
(a)
Interpretation: Soap property in a polar solvent and for non-polar molecules needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
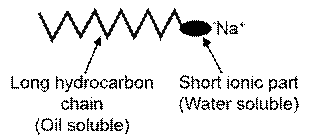
Soap is the chemical compounds that are made by the hydrolysis of fatty acids. Soap structure contains a long hydrocarbon chain and polar and non-polar end. The polar end dissolves in the water like polar solvents.
(a)
Answer to Problem 9STP
The soap contains hydrophobic tail and hydrophilic groups. The soaps non-polar ends cover the non-polar molecules and the polar end dissolves in water.
Explanation of Solution
Soap is made with two types of groups one is polar and another one is non-polar. So the polar end is dissolved with a polar solvent, same as like dissolve like. On the other hand, non-polar groups or hydrophobic groups interact with non-polar molecules and dissolve them.
(b)
Interpretation: A diagram showing a soap solution able to dissolve the grease needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction: Soap is the chemical compounds that are made by the hydrolysis of fatty acids. Soap structure contains a long hydrocarbon chain and polar and non-polar end. The polar end dissolves in the water like polar solvents.
(b)
Answer to Problem 9STP
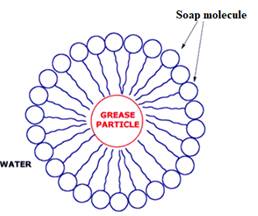
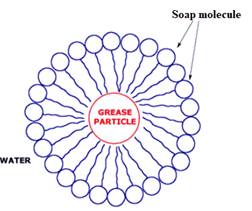
The diagram showing the soap action on grease
Explanation of Solution
The soap contains hydrophobic tail and hydrophilic groups. The non-polar ends of soaps cover grease molecules which is a non-polar molecule, and the polar end of soap dissolves in water. The polar end of soap contains the hydrophilic group, which is dissolved in water.
(c)
Interpretation: Hard water needs to be explained. The reason for the soap solution to be less effective in it needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Hard water is a less effective water type. In hard water, a large number of minerals are dissolved, the minerals are mainly calcium and magnesium.
Soap is the chemical compound that is made by the hydrolysis of fatty acids. Soap structure contains a long hydrocarbon chain and polar and non-polar end. The polar end dissolves in the water like polar solvents.
(c)
Answer to Problem 9STP
A large quantity of minerals containing water is hard water. The insoluble substances are formed when soap is mixed with hard water. So the activity of soap is decreased.
Explanation of Solution
Hard water contains calcium and magnesium minerals. Soaps contain hydrophilic groups that are replaced by hard water minerals and the activity of soap is decreased.
So the hard water is not suitable for the cleaning action of soap.
Chapter 21 Solutions
World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





