
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The electron-dot structure of the given structure is to be drawn and described.

Concept introduction:
The electron dot structures can be described as the structure in which electrons are represented around the atoms in the molecule.
In the resonance structure, the electrons are moved towards the more electronegative atoms and more positive charges. The arrow will be originated from pi electrons or unshared pair of electrons and move towards the more electronegative atoms and positive charges.
(b)
Interpretation:
The electron-dot structure of the given structure is to be drawn and described.
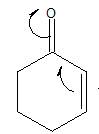
Concept introduction:
The electron dot structures can be described as the structure in which electrons are represented around the atoms in the molecule.
In the resonance structure, the electrons are moved towards the more electronegative atoms and more positive charges. The arrow will be originated from pi electrons or unshared pair of electrons and move towards the more electronegative atoms and positive charges.
(c)
Interpretation:
The electron-dot structure of the given structure is to be drawn and described.
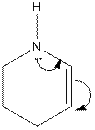
Concept introduction:
The electron dot structures can be described as the structure in which electrons are represented around the atoms in the molecule.
In the resonance structure, the electrons are moved towards the more electronegative atoms and more positive charges. The arrow will be originated from pi electrons or unshared pair of electrons and move towards the more electronegative atoms and positive charges.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
CHEMISTRY-TEXT
- The structures shown in the second picture are both incorrect. I cannot figure out the correct structure.arrow_forwardChoose the INCORRECT statement. In a Lewis structure, the number of valence electrons shown is one more for each negative charge. The central atom is typically the atom with the highest electronegativity. Formal charges are apparent charges associated with atoms in a Lewis structure. Resonance is when more than one plausible structure can be written but the "correct" structure cannot be written.arrow_forward1. Draw the resonance structures of the following molecule, using curved arrows to show electron movement and appropriate arrows to show the relationship between the structures. All lone pairs and charges must be clearly shown.arrow_forward
- Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. Draw a Lewis structure for one important resonance form of HBRO, (HOBRO3). Include all lone pair electrons in your structure. Do not include formal charges in your structure. draw structurearrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwriting solutionarrow_forwardDraw a second resonance structure for the following ion.The image of the ion with the OH+ and double bond is the original ion to draw the resonance structure from. The other image was my incorrect answer.arrow_forward
- Please don't use hend raiting and don't use Ai solutionarrow_forwardWhich options are true for writing Lewis structures of polyatomic ions.arrow_forwardDraw Lewis structure(s) for the acetate ion (CH2CO0). If there are equivalent resonance structures, draw all of them. • Draw one structure per sketcher box, and separate added sketcher boxes with the Do not include overall ion charges or formal charges in your drawing. • Do not draw double bonds to oxygen unless they are needed in order for the central atom to obey the octet rule. symbol. CH3COO":arrow_forward
- An unknown compound ‘X’ gives positive tests for the following three chemical tests: one, decolorizes orange-red color of bromine (Br2); two, reacts with sodium metal; three, change of color orange to green color with chromic acid. Propose a structure (draw Lewis structure) for an unknown compound ‘X'.arrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forwardDraw all resonance structures for the nitryl chloride molecule, NO2CI. • Explicitly draw all H atoms. Include all valence lone pairs in your answer. Do not include overall ion charges or formal charges in your drawing. Do not draw double bonds to oxygen unless they are needed for the central atom to obey the octet rule.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





