
Concept explainers
In the following diagram of the lac operon, an inducible operon, identify components a through i.
To identify: The components of an inducible operon, the lac operon.
Introduction: An operon is the functioning part of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Each operon consists of a cluster of functionally related genes that share a single promoter and controlled by a shared operator. Lac operon is an inducible operon that controls the lactose metabolism in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria.
Answer to Problem 1IQ
Pictorial representation: The components of lac operon are labeled in Fig.1.
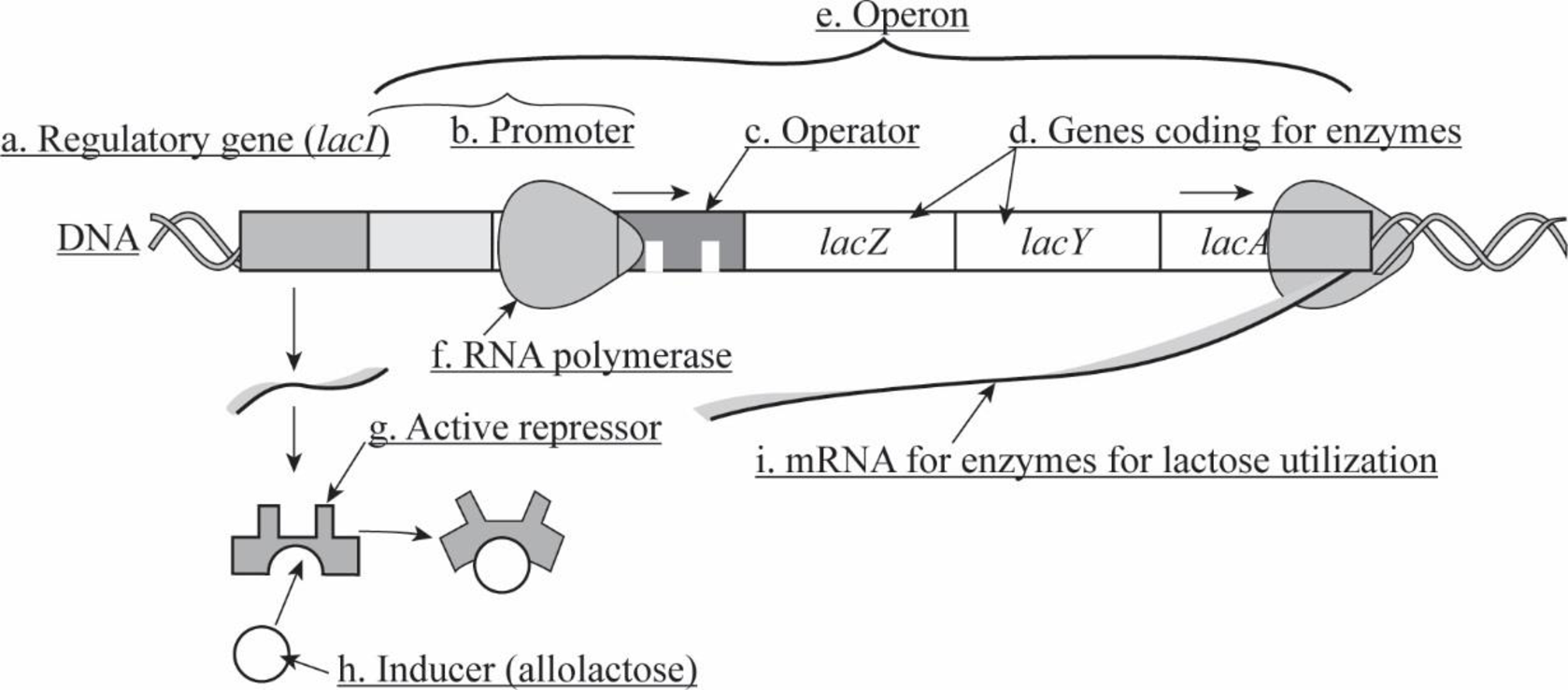
Fig.1: Lac operon
Explanation of Solution
Lac operon is a group of genes with a single promoter. The genes in the lac operon encode proteins that allow a transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli.
- Regulatory gene (lacI): Regulatory gene controls the expression of other genes. The lac regulatory gene (lacI) codes for a repressor protein that can bind to the operator of the lac operon.
- Promoter: Promoter is the region adjacent to the operator in the lac operon, where the RNA polymerase binds to initiate a transcription of lactose genes. Promoter region switches on or off the gene expression through protein binding.
- Operator: Operator is the region that lies partially within the promoter in the lac operon. Operator region interacts with the regulatory protein that controls the transcription of the operon.
- Genes coding for enzymes: The lac operon consists of three genes such as lacZ, lacY, and lacA. lacZ gene transcribes as a single mRNA sequence. The lacZ gene encodes an enzyme β-galactosidase, lacY gene encodes an enzyme permease, and the lacA gene encodes trans-acetylase enzyme.
- Operon: Operon is the functional part of a DNA that consists of a group of functionally related genes regulated by a shared operator.
- RNA polymerase: RNA polymerase is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA and catalyzes the initiation and elongation of RNA using a process called transcription. In lac operon, RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region to initiate transcription.
- Active repressor: The activity of repressor (allosteric protein) may be determined by the presence or absence of the co-repressor. The repressor protein is produced by the regulatory gene and is activated by the association of a co-repressor. The activated repressor binds to the operator region, and it inhibits the transcription of lac operon genes.
- Inducer (allolactose): Inducer is allolactose, an isomer of lactose, which triggers or induces transcription. The inducer binds to and inactivates the repressor protein to induce the transcription of operon.
- mRNA for enzymes for lactose utilization: The genes of lac operon transcribe a single mRNA that encodes enzymes. The lacZ gene encodes an enzyme β-galactosidase, lacY gene encodes an enzyme permease, and the lacA gene encodes trans-acetylase enzyme for lactose utilization in Escherichia coli.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Physical Science
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- Compare the cloning efficiencies: SmaI vs. EcoRI.arrow_forwardHydrogen bonds play an important role in stabilizing and organizing biological macromolecules. Consider the four macromolecules discussed. Describe three examples where hydrogen bond formation affects the form or function of the macromolecule.arrow_forwardImagine you are a botanist. Below are characteristics of a never-before described plant species recently identified as part of the ‘All Taxa Biodiversity Inventory’ (ATBI). Field Notes: Specimen collected from shaded area along stream in South Cumberland State Park (Grundy County, TN). Laboratory Analysis: Body: Large leaves emerging from underground rhizome. Size: 63 cm Chromosomal Analysis: Plant body is diploid—chromosome number of 44. Lignin test: Positive Cuticle: Present Leaves: Present—large with branched veins. Underside has sori (containing haploid spores). Roots: Present—branch from the inside. Stem: Present—vascular tissue (xylem & phloem) present. Life History: Diploid sporophyte dominant generation. Haploid spores germinate into heart-shaped, haploid, gametophyte. Water required for fertilization; no seed is produced. Diploid zygote develops into sporophyte. Explain which domain, kingdom and phylum you believe this plant should be classified…arrow_forward
- CUÁ Glycine A C C Newly formed molecule Glycine Arginine Proline Alanine A C C CC G GGAUUGGUGGGGC Structure X I mRNAarrow_forwardAdaptations to a Changing Environment Why is it necessary for organisms to have the ability to adapt? Why is the current environment making it difficult for organisms like the monarch butterfly to adapt? Explain how organisms develop adaptations.arrow_forwardArtificial Selection: Explain how artificial selection is like natural selection and whether the experimental procedure shown in the video could be used to alter other traits. Why are quail eggs useful for this experiment on selection?arrow_forward
- Don't give AI generated solution otherwise I will give you downwardarrow_forwardHello, Can tou please help me to develope the next topic (in a esquematic format) please?: Function and Benefits of Compound Microscopes Thank you in advance!arrow_forwardIdentify the AMA CPT assistant that you have chosen. Explain your interpretation of the AMA CPT assistant. Explain how this AMA CPT assistant will help you in the future.arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
