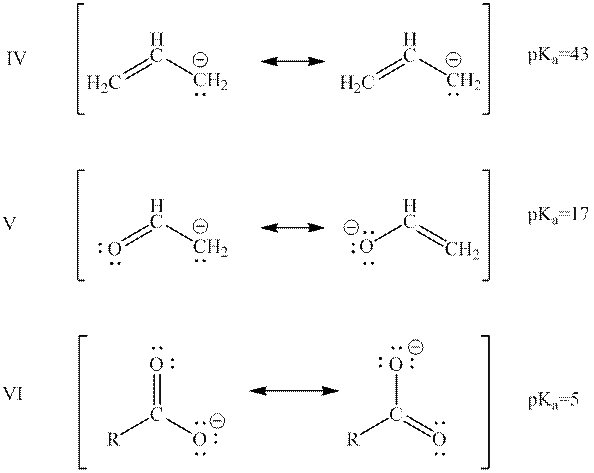
Concept introduction: When one single structure is unable to describe all the properties of single molecule, a phenomenon called resonance comes into play. This arises when two or more than two Lewis structures are possible for one molecule. All such structures are called resonating structures and have same placement of atoms in them but these have different locations of bond pairs and lone pairs. The resonating structures are inter-convertible with each other. The resultant of all the resonating or contributing structures is called the resonance hybrid.
(c)
Interpretation: The rank of below anions from highest to lowest potential energy on the basis of resonance should be determined.
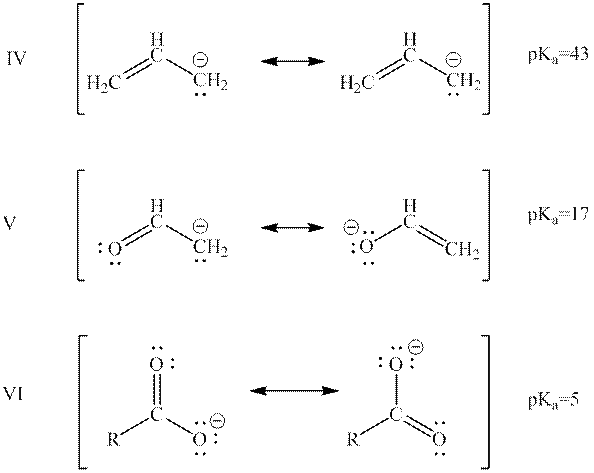
Concept introduction: When one single structure is unable to describe all the properties of single molecule, a phenomenon called resonance comes into play. This arises when two or more than two Lewis structures are possible for one molecule. All such structures are called resonating structures and have same placement of atoms in them but these have different locations of bond pairs and lone pairs. The resonating structures are inter-convertible with each other. The resultant of all the resonating or contributing structures is called the resonance hybrid.
(d)
Interpretation: The quantity and quality of resonance structures of below anions can affect their potential energy should be summarized.
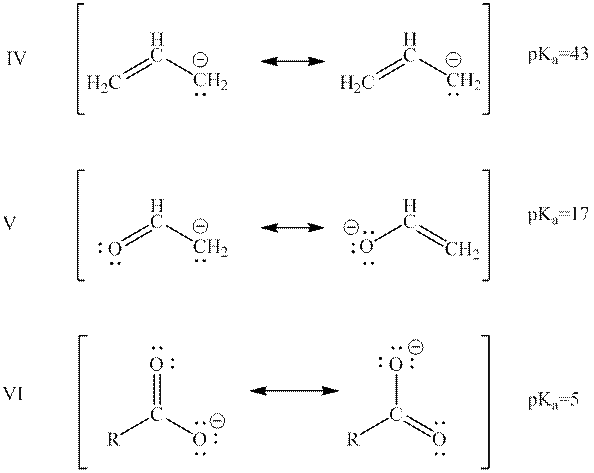
Concept introduction: When one single structure is unable to describe all the properties of single molecule, a phenomenon called resonance comes into play. This arises when two or more than two Lewis structures are possible for one molecule. All such structures are called resonating structures and have same placement of atoms in them but these have different locations of bond pairs and lone pairs. The resonating structures are inter-convertible with each other. The resultant of all the resonating or contributing structures is called the resonance hybrid.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- 7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forwardIndicate the compound formula: dimethyl iodide (propyl) sulfonium.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole


