
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The line structure of
Concept Introduction:
Line structure: Line structure is a simplest representation of a hydrocarbon. In line structure, the chain of carbon atoms is shown as a zigzag line. The end of each short line in the zigzag represents a carbon atom. Since the carbon nearly always has a valence of four in organic compounds, it is not necessary to show the hydrogen atoms.
Class of hydrocarbons:
(a)
Answer to Problem 11A.1E
The line structure of

Explanation of Solution
The given condensed formula is

The presence of triple bond in the compound shows that it belongs to alkyne.
(b)
Interpretation:
The line structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 11A.1E
The line structure of

Explanation of Solution
The given condensed formula is

The presence of single bond in the compound shows that it belongs to alkane.
(c)
Interpretation:
The line structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem 11A.1E
The line structure of

Explanation of Solution
The given condensed formula is

The presence of double bond in the compound shows that it belongs to alkene.
(d)
Interpretation:
The line structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Answer to Problem 11A.1E
The line structure of
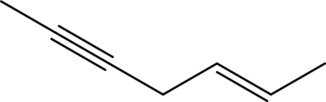
In
Explanation of Solution
The given condensed formula is
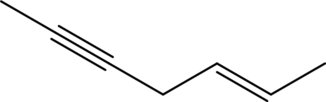
In
(e)
Interpretation:
The line structure of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(e)
Answer to Problem 11A.1E
The line structure of
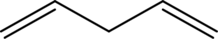
Explanation of Solution
The given condensed formula is
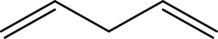
The presence of double bonds in the compound shows that it belongs to alkene.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemical Principles: The Quest for Insight
- (a) What structural feature is associated with each type of hydrocarbon: alkane, cycloalkane, alkene, and alkyne?(b) Give the general formula for each type.(c) Which hydrocarbons are considered saturated?arrow_forwardDraw condensed formulas for the following compounds:(a) 3-ethyl-3-methyloctane; (b) 1-ethyl-3-propylcyclohexane (also draw a carbon-skeleton formula for this compound); (c) 3,3-diethyl-1-hexyne; (d) trans-3-methyl-3-heptene.arrow_forwardThere are 11 structures (ignoring stereoisomerism) with the formula C4H8O that have no carbon branches. Draw the structures and identify the functional groups in each.arrow_forward
- Illustrate this phenomenon, compare ethane (CH3CH3), ethylene (CH2=CH2), and acetylene (HC=CH).arrow_forwardGiven each of the IUPAC names provided, draw the corresponding structure. (a) 2,2,4-trimethylpentane;(b) 3-ethyl-2,3-dimethylpentane; (c) 2,2,3,3-tetramethylhexanearrow_forwardDraw the structure(s) of all of the branched alkene isomers, C6H12, that contain 2 methyl branches.arrow_forward
- Draw and name the five cycloalkane structures of formula C5H10. Can any of these structures give rise to geometric (cis-trans) isomerism? If so, show the cis and trans stereoisomersarrow_forward2. a) Explain what structural feature of the double bond is required for an alkene to exhibit cis-trans (geometric) isomerism? b) Which of the following alkenes can exhibit cis-trans isomerism? If the molecule exhibits cis- trans isomerism, draw and name the associated isomer. 1- pentene CH2=CHCH2CH2CH3 i) ii) 2- pentene CH3CH=CHCH₂CH3 -0arrow_forwardPlease answer letters a and barrow_forward
- Cyclopropane (C3H6, a three-membered ring) is more reactive than most other cycloalkanes.(a) Draw a Lewis structure for cyclopropane.(b) Compare the bond angles of the carbon atoms in cyclopropane with those in an acyclic (noncyclic) alkane.(c) Suggest why cyclopropane is so reactive.arrow_forwardAn alkane has 70 hydrogen atoms. How many carbon atoms would it contain if it were (a) a straight-chain alkane; (b) a branched-chain alkane; (c) a cycloalkane? (a) C's (b) C's (c) C'sarrow_forward5. Give the structural formulae and name the functional groups of the following compounds. (a) 3-chlorobut-1-ene (b) butanedioic acid Name the functional group: (c) propanamide Name the functional group: (d) 3-methylbutanal Name the functional group: Name the functional group:arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

