
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The reason that how
Concept Introduction:
The series of reaction present in these reactions is called as
First the consumption of food gets digested which results in production of small molecules.
Glycolysis is a pathway which describes conversion of one molecule of glucose into 2
Pyruvate molecules. It involves totally 10 set of reactions with it.
Krebs cycle essentially involves the oxidation of acetyl CoA to
Citric Acid Cycle: It involves 8 series reaction which converts acetyl group present in acetyl coenzyme A into 2
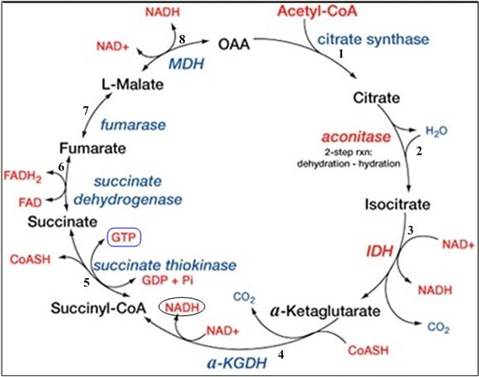
Figure 1
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 21 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
- The citric acid cycle generates NADH and FADH2, which are then used in the process of oxidative phosphorylation to make ATP. If the citric acid cycle (which does not use oxygen) and oxidative phosphorylation are separate processes, as they are, then why is it that the citric acid cycle stops almost immediately when O2 is removed?arrow_forwardFollow the two carbon atoms that enter the citric acid cycle (C₂). Are the two CO₂ molecules given off in one turn of the citric acid cycle composed of the same 2 carbon atoms that entered the cycle? NADH + H+ NAD+ H HỌ—C—COO- H₂C-COO- °↑ 7 FADH₂ 0 C-C00 H₂C-COO- Oxaloacetate Malate HC-COO- -OOC-CH Fumarate FAD Succinate H₂C-COO H₂C-COO CH,CO—S-CoA Acetyl coenzyme A GTP COA GDP COA H₂C-COO- HỌ–C–COO- H₂C-COO- Citrate H₂C-COO- Isocitrate HC-COO- HO–C–COO H e T CO₂ Succinyl COA H₂C-COO- CO₂ a-Ketoglutarate CoA H₂C-CO-S-CoA H₂C-COO H₂C 0-C-COO- NAD+ NADH + H+ NAD+ NADH + H+arrow_forwardThe end product of glycolysis, pyruvate, cannot enter as such into the citric acid cycle. Which process converts this C3 compound to a C2 compound?arrow_forward
- Which of the following catalyzes the reduction of oxygen by using the electrons released from oxidizing coenzyme Q to reduce cytochrome c? NADH dehydrogenase Succinate dehydrogenase Cytochrome c reductase Cytochrome c oxidasearrow_forwardWhich of the following best describes the net organic products formed during the oxidation of one acetyl group to two molecules of carbon dioxide via the citric acid cycle? 3 NADH + 1 FADH2 + 1 GTP 2 NADH + 2 FADH2 + 2 ATP 1 NADH + 3 FADH2 + 1 GTP 6 NADH + 6 ATP 3 NADHarrow_forwardMeasuring CO2 would be a good way to measure whether pyruvate oxidation and the Citric Acid cycle were functioning below normal levels a) True b) Falsearrow_forward
- A) Consider what would happen if you added any of the citric acid cycle intermediiates: would the rates of ATP produce increase or decrease? What about CO2 production rates? B)What if pyruvate oxidation was blocked? What would you expect to happen to the levels of oxaloacetate and citric acid when looking at the citric and cyclearrow_forwardDo any of the respiratory complexes play a role in the citric acid cycle? If so, what is that role?arrow_forwardAll of the following occurs during the citric acid cycle EXCEPT Choose one from the following: (A) oxaloacetic acid, a 4 carbon molecule, binds to the 2 carbon acetyl group to form citric acid (B) hydrogen ions are bound to the co-enzyme FAD (C) energy is stored in the formation of GTP (D) oxygen is used (E) carbon dioxide is releasedarrow_forward
- Draw the predicted graph of O2 consumption and ATP synthesis for the followingarrow_forwardAll of the following statements about the citric acid cycle are true except: O The citric acid cycle occurs in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes. O The citric acid cycle regenerates NAD+ and FAD. O The citric acid cycle involves one or more redox reactions. O The citric acid cycle is part of cellular respiration.arrow_forwardWe often describe respiration by the simple equation of 6 O2 + C6H1206 - 6 CO2 + 6 H20. However, as we've now covered, there's way more going on than what's represented by this one equation. Summarize the entire process of energy generation starting from glucose, covering the substances produced through each process involved (no need to summarize the individual steps), where these processes take place, how they interact with each. other, changes in energy and oxidation along the way, and what happens to the molecules produced in the end.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





