
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
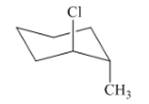
Concept Introduction: If the conformer shows the minimum steric hindrance of the substituent and minimum torsional strain then that conformer is in stable form.
(b)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
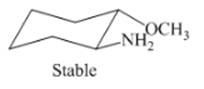
Concept Introduction: Trans-isomer has opposite attachment of all groups on the ring.
(c)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.

Concept Introduction:All groups are situated in one side, it is cis-isomer. Stability is defined in terms of axial interactions.
(d)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
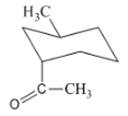
Concept Introduction:In trans-isomer all groups are attached in opposite side of the ring.
(e)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
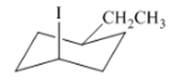
Concept Introduction:When groups are on one side then that isomer is cis-isomer.
(f)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
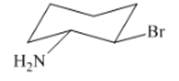
Concept Introduction:Trans-isomer consist all different groups on the opposite side of the ring.
(g)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
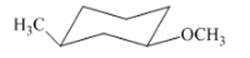
Concept Introduction:If all groups of the ring are attached on same side then that isomer is cis-isomer.
(h)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
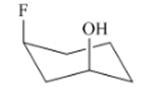
Concept Introduction:If the groups are attached on the same side then that isomer is cis-isomer.
(i)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
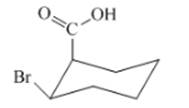
Concept Introduction:In cis-isomer the all different groups are situated on the same side of the ring.
(j)
Interpretation: The isomer type needs to be determined and the stable conformation needs to be drawn.
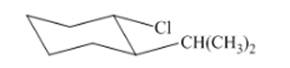
Concept Introduction:Trans-isomers have the different groups on the opposite side of the ring.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- I don't understand why the first one and second one are cis and trans respectively. Wouldn't the first one be trans-1,2-dimethylcyclobutane because the torsional strain wouldn't allow the carbons to be in the same conformation. Meaning one of the carbons would be up and then the next would be down and so on. Since both methyl groups are equatorial and the first and second carbons are arranged up and down, wouldn't it be trans. Same logic for the second molecule. Carbon 1, which is attached to the methyl is down, carbon 3 which is attached to the methyl should be down also because of torsional strain, and since both methyl are in axial (or equatorial?), it would be cis. Or is it based off of the way the carbons are positioned in the picture?arrow_forwarda) Draw all Newman projections of your molecule's conformations in which the CH3 group and the H of the CHY2 group are positioned 'ANTI' to each other. Be sure to put in the correct X and Y atoms, bonded to the correct C atoms, for your molecule. X = FY=I Conformations = 60 deg and - 180 deg 60 deg dihedral angle = - 179.987 deg 180 deg · - dihedral angle = 179.814 degarrow_forwardWrite a conformational structure for 1,2,3-trimethylcyclohexane in which all the methyl groups are axial and then show its more stable conformation.arrow_forward
- 4.(a). Draw the structures of (i) cis-1,4-Dibromocyclohexane and (ii) trans-1,4- Dibromocyclohexane. 4(b). Draw the most stable conformers of (i) cis-1,4-Dibromocyclohexane and (ii) trans-1,4-Dibromocyclohexane. 4(c)Which is more stable? (i) cis-1,4-Dibromocyclohexane or (ii) trans-1,4- Dibromolcyclohexane. Explain the reason for your choice.arrow_forwardPerform a conformational analysis of 1,2-dibromo-1-fluoroethane, BrFCH-CH2Br. Pay attention to the relative energies of the various conformations, but do not concern yourself with the actual energy values.arrow_forwardAcetylcholine is a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system in humans. Sighting along the C-C bond, draw Newman projection formulas for all the eclipsed and staggered conformers of acetylcholine. Which among the conformers is the least stable? The most stable? Plot a conformational analysis for these conformers.arrow_forward
- Square planar molecules with formula AB2C2 and octahedral molecules with formulas AB4C2 and AB3C3 feature diastereoisomers. Recall that trigonal bipyramidal geometry features two distinct positions: axial and equatorial. Draw all diastereoisomers for trigonal bipyramidal molecules with formula (a) AB4C and (b) AB3C2. You must indicate the stereochemistry using full and dashed wedges and label all positions as either axial (ax) and equatorial (eq)..arrow_forwardSight along the C2-C1 bond of 2-methylpropane (isobutane).(a) Draw a Newman projection of the most stable conformation.(b) Draw a Newman projection of the least stable conformation.(c) Make a graph of energy versus angle of rotation around the C2-C1 bond.(d) Assign relative values to the maxima and minima in your graph, given that an H↔H eclipsing interaction costs 4.0 kJ/mol and an H↔CH3 eclipsing interaction costs 6.0 kJ/mol.arrow_forwardThere are four cis,trans isomers of 2-isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexanol:(a) Using a planar hexagon representation for the cyclohexane ring, draw structural formulas for the four cis,trans isomers.(b) Draw the more stable chair conformation for each of your answers in part (a).(c) Of the four cis,trans isomers, which is most stable? (Hint: If you answered thispart correctly, you picked the isomer found in nature and given the name menthol.)arrow_forward
- Consider 1-bromopropane, CH3CH2CH2Br. (a) Draw a Newman projection for the conformation in which CH3 and -Br are anti (dihedral angle 180°). (b) Draw Newman projections for the conformations in which - CH3 and -Br are gauche (dihedral angles 60° and 300°). (c) Which of these is the lowest energy conformation? (d) Which of these conformations, if any, are related by reflection?arrow_forwardFor 1,2-dichloroethane: (a) Draw Newman projections for all eclipsed conformations formed by rotation from 0 to 360° about the carbon-carbon single bond. (b) Which eclipsed conformation(s) has the lowest energy? Which has the highest energy? (c) Which, if any, of these eclipsed conformations are related by reflection?arrow_forwardGiven cyclohexane in a chair conformation, construct the more stable conformation of cis‑1‑methyl‑2‑propylcyclohexane by filling in the missing atoms or groups. Use the numbering provided on the ring.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





