
Interpretation:
The given options should be identified that whether they are found in the structure of coenzyme FAD.
Concept Introduction:
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide
Coenzyme: They are non-proteins molecules which helps enzymes for catalyzing the reaction.
Enzyme: The proteins that helps
ADP contains adenine attached to sugar backbone and 2 phosphate groups get attached to five carbon atoms present in ribose. The structure is as follows,
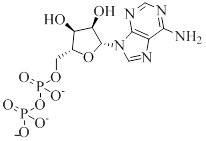
Phosphate anhydride bond: The bond that keeps phosphate groups and ribose together is termed as phosphate anhydride bond.
Benzene: The molecule that has 6 carbon atoms present in a ring to which each carbon has one hydrogen atom with it.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 21 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
- Indicate the FALSE alternative: a) The formation of osazones is a characteristic reaction of aldoses and ketoses. b) Disaccharides formed by aldoses with 1-1' linkages do not have reducing power or mutarotation. c) Glycosides have no reducing power. d) Glycosidic bonds allow the formation of branched structures. e) A characteristic of alditols is that they all have optical activity.arrow_forwardAlthough the first two carbons of fructose and glucose are identical in structure to DHAP and GADP (from glycolysis), DHAP and GADP equilibriate on their in solution to favor the ketone over the aldehyde, while fructose and glucose do not. Why? a)The larger size of the molecule sterically hinders the isomerization b)The larger sugars have more OH groups which hydrogen bond and disrupt isomerization c)The larger sugars cyclize, and there is no carbonyl to isomerize in the cyclic form d)The larger sugars cyclize, and in the cyclic form the hydrogen bonding is very strong e)The larger sugars are less soluble in water than the smaller sugarsarrow_forwardWhat are the donor atoms involved in Aspartame-Cu(II) binding? A) Nitrogen atom of alpha amine group of Aspartic acid and an oxygen atom of alpha carboxyilic acid group of Aspartic acid B) Nitrogen atom of alpha amine group of Phenyl alanine methyl ester and an oxygen atom of alpha carboxyilic acid group of Aspartic acid C) Nitrogen atom of alpha amine group of Aspartic acid and an oxygen atom of alpha carboxyilic acid group of Phenyl alanine methyl ester D) Oxygen atoms of the dipeptide Aspartame E) Nitrogen atom of alpha amine group of Aspartic acid and an oxygen atom of carboxyilic acid group of the R group of Aspartic acidarrow_forward
- 22) A) Write the structure for a generic triacvlglyceride at pH 7.4. B) Show the mechanism of a lipase including the catalytic triad and the oxyanion hole up to the tetrahedral intermediate of the cleavage of the acyl-alcohol bond. C) What is the purpose of the þxyanion hole? D) How does the catalytic triad function to lower the pKa of serine. coo coo H,N-C-H H,N-C-H CH, CH2 он Serine (S) (Ser) HN Histidine (H) (His) coo co H,N-C-H H,N-C-H H CH, Glycine (G) (Gly) coo Aspartate [D] (Asp)arrow_forward1) Please list all glycosidic linkages between each monosaccharide units. For example, α(1→4)2) Please discuss whether these oligo/polysaccharides would be reducing or non-reducing sugar. Remember to state your reasoning in complete sentence.arrow_forward1) Draw the structures and provide the systematic names of the following fatty acids (all double bonds are in cis- configuration).a) 24:0b) 18:3(Δ6,9,12)c) 20:3(Δ8,11,14)2) Define and briefly explain the process of saponification.3) Commercial vegetable oils are subjected to partial hydrogenation processing before they are made available on the market;a) Explain the importance of this partial hydrogenation on cooking oil.b) Give two reasons why un-hydrogenated vegetable oil is not suitable for cooking.c) What undesirable effect does partial hydrogenation cause?4) Platelet-activating factor and Prostacyclin are lipids that play roles affecting coagulation.a) Differentiate the roles of each aforementioned lipid with reference to coagulation. b) What specific type of lipids does each molecule belong to?5) Draw the structures of lecithin and cephalin, outlining the general features. 6) Explain the chemical importance of having 2-deoxy-D-ribose in DNA over D-ribose.7) Draw a schematic…arrow_forward
- draw all the structures of the tribasic amino acid lysine involved in the equilibrium reactions that would take place during titration against NaOH, starting with the fully protonated form below (draw the R-group in full). H;N+- CH - COOH (CH2)4 NH3+arrow_forwardThe 6-member pyranose ring of glucose is formed through the interaction of the hydroxyl group on C5 with the aldehyde group What kind of ring is formed when the hydroxyl group on C4 attacks instead? Draw the Haworth projection of the products with all the carbons labelled accordingly and name them Why would ring formation through C6 or C3 be unfavorable?arrow_forwardDraw the first tetrahedral intermediate of the chymotrypsin mechanism (a single structure, no arrows required). Circle the oxyanion hole. How does the oxyanion hole of chymotrypsin compare to that of carboxypeptidase?arrow_forward
- Using Figure 1.3 of the Introduction as an example, a) draw all the structures of the tribasic amino acid lysine involved in the equilibrium reactions that would take place during titration against NaOH, starting with the fully protonated form below (draw the R-group in full). HAN+-CH- COOH (CH2)4 NH°+ b) indicate the numerical pa value of each equilibrium reaction, and which ionizable group is being dissociated in each step. c) indicate the net charge of the amino acid at each step and identify the zwitterion. d) Calculate the pI of this amino acid (show the calculation). e) What would be the predominant ionization states of this amino acid at physiological pH (7.4) and at this pH, what would the ratio of these two states be (show the calculation)?arrow_forward15.6) Match each of the coenzymes listed below with the species that they transport. i) ADP (b) phosphate groups ii) Coenzyme A (CoA) (a) acyl groups iii) FAD (c) hydride ions (H:-) or electrons iv) Coenzyme Q (CoQ) (c) hydride ions (H:-)/electrons v) NAD+ (c) hydride ions (H:-)/electrons EXPLANATION: A coenzyme is a species that must bind to an enzyme in order for the enzyme to function. In most cases, a coenzyme is actually one of the substrates (reactants) in the catalyzed reaction. The reason that certain substrates are also referred to as coenzymes is that these substrates are common substrates in many different enzymatic reactions in which they donate electrons, atoms, or groups of atoms to other substrates, or accept electrons, atoms or groups of atoms from other substrates. The five group-transfer coenzymes that are central to the metabolization of food, along with the species each transfers are listed in the table on the right. transported species choices: a) acyl groups b)…arrow_forwardConsider the following fatty acid attached below. a) What is the number convention for this fatty acid above, including the location of the double bond from the α carbon end? Remember to use the Δ (delta) in your answer for the double bond location b) What is the ω (omega) numbering of the double bond for the fatty acid above? c) What is the product after two hypothetical additional rounds of synthesis for the fatty acid? Remember that synthesis adds 2 carbons at a time to the carboxylic end.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





