
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
12th Edition
ISBN: 9780134604718
Author: William S. Klug, Michael R. Cummings, Charlotte A. Spencer, Michael A. Palladino, Darrell Killian
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 20, Problem 31ESP
Most of the techniques described in this chapter (blotting, cloning, PCR, etc.) are dependent on hybridization (annealing) between different populations of
Tm = 81.5 + 16.6(logM[Na+]) + 0.41(%GC) − 0.72(%formamide)
- (a) For the following concentrations of Na+ and formamide, calculate the Tm. Assume 45% GC content.
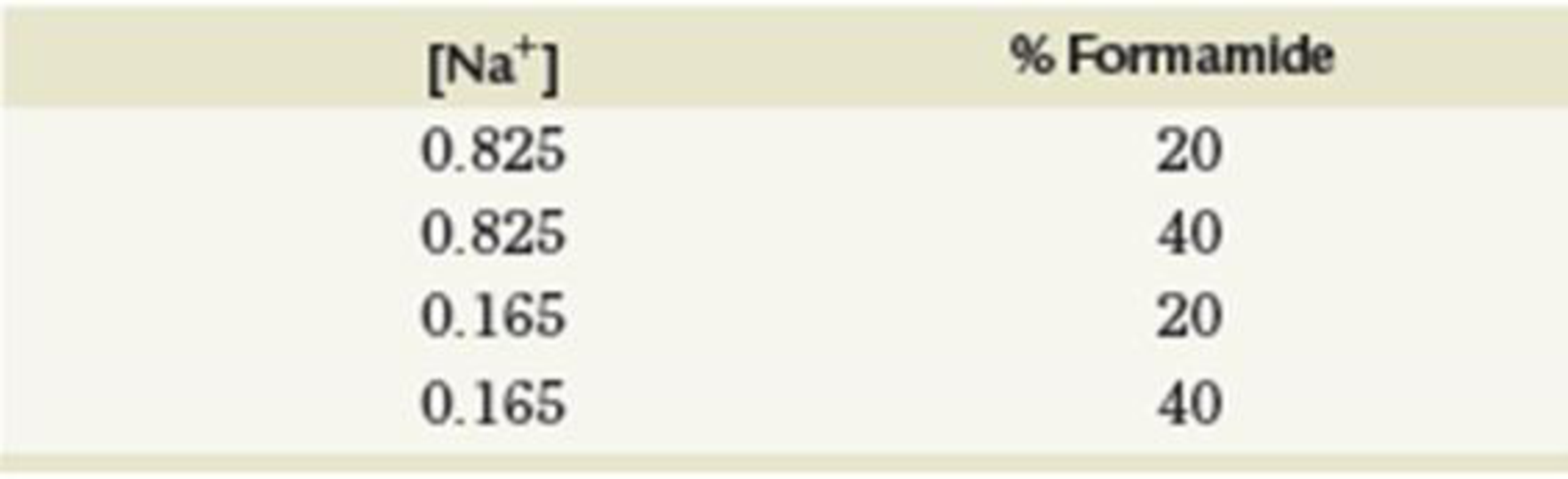
- (b) Given that formamide competes for hydrogen bond locations on nucleic acid bases and monovalent cations are attracted to the negative charges on nucleic acids, explain why the Tm varies as described in part (a).
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Quantification of DNA can be done by using a Nanodrop, a UV spectrophotometer, by
measuring its absorbance in units of optical density (OD) (see “Nanodrop Microvolume
Quantitation of Nucleic Acids" video in Lab 3 on Laulima). DNA absorbs light most strongly at
the ultraviolet wavelength of 260 nm. The absorbance of double stranded DNA (dsDNA) at
260 nm (A260) is used to estimate concentration, with 1.0 OD equal to a dsDNA
concentration of 50 µg/ml. Using this information we can calculate the concentration of dsDNA
in our extractions using the following formula:
dsDNA concentration = 50 µg/ml x OD260 x dilution factor
Using the formula provided above, calculate the concentration of dsDNA in an extraction that
was diluted 20X and had an A260 reading of 0.64 OD. Show your work
You're purifying some plasmid DNA from a culture of bacteria and you want to know how pure it is. You measure the optical density at 260 m and 280 m and find the ratio is 2.0. You suspect there is RNA contamination in your preparation, so you treat your preparation with RNase. But the ratio is still 2.0. Protein assays tell you there is no protein in your solution, and no other biological molecules absorb light very efficiently at those wavelengths. What's the explanation?
Explain how to prepare 2 ml of a solution with a concentration of 1 μg/5ml from a stock solution of a DNA sample with a concentration of 0.1 mg/ml.
Chapter 20 Solutions
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Ch. 20 - A plasmid that is both ampicillin and tetracycline...Ch. 20 - You have just created the worlds first genomic...Ch. 20 - What undesirable or unforeseen consequences might...Ch. 20 - Do we have the ethical right to alter the genomes...Ch. 20 - Should these new technologies be regulated...Ch. 20 - HOW DO WE KNOW? In this chapter we focused on how...Ch. 20 - CONCEPT QUESTION Review the Chapter Concepts list...Ch. 20 - What roles do restriction enzymes, vectors, and...Ch. 20 - The human insulin gene contains a number of...Ch. 20 - Although many cloning applications involve...
Ch. 20 - Using DNA sequencing on a cloned DNA segment, you...Ch. 20 - Restriction sites are palindromic; that is, they...Ch. 20 - List the advantages and disadvantages of using...Ch. 20 - What are the advantages of using a restriction...Ch. 20 - In 1975, the Asilomar Conference on Recombinant...Ch. 20 - In the context of recombinant DNA technology, of...Ch. 20 - If you performed a PCR experiment starting with...Ch. 20 - Prob. 13PDQCh. 20 - Prob. 14PDQCh. 20 - You have recovered a cloned DNA segment from a...Ch. 20 - Prob. 16PDQCh. 20 - Although the capture and trading of great apes has...Ch. 20 - Prob. 18PDQCh. 20 - Prob. 19PDQCh. 20 - Prob. 20PDQCh. 20 - Traditional Sanger sequencing has largely been...Ch. 20 - How is fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH)...Ch. 20 - What is the difference between a knockout animal...Ch. 20 - Prob. 24PDQCh. 20 - When disrupting a mouse gene by knockout, why is...Ch. 20 - Prob. 26PDQCh. 20 - Prob. 27PDQCh. 20 - As you will learn later in the text (Special...Ch. 20 - The gel presented here shows the pattern of bands...Ch. 20 - A widely used method for calculating the annealing...Ch. 20 - Most of the techniques described in this chapter...Ch. 20 - In humans, congenital heart disease is a common...Ch. 20 - The U.S. Department of Justice has established a...Ch. 20 - Prob. 34ESP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- When you run a sequencing reaction, you should include: a) only dideoxynucleoside triphosphates (ddNTPs) . b) only deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs). c) equal amounts of dideoxynucleoside triphosphates (ddNTPs) and deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs). d) a higher concentration of deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs) than dideoxynucleoside triphosphates (ddNTPs). e) a higher concentration of dideoxynucleoside triphosphates (ddNTPs) than deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs).arrow_forward2) Considering the technologies that pave the way for the identification of molecules on the basis of hybridization in the classical sense, within the scope of Recombinant DNA Technology; (20P) a) Which of these is used to identify which macromolecule,b) What do you understand in the context of hybridization and between which molecules there are technique-specificinteractions take placec) “Nylon membrane” or “nitrosdulose” commonly used in these technologieswhy "membranes" are needed,d) Explain how to design an application example for each technique you mentioned.arrow_forwardYou're purifying some plasmid DNA from a culture of bacteria and you want to know how pure it is. You measure the optical density at 260 nm and 280 nm and find the ratio is 2.0. You suspect there is RNA contamination in your preparation, so you treat your preparation with RNase. But the ratio is still 2.0. Protein assays tell you there is no protein in your solution, and no other biological molecules absorb light very efficiently at those wavelengths. What's the explanation?arrow_forward
- Sanger sequencing originally used 4 lanes in gels. These lanes represented sequences of different lengths obtained by adding: All of the 4 dideoxynucleotides (ddATP; ddGTP; ddCTP; ddTTP), together with all of the 4 deoxynucleotides (dATP, dGTP, dCTP and dTTP), to all of the reaction vials All of the 4 dideoxynucleotides (ddATP; ddGTP; ddCTP; ddTTP) to the reaction vials; together with one of the 4 deoxynucleotides (dATP, dGTP, dCTP and dTTP), one for each lane, in each vial. One of the 4 dideoxynucleotides (ddATP; ddGTP; ddCTP; ddTTP) to the reaction vials; one for each lane, together with all of the 4 deoxynucleotides (dATP, dGTP, dCTP and dTTP) in each vial One of the 4 dideoxynucleotides (ddATP; ddGTP; ddCTP; ddTTP) to the reaction vials; one for each lanearrow_forwardWatch the demonstration video on nucleic acid quantification on the NanoDrop spectrophotometer: https://cutt.ly/bio150dnaquantification Note: the video is entitled RNA but the method is identical for DNA quantification. 1. At what ratio of A260/280 can we say that DNA is pure? What about RNA and protein?2. While spectrophotometric methods are effective at detecting DNA, a more sensitive but expensive technique called fluorometry is used in sensitive applications. What is the principle behind fluorometry and why is it better than spectrophotometry in detecting DNA?arrow_forwardIn fluorescent Sanger DNA Sequencing, choose one of the following: A):The deoxynucleotides are fluorescently labelled B):Each capillary gel contains a single fluorescent nucleotide C):Chain termination does not occur D):The reaction must be run in the dark E):The incorporated fluorescent nucleotides are detected by a sensor at one end of the capillary gelarrow_forward
- What are some applications of nucleic acid hybridization inmolecular biology?arrow_forwardBelow is an EMSA showing four different reactions, A-D. In each tube there is some combination of labelled DNA probe, Protein X (the protein you are studying), and an antibody for Protein X. Identify which combination of components are found in each of the four reactions and explain how you determined that based on the molecular interactions being studied and your knowledge of gel electrophoresis. It is possible that multiple lanes have the same component(s). A B C D EMSAarrow_forwardBoth protein and DNA are run together in an isoelectric focusing (IEF) electrophoresis using the immobilised pH gradient (IPG) strip with pH range of 4-7. After the electrophoresis and staining, only ONE band is observed on the middle of the IPG strip. The band is a protein band. Briefly explain why only the protein band and NOT the DNA band appear on the IPG strip.arrow_forward
- During agarose gel electrophoresis, why does DNA move through the gel when electric current is applied? because DNA is negatively charged because a charged chemical from the loading buffer is bound to the DNA because DNA is positively charged because DNA absorbs electricityarrow_forwardWhat is the chemical basis of molecular hybridization?arrow_forwardTotal nucleic acids are extracted from a growing culture of yeast cells. They are then mixed with specialized beads to which the single-stranded DNA molecule with sequence 5’-TTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTT-3’ has been covalently attached to the surface (see image to the right, where each black line represents a polynucleotide sequence). After a short incubation time, the beads are removed from the mixture. When you analyze the cellular nucleic acids stuck to the beads, which type of nucleic acid (i.e. DNA, rRNA, etc.) do you expect to be the most abundant? Why?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

Molecular Techniques: Basic Concepts; Author: Dr. A's Clinical Lab Videos;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7HFHZy8h6z0;License: Standard Youtube License