
(a)
Interpretation: The two characteristic arrow pushing patterns for the given mechanism is to be interpreted.
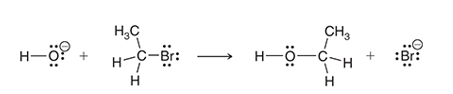
Concept introduction:
A
(b)
Interpretation: The process is the be interpreted as exothermic and endothermic for the given reaction with the help of the energy profile diagram.
Concept introduction:
The energy profile diagram shows the progress of the chemical reaction. It is the curve between the energy and reaction coordinate of the reaction. It can be used to predict the formation of transition state and product from the given reactant.
(c)
Interpretation: The
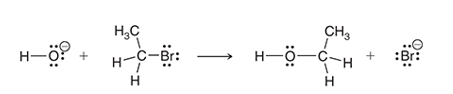
Concept introduction:
Entropy is the measurement of the randomness of a chemical system. As the randomness increases, the entropy of the system also increases. Entropy gets affected by the number of molecules in a system, physical state, and presence of ions.
(d)
Interpretation: The
Concept introduction:
A chemical reaction involves the conversion of one or more reactant molecules to product molecules. The Gibb’s equation provides the relation between
(e)
Interpretation: The transition state and its location on the energy diagram for the given reaction is to be interpreted.
Concept introduction:
A chemical reaction involves the conversion of one or more reactant molecules to product molecules. The reactant molecules come close to each other and collide effectively to form the transition state that further changes to the product.
(f)
Interpretation: The closeness of transition state to reactant or product is to be interpreted for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
A chemical reaction involves the conversion of one or more reactant molecules to product molecules. The reactant molecules come close to each other and collide effectively to form the transition state that further changes to the product.
(g)
Interpretation: The order of reaction is to be interpreted for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
The rate of a chemical reaction can be defined as the change in the concentration of the reactant within the given time. The rate law states that the rate of the chemical reaction is directly proportional to the active concentration of the reactant molecules. The proportionality constant is called the rate constant.
(h)
Interpretation: The effect of the doubled concentration of the hydroxide ion is to be interpreted for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
The rate of a chemical reaction can be defined as the change in the concentration of the reactant within the given time. The rate law states that the rate of the chemical reaction is directly proportional to the active concentration of the reactant molecules. The proportionality constant is called the rate constant.
(i)
Interpretation: The effect of increasing the temperature is to be interpreted for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
The energy profile diagram shows the progress of the chemical reaction. It is the curve between the energy and reaction coordinate of the reaction. It can be used to predict the formation of transition state and product from the given reactant.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PRINT COMPANION (
- During polymerization, the system usually becomes more ordered as monomers link together. Could an endothermic polymerization reaction ever occur spontaneously? Explain.arrow_forwardThe reaction of carbon monoxide with hydrogen to form methanol is quite slow at room temperature. As a general rule, reactions go faster at higher temperatures. Suppose that you tried to speed up this reaction by increasing the temperature. (a) Assuming that rH does not change very much as the temperature changes, what effect would increasing the temperature have on rSsurroundings? (b) Assuming that rS for a reaction System does not change much as the temperature changes, what effect would increasing the temperature have on rSuniverse?arrow_forwardCobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate, CoCl26H2O, is a bright pink compound, but in the presence of very dry air it loses water vapor to the air to produce the light blue anhydrous salt CoCl2. Calculate the standard free-energy change for the reaction at 25C: CoCl26H2O(s)CoCl2(s)+6H2O(g) Here are some thermodynamic data at 25C: What is the partial pressure of water vapor in equilibrium with the anhydrous salt and the hexahydrate at 25C? (Give the value in mmHg.) What is the relative humidity of air that has this partial pressure of water? The relative humidity of a sample of air is Relativehumidity=partialpressureofH2O(g)inairvaporpressureofwater100 What do you expect to happen to the equilibrium partial pressure over the hexahydrate as the temperature is raised? Explain.arrow_forward
- 2 A2B (Green)_+ 3 C2 = 2 A2C (yellow) + 2 BC2 AH = -288 kJ A.The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants and the color observed will be green. B.The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products and the color observed will be yellow. C.The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants and the color observed will be yellow. D.The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products and the color observed will be green. D. No effect will be observed. I D. Focus Warrow_forwardCalculate ∆rHofor the overall reaction 3P + Q → S, given the following data below: 2P + 3Q → R + T ∆rHo = -64 kJ/mol ---------(1)S + P → R ∆rHo = 100 kJ/mol ----------(2)P + ½T → Q ∆rHo = 74 kJ/mol ---------(3)arrow_forwardQ7. Some spontaneous reactions take 20 million years for half of the reactants to be converted into products while other reactions take 10 seconds. What is the basis for this difference in rate? A. Reactions take longer the closer their ΔG is to zero. B. The rate is dependent upon the concentration of substrate molecules. C. Reactions where substrate molecules can more readily reach the transition state occur faster. D. The rate of the reaction is dependent upon a supply of energy - thus coupled reactions that utilize ATP are the fastest.arrow_forward
- O(g) +e- O-(g) ∆Ho= -142 kJmol-1 O+2e- O2-(g) ∆Ho= + 712 kJ mol-1Calculate ∆Hofor the reaction : O- + e- O2-(g) .arrow_forwardAnalyze the following reaction mechanism. What is true for the first step? OH isi t + H₂O Acetone (CH3COCH3) Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. а It is reactant-favored because the reactants involve the weaker base b It is product-favored because the products involve the stronger base с It is reactant-favored because the reactants involve the stronger base d It is product-favored because the products involve the weaker base Ö: :OH e.. :OHarrow_forwardFor the reaction given below, the arrhenius actication energy is 15.5 kj.mol-1. Find Δ≠ H0arrow_forward
- uestion 17 W Product Reactant Product Reactant Time Time Reaction 1 Reaction 2 e graphs above represent the changes in concentration over time for the reactant and product of two separate reactions at 25 C. Based on these graphs, which of the following best supports the claim that action 1 is thermodynamically favorable but reaction 2 is not? [Product] Product) [Reactant >> 1 and AG"Trn 0. At equilibrium, for reaction 1 [Reactant A Product] [Reactant > 1 and AG" ran > 0 but for reaction 2 0. Reactant] Product) At equilibrium, for reaction 1 = 1 and AG" Reactant] [Product] Reactant) = 0 and AGTzn > 1 and AG" Tzn < 0 but for reaction 2 D At equilibrium, for reaction 1 Q Search or enter website name * Concentration Concentrationarrow_forwardThe combustion of ethane is shown below. 1 C2H6 (g) + 7/2 O2 (g) + 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H20 (g) AH = +1559.7 kJ Which energy diagram corresponds to this process? -1559 kl -1559 kJ А. Reaction coordinate В. Reaction coordinate VE HA -1559 kJ -1559 kJ С. Reaction coordinate D. Reaction coordinate А. А В. В O C. C D. D Enthalpy Enthalpyarrow_forwardWhich statement is NOT true? ΔH° determines the height of the energy barrier. Two reactions can have identical values for ΔH° but very different Ea values. The lower the activation energy, the faster the reaction. The larger the activation energy, the slower the reaction.arrow_forward

 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning





