
Foundations of Materials Science and Engineering
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696558
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.15, Problem 31AAP
In the copper–lead (Cu–Pb) system (Fig. 8.24) for an alloy of Cu–10 wt% Pb, determine the amounts and compositions of the phases present at (a) 1000°C, (b) 955°C + ΔT, (c) 955°C − ΔT, and (d) 200°C.
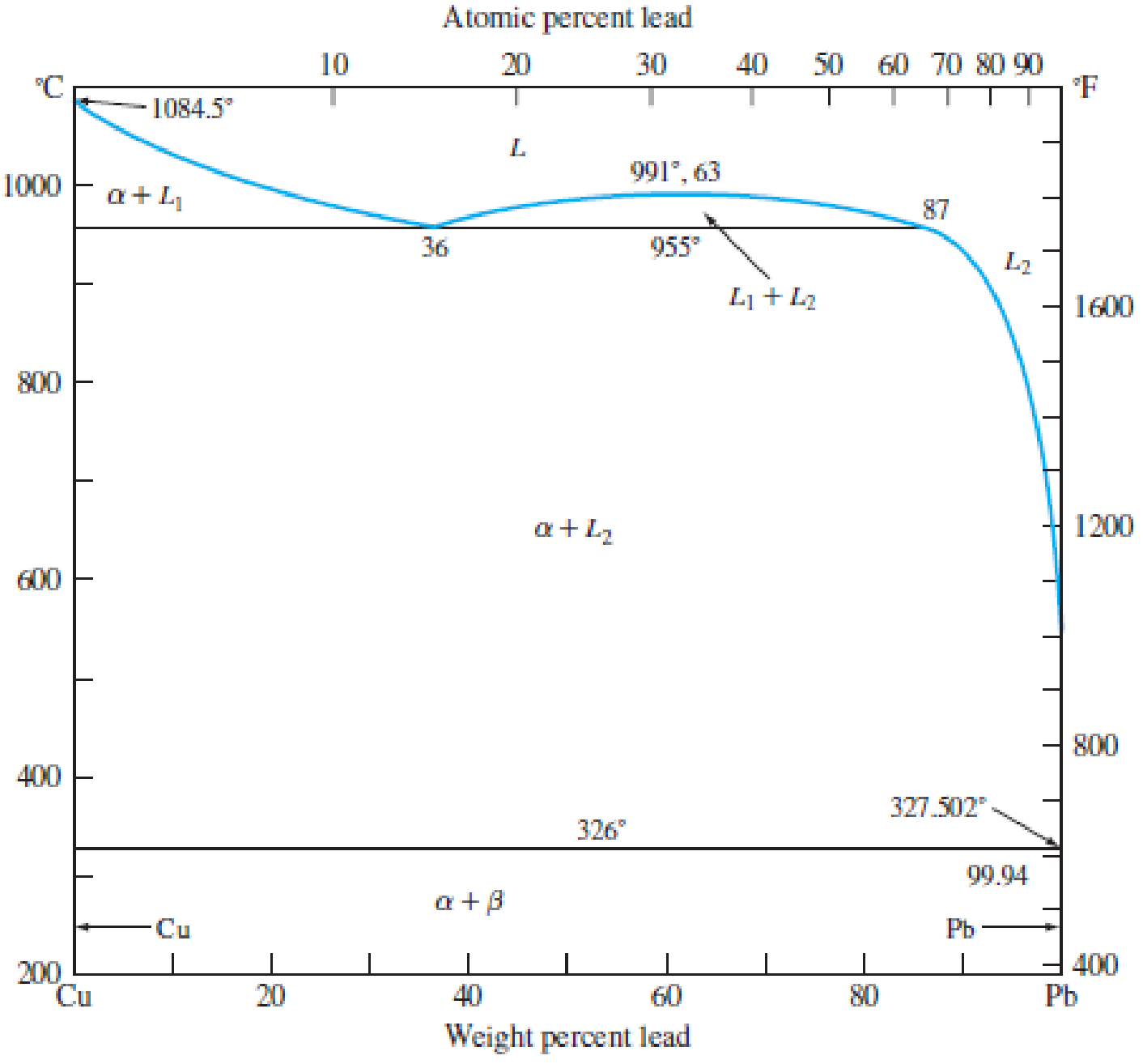
Figure 8.24
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
c)
The Cu-Zn phase diagram is shown in Figure 2.
i)
For a sample of composition 40 wt% Zn and 60 wt% Cu at 700°C, determine:
(1)
(ii)
the composition of the a-phase present at equilibrium
the composition of the B-phase present at equilibrium
(ii)
the relative amounts of both phases present at equilibrium
ii)
(ii)
For a sample of composition 50 wt% Zn and 50 wt% Cu at 700°C, determine
what phases are present at equilibrium?
(ii)
what is the composition of each phase?
ii)
For a 68 wt% Zn-32 wt% Cu alloy, make schematic sketches of the
microstructure that would be observed for conditions of very slow cooling at the
following temperatures: 1000°C, 760°C, 600°C and 400°C. Label all phases
and indicate their approximate compositions.
Compostion (2: In
20
40
60
100
12200
H2000
1000
1800
H1600
400
1200
600
400
600
200
400
100
20
40
60
Conporiton twt% Zro
Question:
For 5.7 kg of a magnesium–lead alloy of composition 50 wt% Pb–50 wt% Mg, is it possible, at equilibrium, to have α and Mg2Pb phases with respective masses of 5.13 and 0.57 kg? If so, what will be the approximate temperature of the alloy? If such an alloy is not possible, then explain why.
QUESTION 3:
Consider 2 kg of tin-bismuth alloy (Sn-Bi) containing 30 wt% Bi. The phase diagram of the alloy is shown in
the figure below. The alloy is cooled to 138 °C (just below the eutectic temperature).
300
271°C
232°C
L
9 200
Bi +L
B +L
139°C
21
57
100
Bi
B + Bi
13°C
20
40
60
80
100
(Sn)
(Bi)
Composition (wt% Bi)
a) What is the proeutectic phase?
b) How many kilograms of total phase B and Bi form?
c) How many kilograms of the proeutectic phase form?
d) How many kilograms of the eutectic phase B and eutectic phase Bi form?
e) Schematically sketch and label the resulting microstructure.
Temperature (°C)
Chapter 8 Solutions
Foundations of Materials Science and Engineering
Ch. 8.15 - Define (a) a phase in a material and (b) a phase...Ch. 8.15 - In the pure water pressure-temperature equilibrium...Ch. 8.15 - How many triple points are there in the pure iron...Ch. 8.15 - Write the equation for the Gibbs phase rule and...Ch. 8.15 - Refer to the pressuretemperature equilibrium phase...Ch. 8.15 - (a) What is a cooling curve? (b) What type of...Ch. 8.15 - Prob. 7KCPCh. 8.15 - What is an alloy? What is the difference between...Ch. 8.15 - Prob. 9KCPCh. 8.15 - What is the significance of the liquidus curve?...
Ch. 8.15 - Prob. 11KCPCh. 8.15 - Prob. 12KCPCh. 8.15 - Prob. 13KCPCh. 8.15 - Describe the mechanism that produces the...Ch. 8.15 - Can coring and surrounding occur in a...Ch. 8.15 - What is a monotectic invariant reaction? How is...Ch. 8.15 - Write equations for the following invariant...Ch. 8.15 - How are eutectic and eutectoid reactions similar?...Ch. 8.15 - Distinguish between (a) a terminal phase and (b)...Ch. 8.15 - Distinguish between (a) an intermediate phase and...Ch. 8.15 - What is the difference between a congruently...Ch. 8.15 - Consider an alloy containing 70 wt% Ni and 30 wt%...Ch. 8.15 - Consider the binary eutectic coppersilver phase...Ch. 8.15 - If 500 g of a 40 wt% Ag60 wt% Cu alloy is slowly...Ch. 8.15 - A lead-tin (PbSn) alloy consists of 60 wt%...Ch. 8.15 - A PbSn alloy (Fig. 8.12) contains 40 wt% and 60...Ch. 8.15 - An alloy of 30 wt% Pb70 wt% Sn is slowly cooled...Ch. 8.15 - Consider the binary peritectic iridiumosmium phase...Ch. 8.15 - Consider the binary peritectic iridiumosmium phase...Ch. 8.15 - Consider the binary peritectic iridiumosmium phase...Ch. 8.15 - In the copperlead (CuPb) system (Fig. 8.24) for an...Ch. 8.15 - For an alloy of Cu70 wt% Pb (Fig. 8.24), determine...Ch. 8.15 - What is the average composition (weight percent)...Ch. 8.15 - Consider an Fe4.2 wt% Ni alloy (Fig. 8.17) that is...Ch. 8.15 - Consider an Fe5.0 wt% Ni alloy (Fig. 8.17) that is...Ch. 8.15 - Determine the weight percent and composition in...Ch. 8.15 - Determine the composition in weight percent of the...Ch. 8.15 - Draw, schematically, the liquidus and the solidus...Ch. 8.15 - Consider the CuZn phase diagram of Figure 8.26. a....Ch. 8.15 - Consider the nickelvanadium phase diagram of...Ch. 8.15 - Consider the titaniumaluminum phase diagram of...Ch. 8.15 - What is the composition of point y in Figure...Ch. 8.15 - In Figure 8.12, determine the degree of freedom,...Ch. 8.15 - The cooling curve of an unknown metal shows a...Ch. 8.15 - In the PbSn phase diagram (Fig. 8.12), answer the...Ch. 8.15 - Based on the CuAg phase diagram in Figure P8.23,...Ch. 8.15 - Based on the PdAg phase diagram in Figure EP 8.3,...Ch. 8.15 - Prob. 49SEPCh. 8.15 - Derive the lever rule for the amount in weight...Ch. 8.15 - Based on the AlNi phase diagram given in Figure...Ch. 8.15 - Prob. 52SEPCh. 8.15 - Based on the Al2O3SiO2 phase diagram in Figure...Ch. 8.15 - (a) Design a CuNi alloy that will be completely...Ch. 8.15 - Prob. 55SEPCh. 8.15 - Given that Pb and Sn have similar tensile...Ch. 8.15 - Consider the sugarwater phase diagram shown in...Ch. 8.15 - In Figure P8.57, if 60 g of water and 140 g of...Ch. 8.15 - In Figure P8.57, if 30 g of water and 170 g of...Ch. 8.15 - At 80C, if the wt% of sugar is 80%, (a) what...Ch. 8.15 - (a) Based on the phase diagram in Figure P8.61,...Ch. 8.15 - Referring to Figure P8.61. explain what happens as...Ch. 8.15 - Referring to Figure P8.61, (a) explain what...Ch. 8.15 - Using Figure P8.40, explain what the phase diagram...Ch. 8.15 - Using Figure P8.40. explain why, according to the...Ch. 8.15 - (a) In the TiAl phase diagram. Figure P8.42, what...Ch. 8.15 - Draw an approximate hypothetical phase diagram for...Ch. 8.15 - Draw the hypothetical phase diagram for a binary...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For a Pb-30% Sn alloy, determine the phases 400 present, their amounts, and their compositions at 300°C, 200°C, and 0°C Hypoeutectic Hypereutectic ----- L L. 300 Liquidus Solidus Liquidus L+B a+L -Solidus 200 19 183° 97.5 Solvus Eutectic Solvus- 100 (E) a+ B a + E E+B Pb 20 40 60 80 Sn Temperature ("C)arrow_forwardA 45 wt% Pb-55 wt% Mg alloy is rapidly quenched to room temperature from an elevated temperature in such a way that the high- temperature microstructure is preserved. This microstructure is found to consist of the a phase and Mg2Pb, having respective mass fractions of 0.65 and 0.35. Determine the approximate temperature from which the alloy was quenched. Use Animated Figure. °℃arrow_forwardConsider the binary alloy phase diagram shown schematically below. The left-hand side denotes phase a, and the right-hand side the phase ß. The intermediate region is a coexistence regime with both a and ß phases. The three points 1, 2 and 3 in the coexistence region are at 22.8 wt% A, 28.2 wt% A, and 33.7 wt % A respectively. If the points on the phase boundaries L and R are at 20 wt% A and 39 wt % A, respectively, what is the fraction of a phase at 1, 2 and 3? (This question has only one correct answer) T(°C) A-B binary alloy 1400 Coexistence region 3 1 2 1100 B 20 % 40 % Weight % Aarrow_forward
- Calculate the amounts and compositions of phases at 726oC in a Fe-0.6% C alloy cooled under equilibrium conditions. Disregard the amounts of proeutectoid phases. A. 77.3% α, 22.7% Fe3C; C in α = 6.7% and C in Fe3C = 0.02% B. 91.3% α, 8.7% Fe3C; C in α = 0.02% and C in Fe3C = 6.7% C. 77.3% α, 22.7% Fe3C; C in α = 0.02% and C in Fe3C = 6.7% D. 91.3% α, 8.7% Fe3C; C in α = 0.05% and C in Fe3C = 8.4% E. None of the mentionedarrow_forwardASAParrow_forwardWhat is the composition, in wt% Cr2O3, of the liquid phase in an alloy containing 71 wt% Cr2O3 at 2200C?arrow_forward
- iii) For a 68 wt% Zn-32 wt% Cu alloy, make schematic sketches of the microstructure that would be observed for conditions of very slow cooling at the following temperatures: 1000°C, 760°C, 600°C and 400°C. Label all phases and indicate their approximate compositions. Comportion a In 20 40 60 100 1200 |2200 H2000 Liquid 1000 - 1800 デ+ダ H1600 J400 E 1200 600 400 『+キ 600 200 400 40 60 Conpositon tet% Zroarrow_forwarda. Determine the composition of each phase in a Cu-40% Ni alloy at 1300°C, 1270°C, 1250°C, and 1200°C. b. Calculate the amounts of α and L at 1250°C in the Cu-40% Ni alloyarrow_forwardHOME WORK re-No For a Pb-30% Sn alloy, determine the phases present, their amounts, and their compositions 400 sim Shaeen B at 300°C, 200°C, and 30°C L. 300 Liquidus Solidus Liquidus L+B a+L Solidus 200 19 183 61.9 97.5 Eutectic (E) n Ba Solvus Solvus- تعللق ل لصف 100 a + B a +E E+B Pb 20 40 60 80 Sn Metalurgy | Bassim Shaheen Bachy. Weight percent tin Temperature ("C)arrow_forward
- Question: Construct the hypothetical phase diagram for metals A and B between room temperature (20°C) and 700°C given the following information: The melting temperature of metal A is 480°C. The maximum solubility of B in A is 4 wt% B, which occurs at 420°C. The solubility of B in A at room temperature is 0 wt% B. One eutectic occurs at 420°C and 18 wt% B–82 wt% A. A second eutectic occurs at 475°C and 42 wt% B–58 wt% A. The intermetallic compound AB exists at a composition of 30 wt% B–70 wt% A, and melts congruently at 525°C. The melting temperature of metal B is 600°C. The maximum solubility of A in B is 13 wt% A, which occurs at 475°C. ● The solubility of A in B at room temperature is 3 wt% A.arrow_forwardThe Pb-Sn phase diagram is given: What is the Primary phase for a Pb-75%Sn alloy and what is the amount of Eutectic mixture at 100°C for this alloy? Composition (at% Sn) 20 40 60 80 100 327°C H600 300 Liquid 500 232°C a + L 200 B + L 1400 183°C 18.3 61.9 97.8 B00 100 a + B 200 H100 20 40 60 80 100 (Pb) Composition (wt% Sn) (Sn) Temperature (°C) Temperature (°F)arrow_forward1. Calculate the mass fraction fα of α of Fe-0.45% C at 750 °C by the lever rule. Draw the schematic of microstructure of Fe-0.45% C at 20°C which was gradually cooled from 750°C, and describe the name of each phase.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Intro to Ceramics and Glasses — Lesson 2, Part 1; Author: Ansys Learning;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ArDFnBWH-8w;License: Standard Youtube License