
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The acid-base reaction between the following pairs of reactant should be written by using curved arrows and each curved arrows should be marked with a positive and negative energy change in
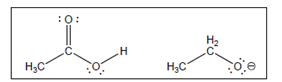
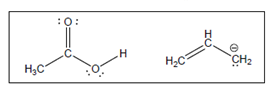
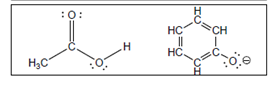
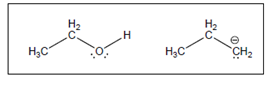
Concept Introduction:
A substance which produces
A substance which produces hydroxide ion when dissolved in aqueous solution is known as a base. These are proton acceptor.
A
The value that defines the relationship between the amount of products and reactants at equilibrium is known as equilibrium constant.
(b)
Interpretation:
The value of
Concept Introduction:
A substance which produces
A substance which produces hydroxide ion when dissolved in aqueous solution is known as a base. These are proton acceptor.
A chemical reaction which takes place between an acid and a base is known as acid-base reaction.
The value that defines the relationship between the amount of products and reactants at equilibrium is known as equilibrium constant.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- 2. Draw the products using curved arrows for the following acid base reaction. Label its conjugated acid-base pair. I—Z Base + N H. Acid H H searrow_forward5. sy For each reaction, identify the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base. Determine which direction the reaction will favor. Ka H₂SO3 = 1.54 x 10-2 and 1.07 x 10-7 Kb of CH3NH₂ = 4.4 x 10-4 Ka of CH3OH = 3.20 x 10-16 a. CH3O+ NH3 CH3OH + NH₂ b. HSO3 + CH3NH2 H₂SO3 + CH3NH3* c. 2HF + Ca(OH)2 2H₂O + CaF2arrow_forwardDraw the major organic product of the Bronsted acid-base reaction. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore any counterions. H I N. NaOH H oarrow_forward
- a. Which of the halide ions (F - , Cl - , Br - , and I - ) is the most stable base? b. Which is the least stable base?arrow_forward... G dou 1. What would be the best base for performing the elimination reaction shown? Br Br 1 / 1 2. What major product(s) will be yielded by the elimination reaction shown? Br NaOCH₂CH3 e 3. What is the product of the elimination reaction? OC(CH3)3 100% + 4. What is the predicted product of the elimination reaction shown? OH conc. H₂SO4 heatarrow_forwardK15. rank from weakest to strongest Bronsted base. Please give explanation and what the rankings look like for this questionarrow_forward
- 5. tert-BUOK ČI KOH ( base, excess) (1R, 2R)-1,2-dibromo-1,2-diflouroethane 7. Br NaCN 8. он HBrarrow_forwardNH4+ + HAsO4- ⇆ H2AsO4 + NH3What is the Bronsted base in the reaction above? a. NH 4 + b. HAsO 4 - c. H2AsO4 d. more than one response is correctarrow_forward6. Rank the indicated a-H's from most to least acidic (most acidic= 1). Be sure to explain your rankings for each by drawing significant resonance structures for the conjugate base and commenting on any other factors that contribute to your rankings. H H H H. A B Cmpd Rank Resonance Structures Reasoning A Вarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
