
Concept explainers
Problem Set
QUANTITATIVE Succinate Oxidation. The oxidation of succinate to fumarate is an important cellular reaction because it is one of the steps in the citric acid cycle (see Figure 10-9). The two hydrogen atoms that are removed from succinate are accepted by a coenzyme molecule called flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), which is thereby reduced to FADH2:
ΔG°′ for Reaction 5-32 is 0 cal/mol.
(a) If you start with a solution containing 0.01 M each of succinate and FAD and add an appropriate amount of the enzyme that catalyzes this reaction, will any fumarate be formed? If so, calculate the resulting equilibrium concentrations of all four species. If not, explain why not.
(b) Answer part a assuming that 0.01 M FADH2 is also present initially.
(c) If the steady-state conditions in a cell are such that the FADH2/FAD ratio is 5 and the fumarate concentration is 2.5 μM, what steady-state concentration of succinate is needed to maintain ΔG′ for succinate oxidation at –1.5 kcal/mol?
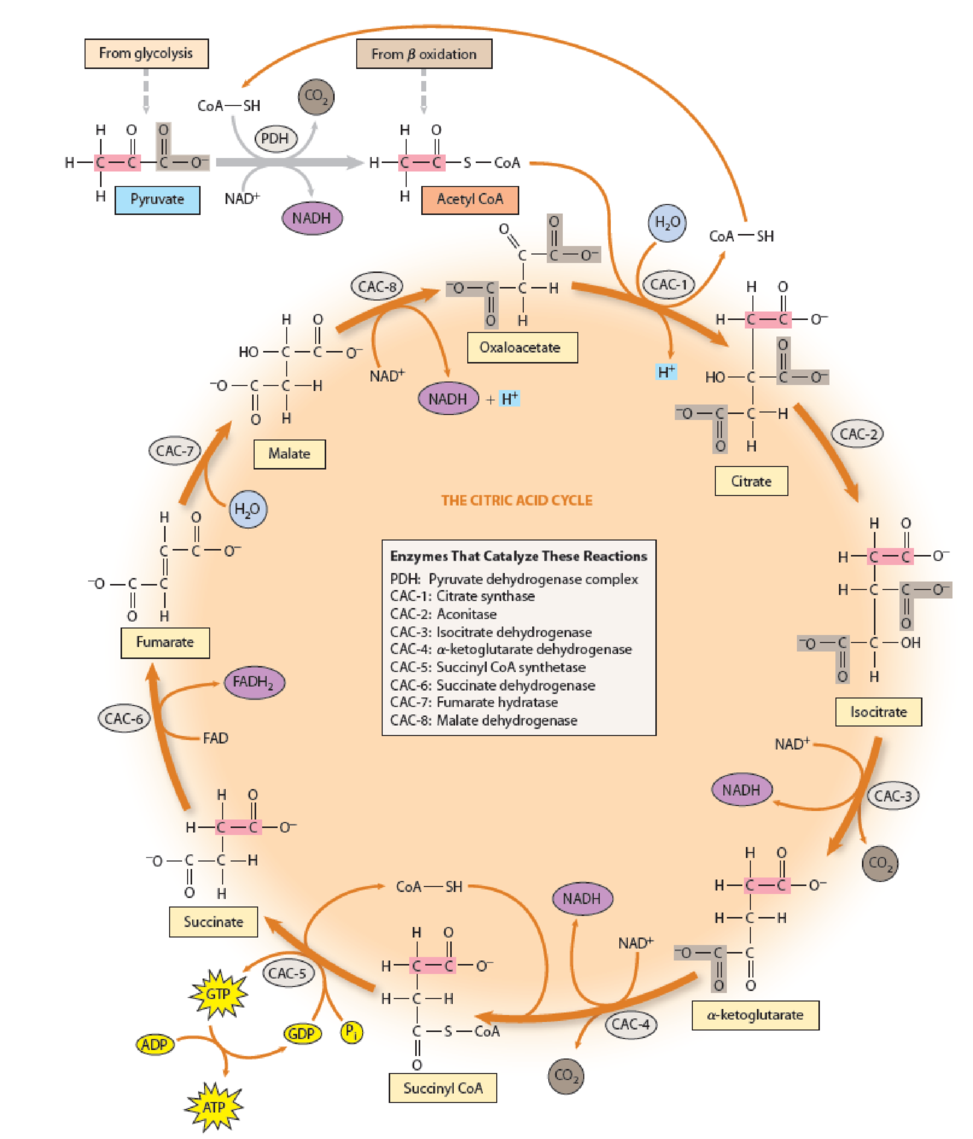
Figure 10-9 The Citric Acid Cycle. The two carbon atoms of pyruvate that enter the cycle via acetyl CoA are shown in pink in citrate and subsequent molecules until they are randomized by the symmetry of the fumarate molecule. The carboxyl group of pyruvate that is lost as CO2 is shaded, as are the two carboxyl groups of oxaloacetate that give rise to CO2 in reactions CAC-3 and CAC-4. Five of the reactions are oxidations, with NAD+ as the electron acceptor in four reactions (PDH, CAC-3, CAC-4, and CAC-8) and FAD as the electron acceptor in one reaction (CAC-6). The reduced form of the coenzyme is shown in purple in each case. Note that when CO2 is released, no H+ is given off during NAD+ reduction, thereby maintaining the charge balance of these reactions. The generation of GTP shown in reaction CAC-5 is characteristic of animal mitochondria. In bacterial cells and plant mitochondria, ATP is formed directly.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Becker's World of the Cell (9th Edition)
- Synthetic stoichiometries. What is the stoichiometry of the synthesis of... (a) ribose 5-phosphate from glucose 6- phosphate without the concomitant generation of NADPH? (b) NADPH from glucose 6-phosphate without the concomitant formation of pentose sugars?arrow_forward6-25 substrate-band enzyme concentrations. The the turnover number is equal to umax- b) V=Umax •57(Km+S) anstont For an enzyme that displays Michaelis-Menten kinetics, what is the reaction velocity, V (as a percentage of Vmax), observed at the following values? a) [S] = KM C) d) e) [S] = 0.5KM [S] = = 0.1KM [S] = 2KM [S] = 10KM w reactores -maximumrate of reaction boteles conc. Would you expect the structure of a competitive inhibitor of a given enzyme to be similar to that of its substrate?arrow_forwardNeed help, please.arrow_forward
- 70 gram lactose working under aerobic conditions. First calculate the total amount of energy units (ATP, GTP, FADH2, NADH) obtained from its degradation to CO2 and H2O. Convert this value to total ATP units.Show your work in detail at each reaction step. Which energy units are obtained after each reaction step.arrow_forwardNeed help, please.arrow_forwardCalculation about delta standard G, delta H, detla S. Question attached as photo below. And my answer attempted. Need my answer verified and corrected if neccesary. Please let me know where I got wrong and what key ideas I had miss. Thanks.arrow_forward
- Need help.arrow_forwardModified TRUE or FALSE. Write the word TRUE if the statement is correct. If the statement is false, write the incorrect underlined word/s and indicate the correct word/s to make the statement true. The Michaelis-Menten Constant (Km) of an enzyme is equal to the enzyme concentration at which the initial velocity of the reaction is one half of maximum velocity (Vmax).arrow_forwardNeed new solutions correctarrow_forward
- O BIOCHEMISTRY Understanding major biochemical energy storage and release. A certain anabolic biochemical reaction A has AG- 17.8 kJ mol , and is always coupled to another reaction B, which has two reactants and two products, I this: R + R2 P + P2 The molecule in the drawing area below is either R, or P. • If it's R, change it into P. But if it's P, change it into R. • In either case, draw the molecule as it would exist at physiological pH. • Also please answer the questions about Reaction B in the table below. OR, Was the molecule in the drawing area R, or P, before you changed it? What is R? Enter its common name, usual symbol, or chemical formula: What is P2? Enter its common name, usual symbol, or chemical formula: O BIOCHEMISTRY Understanding major biochemical energy storage and release.. ODO its common name, usual symbol, or chemical formula: NH, -CH N. H OH OH ...... to IIIarrow_forwardSmall explanation please. what is a product in the first stage of the Q- cycle? a. two electrons b. Q- cation c. cyt c (oxidized) d. two more protons in the matrix e. Q- radical anionarrow_forwardQuestion attachedarrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
