
Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780073380643
Author: Donald A. Neamen
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Companies, The
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 16, Problem D16.56P
Consider the classic CMOS logic circuit in Figure P16.56 (a) What is the logic function performed by the circuit? (b) Design the PMOS network. (c) Determine the transistor W/L ratios to provide symmetrical switching times equal to the basic CMOS inverter with (W/L)n=2 and (W/L)p=4 .
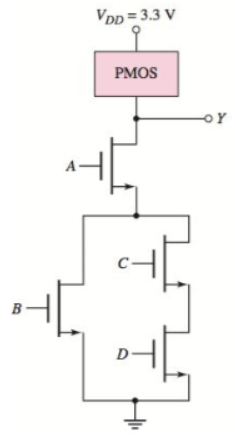
Figure P16.56
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.
Please solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam today, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.
If C is the circle |z|=4 evaluate f f (z)dz for each of the following
functions using residue.
1
f(z)
=
z(z²+6z+4)
Chapter 16 Solutions
Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design
Ch. 16 - Consider the NMOS inverter with resistor load in...Ch. 16 - The enhancementload NMOS inverter in Figure...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.3EPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.4EPCh. 16 - Consider the NMOS inverter with enhancement load,...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.2TYUCh. 16 - (a) Consider the results of Exercise Ex 16.1....Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.5EPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.6EPCh. 16 - (a) Design a threeinput NMOS NOR Logic gate with...
Ch. 16 - Consider the NMOS logic circuit in Figure 16.18....Ch. 16 - Repeat Exercise TYU 16.5 for the NMOS logic...Ch. 16 - The CMOS inverter in Figure 16.21 is biased at...Ch. 16 - swA CMOS inverter is biased at VDD=3V . The...Ch. 16 - A CMOS inverter is biased at VDD=1.8V . The...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.7TYUCh. 16 - Repeat Exercise Ex 16.9 for a CMOS inverter biased...Ch. 16 - Determine the transistor sizes of a 3input CMOS...Ch. 16 - Design the widthtolength ratios of the transistors...Ch. 16 - Design a static CMOS logic circuit that implements...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.10TYUCh. 16 - Prob. 16.11TYUCh. 16 - Sketch a clocked CMOS logic circuit that realizes...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.12EPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.13TYUCh. 16 - Consider the CMOS transmission gate in Figure...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.15TYUCh. 16 - Prob. 16.14EPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.16TYUCh. 16 - Prob. 16.17TYUCh. 16 - Sketch the quasistatic voltage transfer...Ch. 16 - Sketch an NMOS threeinput NOR logic gate. Describe...Ch. 16 - Discuss how more sophisticated (compared to the...Ch. 16 - Sketch the quasistatic voltage transfer...Ch. 16 - Discuss the parameters that affect the switching...Ch. 16 - Prob. 6RQCh. 16 - Sketch a CMOS threeinput NAND logic gate. Describe...Ch. 16 - sDiscuss how more sophisticated (compared to the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 9RQCh. 16 - Sketch an NMOS transmission gate and describe its...Ch. 16 - Sketch a CMOS transmission gate and describe its...Ch. 16 - Discuss what is meant by pass transistor logic.Ch. 16 - Prob. 13RQCh. 16 - Prob. 14RQCh. 16 - Prob. 15RQCh. 16 - Describe the basic architecture of a semiconductor...Ch. 16 - ‘Sketch a CMOS SRAM cell and describe its...Ch. 16 - Prob. 18RQCh. 16 - Describe a maskprogrammed MOSFET ROM memory.Ch. 16 - Describe the basic operation of a floating gate...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.1PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.2PCh. 16 - (a) Redesign the resistive load inverter in Figure...Ch. 16 - Prob. D16.4PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.5PCh. 16 - Prob. D16.6PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.7PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.8PCh. 16 - For the depletion load inverter shown in Figure...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.10PCh. 16 - Prob. D16.11PCh. 16 - Prob. D16.12PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.13PCh. 16 - For the two inverters in Figure P16.14, assume...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.15PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.16PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.17PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.18PCh. 16 - Prob. D16.19PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.20PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.21PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.22PCh. 16 - In the NMOS circuit in Figure P16.23, the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.24PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.25PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.26PCh. 16 - What is the logic function implemented by the...Ch. 16 - Prob. D16.28PCh. 16 - Prob. D16.29PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.31PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.32PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.33PCh. 16 - Consider the CMOS inverter pair in Figure P16.34....Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.35PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.36PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.37PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.38PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.39PCh. 16 - (a) A CMOS digital logic circuit contains the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.41PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.42PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.43PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.44PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.45PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.46PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.47PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.48PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.49PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.50PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.51PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.52PCh. 16 - Prob. D16.53PCh. 16 - Figure P16.54 is a classic CMOS logic gate. (a)...Ch. 16 - Figure P16.55 is a classic CMOS logic gate. (a)...Ch. 16 - Consider the classic CMOS logic circuit in Figure...Ch. 16 - (a) Given inputs A,B,C,A,B and C , design a CMOS...Ch. 16 - (a) Given inputs A, B, C, D, and E, design a CMOS...Ch. 16 - (a) Determine the logic function performed by the...Ch. 16 - Prob. D16.60PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.61PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.62PCh. 16 - Sketch a clocked CMOS domino logic circuit that...Ch. 16 - Sketch a clocked CMOS domino logic circuit that...Ch. 16 - Prob. D16.65PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.66PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.67PCh. 16 - The NMOS transistors in the circuit shown in...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.69PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.70PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.71PCh. 16 - (a) Design an NMOS pass transistor logic circuit...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.73PCh. 16 - What is the logic function implemented by the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.75PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.76PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.77PCh. 16 - Consider the NMOS RS flipflop in Figure 16.63...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.79PCh. 16 - Consider the circuit in Figure P16.80. Determine...Ch. 16 - Prob. D16.81PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.82PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.83PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.84PCh. 16 - (a) A 1 megabit memory is organized in a square...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.86PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.87PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.88PCh. 16 - Prob. D16.89PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.90PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.91PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.92PCh. 16 - Prob. D16.93PCh. 16 - Prob. D16.94PCh. 16 - Prob. D16.95PCh. 16 - An analog signal in the range 0 to 5 V is to be...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.97PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.98PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.99PCh. 16 - The weightedresistor D/A converter in Figure 16.90...Ch. 16 - The Nbit D/A converter with an R2R ladder network...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.102PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.103PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.104PCh. 16 - Prob. 16.105PCh. 16 - Design a classic CMOS logic circuit that will...Ch. 16 - Prob. D16.111DPCh. 16 - Prob. D16.112DPCh. 16 - Prob. D16.113DP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If C is the circle |z|=4 evaluate ff(z)dz for each of the following functions using residue. f(z) z(z²+6z+4)arrow_forwardDetermine X(w) for the given function shown in Figure (1) by applying the differentiation property of the Fourier Transform. 1 x(t) Figure (1) -2 I -1 1 2arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forward
- Please solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forward
- Please solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forward
- Please solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardIt is a past exam for practice, please explain what you do so I can be prepared for exam tomorrowarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Diode Logic Gates - OR, NOR, AND, & NAND; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9lqwSaIDm2g;License: Standard Youtube License