
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:The strain energy determined in prismane should be compared to two three membered and three four membered rings.
Concept introduction:Ring strain is a kind of instability that results when bonds deviate from ideal bond-angle. The cyclic system have different amount of strain as illustrated below:
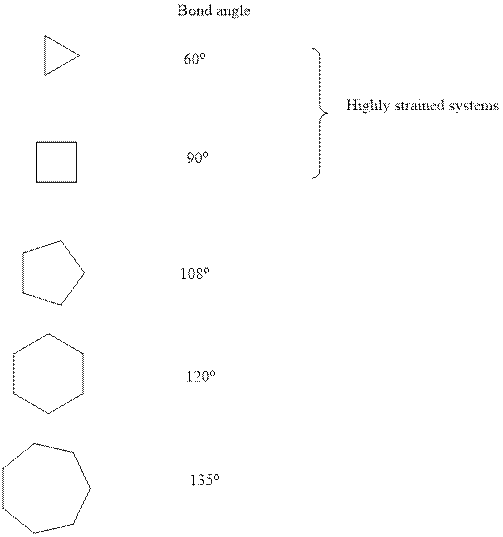
It is evident that three and four membered small ring systems have considerable degree of angular and ring strain that leads to their instability. Therefore it can be concluded that as one moves to higher order cycloalkanes, ring size expands and strain diminishes.
(b)
Interpretation:The estimated strain energy released when one side of three membered ring is broken should be determined.
Concept introduction:Ring strain is a kind of instability that results when bonds deviate from ideal bond-angle. The cyclic system have different amount of strain as illustrated below:
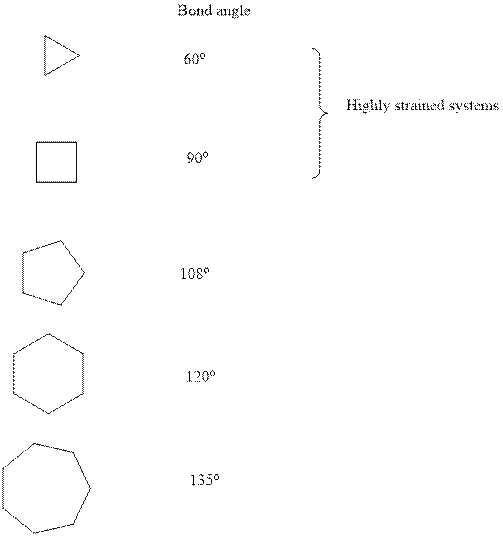
It is evident that three and four membered small ring systems have considerable degree of angular and ring strain that leads to their instability. Therefore it can be concluded that as one moves to higher order cycloalkanes, ring size expands and strain diminishes.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- (b) Study the following themochemical data very carefully: Ciz(g) - 2ci(g) I2(g) IC(g) - 1(g) + CI(g) I2(s) → 12(g) AH° = 242.3 kJ AH° = 151.0 kJ 21(g) AH° = 211.3 kJ AH° = 62.8 kJ I2(s) reacts with Cl2(g) to produce ICI(g). Write the chemical equation to produce ONLY one mole of ICI(g) (i) Calculate AH° for the reaction of I2(s) with Cl2(g) to form 1 mole of ICI(g). Use all the data given above. (ii) What law did you use to calculate AH° above? (iii) What are the names of the following processes? I2(s) → 12(g) I2(g) 21(g) ICI(g) I(g) + Cl(g)arrow_forwardWhat is the heat of combustion of ethane, C₂H, in kilojoules per mole of ethane? Enthalpy of formation values can be found in this list of thermodynamic properties. AH = kJ/mol ethanearrow_forwardGiven the following data: 4C(s) + 4H2(g) + O2(g) → CH3CH2OCOCH3(l) ΔH°=-480.0 kJ CH3CH2OH(l) + O2(g) → CH3COOH(l) + H2O(l) ΔH°=-492.0 kJ 2C(s) + 3H2(g) + 1/2O2(g) → CH3CH2OH(l) ΔH°=-278.0 kJ H2(g) + 1/2O2(g) → H2O(l) ΔH°=-286.0 kJ calculate ΔH° for the reaction:CH3COOH(l) + CH3CH2OH(l) → CH3CH2OCOCH3(l) + H2O(l)arrow_forward
- Given : (a) BCl3(g) + 3H2O(l) →H3BO3(s) + 3HCl(g) ΔH = -112.5 kJ (b) B2H6(g) + 6H2O(l) →2H3BO3(s) + 6H2(g) ΔH = -493.4 kJ (c) 1/2H2(g) + 1/2Cl2(g) →HCl(g) ΔH = -92.3 kJ Calculate the value of ΔH for the reaction: B2H6(g) + 6Cl2(g) →2BCl3(g) + 6HCl(g) ΔH = ? Select one: a.-1476KJ b.-1376KJ c. -1576KJ d.-1576KJarrow_forwardThe mean bond enthalpies of the C-C , C-H, C=O, and O-H bonds are 348,412,743, and 463 kJ mol-1, respectively. The combustion of a fuel such as octane is exothermic because relatively weak bonds break to form relatively strong bonds. Use this information to justify why glucose has a lowerspecific enthalpy than the lipid decanoic acid (C10H20O2) even though these compounds have similar molar masses.arrow_forwardGiven the standard enthalpy changes for the following two reactions: (1) 2C(s) + H₂(g) → C₂H₂ (9) AH° = 226.7 kJ (2) 2C(s) + 2H₂(g) → C₂H₁ (9) ΔΗ° = 52.3 kJ What is the standard enthalpy change for the following reaction? (3) C₂H₂(g) + H2 (9) → C2H4 (9) AH° =? Standard enthalpy change = kJarrow_forward
- calculate (d) the molar enthalpy of combustion (AHcomb; in kJ/mol) of benzoic acid. I just need to understand how to calculate part d) the molar enthalpy of benzoic acid.arrow_forwardbenzene, C6H6, gives thecompound special stability.(a) By using data in Appendix C, compare the heat of combustionof 1.0 mol C6H6(g) to the heat of combustion of 3.0 mol acetylene,C2H2(g). Which has the greater fuel value, 1.0 mol C6H6(g) or 3.0mol C2H2(g)? Are your calculations consistent with benzene beingespecially stable?arrow_forwardA.) What is the heat of reaction, ΔH°? CO2(g) + H2O(l) à H2CO3(aq) –20.2 kJ mol–1 –1379 kJ mol–1 –592 kJ mol–1 B.) What is the average bond energy in CO2? CO2(g) ΔH°f, = –393.5 kJ mol–1 CO(g) ΔH°f, = –110.5 kJ mol–1 C(g) ΔH°f, = +715 kJ mol–1 CO32–(aq) ΔH°f, = –676.3 kJ mol–1 O(g) ΔH°f, = +249.0 kJ mol–1 207 kJ mol–1 1607 kJ mol–1 804 kJ mol–1arrow_forward
- Acetylene burns in air according to the following equation. C2H2(g) + 5/2 02(g) → 2 CO2(g) + H20(g) AH°, rxn = -1255.8 k) Given that AHO of CO2(g) = -393.5 kJ/mol and AH°; of H20(g) = -241.8 kJ/mol, what is AHO, of C2H2(g)? 4.0 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. kJ/mol Submit Answerarrow_forward5.69 Methanol, ethanol, and n-propanol are three commonalcohols. When 1.00 g of each of these alcohols isburned in air, heat is liberated as follows: (a) methanol(CH3OH), −22.6 kJ; (b) ethanol (C2H5OH), −29.7 kJ;(c) n-propanol (C3H7OH), −33.4 kJ. Calculate the heatsof combustion of these alcohols in kJ/mol.arrow_forward19 Hydrogenation of double and triple bonds is an important industrial process. Calculate (in kJ) the standard enthalpy change ΔH° for the hydrogenation of ethyne (acetylene) to ethane using average bond enthalpies (use exam data sheet values). H–C≡C–H(g) + 2H2(g) → H3C–CH3(g)arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
