
Concept explainers
a)
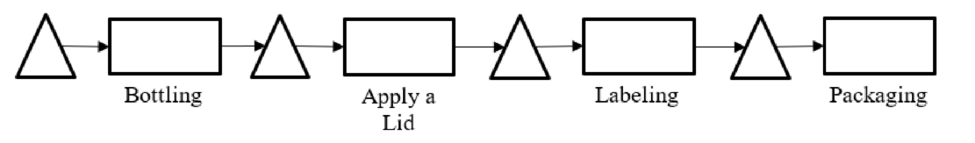
To draw: A process flow diagram for this process.
a)
Explanation of Solution
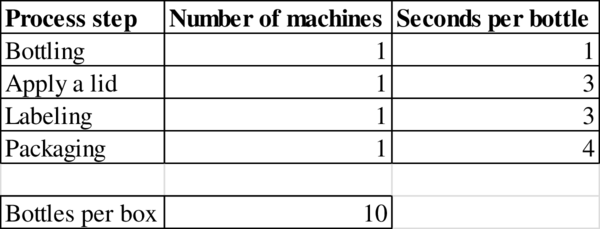
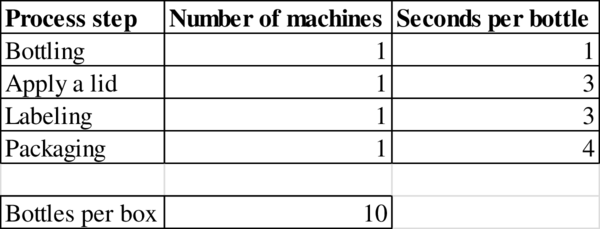
Given information:
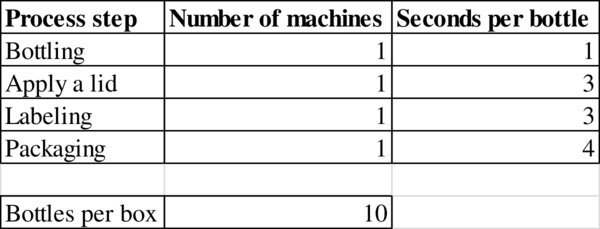
Process flow diagram:
b)
To determine: The capacity at the resource “Apply a lid”.
b)
Explanation of Solution
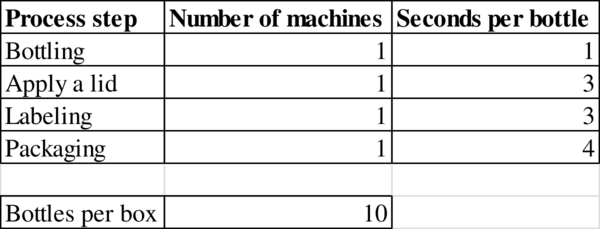
Given information:
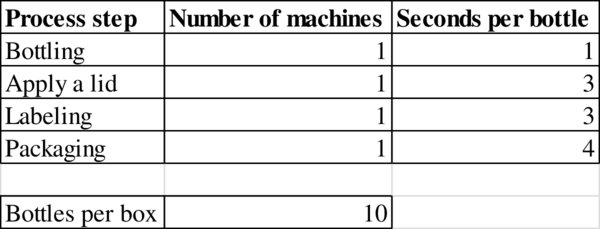
Calculation of capacity:
The capacity is 1,200 bottles.
c)
To determine: The bottleneck in the process.
c)
Explanation of Solution
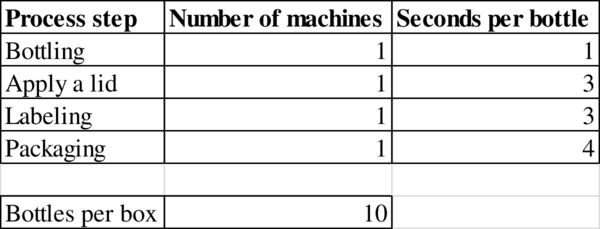
Given information:
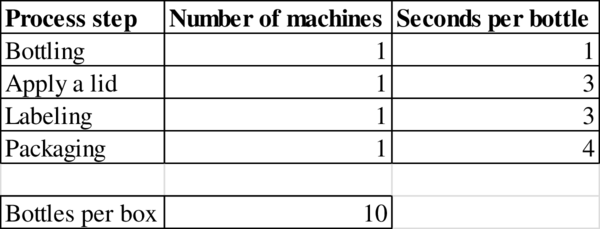
Determination of bottleneck:
The process step with the longest processing time “seconds per bottle” is the bottleneck in the process. Packaging has the highest time of 3 seconds per bottle.
Hence, the bottleneck is Packaging.
d)
To determine: The flow rate.
d)
Explanation of Solution
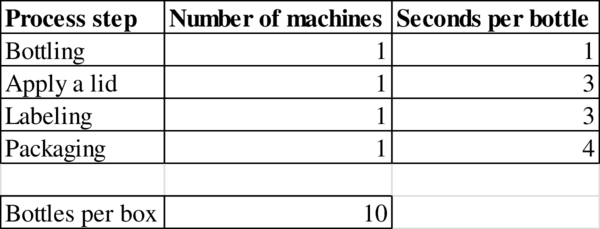
Given information:
Determination of flow rate:
The flow rate is 900 bottles.
e)
To determine: The utilization of resource “Apply a lid”
e)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation of utilization:
The utilization is 75%.
f)
To determine: The utilization of bottling.
f)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation of utilization:
The utilization is 20%.
g)
To determine: The cycle time of the process.
g)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation of cycle time:
The demand is constrained and has a flow rate of
The cycle time is 5 seconds.
h)
To determine: The time taken to produce 500 bottles.
h)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation of time taken to produce 500 bottles:
The time taken to produce 500 bottles is 2,515 seconds.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Operations Management
- A small, privately owned Asian company is producing a private-label soft drink called Yoggo. A bottling line puts the soft drinks into plastic bottles and then packages the bottles into boxes holding 10 bottles each. The bottling line is comprised of the following four steps: (1) the bottling machine takes 1 second to fill a bottle, (2) the lid machine takes 3 seconds to cover the bottle with a lid, (3) a labeling machine takes 3 seconds per bottle, and (4) the packaging machine takes 4 seconds to place a bottle into a box. When a box has been filled with 10 bottles, a worker tending the packaging machine removes the filled box and replaces it with an empty box. Assume that the time for the worker to remove a filled box and replace it with an empty box is negligible and hence does not affect the capacity of the line. Problem data are summarized in the following table. Process Step Number of Machines Seconds per Bottle Bottling 1 1 Apply a lid 1 3 Labeling 1 3 Packaging 1 4…arrow_forwardA small, privately owned Asian company is producing a private-label soft drink called Yoggo. A bottling line puts the soft drinks into plastic bottles and then packages the bottles into boxes holding 10 bottles each. The bottling line is comprised of the following four steps: (1) the bottling machine takes 1 second to fill a bottle, (2) the lid machine takes 3 seconds to cover the bottle with a lid, (3) a labeling machine takes 3 seconds per bottle, and (4) the packaging machine takes 4 seconds to place a bottle into a box. When a box has been filled with 10 bottles, a worker tending the packaging machine removes the filled box and replaces it with an empty box. Assume that the time for the worker to remove a filled box and replace it with an empty box is negligible and hence does not affect the capacity of the line. Problem data are summarized in the following table. Assuming unlimited demand, what would be the flow rate? Assuming unlimited demand, what would be the utilization at…arrow_forwardCPFR is typically a(n) ________ firm process. Group of answer choices External Internal Both of these answers None of these answersarrow_forward
- JCL Inc. is a major chip manufacturing firm that sells its products to computer manufacturers like Dell, HP, and others. In simplified terms, chip making at JCL Inc. involves three basic operations: depositing, patterning, and etching. Depositing: Using chemical vapor deposition (CVD) technology, an insulating material is deposited on the wafer surface, forming a thin layer of solid material on the chip. Patterning: Photolithography projects a microscopic circuit pattern on the wafer surface, which has a light-sensitive chemical like the emulsion on photographic film. It is repeated many times as each layer of the chip is built. Etching: Etching removes selected material from the chip surface to create the device structures. The following table lists the required processing times and setup times at each of the steps. Assume that the unit of production is a wafer, from which individual chips are cut at a later stage. Note: A setup can only begin once the batch has arrived at the…arrow_forwardcharacteristic of process technology relates to the integration of separate processes a. Degree of connectivity b. Degree of automation c. Scale d. Cushionarrow_forward. A small, privately owned Asian company is producing a private-label soft drink calledYoggo. A bottling line puts the soft drinks into plastic bottles and then packagesthe bottles into boxes holding 10 bottles each. The bottling line is comprised of thefollowing four steps: (1) the bottling machine takes 1 second to fill a bottle, (2) the lidmachine takes 3 seconds to cover the bottle with a lid, (3) a labeling machine takes3 seconds per bottle, and (4) the packaging machine takes 4 seconds to place a bottleinto a box. When a box has been filled with 10 bottles, a worker tending the packagingmachine removes the filled box and replaces it with an empty box. Assume that thetime for the worker to remove a filled box and replace it with an empty box is negligibleand hence does not affect the capacity of the line. Problem data are summarized in thefollowing table. a. Draw a process flow diagram of this process. b. What is the capacity (bottles/hour) at the resource “Apply a lid”? c. What…arrow_forward
- JCL Inc. is a major chip manufacturing firm that sells its products to computer manufacturers like Dell, Gateway, and others. In simplified terms, chip making at JCL Inc. involves three basic operations: depositing, patterning, and etching. Depositing: Using chemical vapor deposition (CVD) technology, an insulating material is deposited on the wafer surface, forming a thin layer of solid material on the chip. Patterning: Photolithography projects a microscopic circuit pattern on the wafer surface, which has a light-sensitive chemical like the emulsion on photographic film. It is repeated many times as each layer of the chip is built. Etching: Etching removes selected material from the chip surface to create the device structures. The table below lists the required processing times and setup times at each of the steps. There is unlimited space for buffer inventory between these steps. Assume that the unit of production is a wafer, from which individual chips are cut at a later…arrow_forwardHammond Inc. has analyzed the setup time on its computer-controlled lathe. The setup requires changing the type of fixture that holds a part. The average setup time has been 135 minutes, consisting of the following steps: Step Time (in minutes) Turn off machine and remove fixture from lathe 13 Go to tool room with fixture 15 Record replacement of fixture to tool room 18 Return to lathe 20 Clean lathe 17 Return to tool room 20 Record withdrawal of new fixture from tool room 12 Return to lathe 15 Install new fixture and turn on machine 8 Total setup time 138 Why should management be concerned about improving setup time? What do you recommend to Hammond Inc. for improving setup time? How much time would be required for a setup, using your suggestion in (b)?arrow_forwardThe Flip Chip Company manufactures nacho chips, potato chips, and related products. There has been a problem in the manufacture of nacho chips. The process begins with the mixing of water, corn and lime (called the MASA). A mixer can produce a batch of 300 lbs of MASA in 2 minutes. The MASA is then cooked. This takes 30 minutes. Only 95% of the MASA makes it to the ovens and of that only 75% is transferred to the next step. There are four ovens. The next step is chip making. The MASA is extruded into the chip itself and the chips are baked. There are 2 chip machines. A total of 950 chips/minute are produced (each chip weighs approximately .5oz). The yield from this process is 72%. The chips are then placed in 20 oz bags. This step takes 2 seconds for each bag. Where is the bottleneck? What recommendation would you make?arrow_forward
- Within a process approach the desired results are most effectively achieved when: Select one: related activities are part of the process. Resources and related activities are managed as a process. the process includes the resources.arrow_forwardDesign a process for the following activitiy, preparing for an exam.arrow_forwardPrinted Circuit Boards You are a supplier of printed circuit boards (PCBs). Production of the circuit boards consists of several steps – Surface Mounting, Baking, and Final Assembly. Surface Mounting puts integrated circuits (ICs) and other components on a PCB. These PCBs are then Baked as a batch and kept in an oven for some time so that the ICs are soldered onto the PCBs. Finally, these PCBs are taken and manually assembled into a case, and wired with connectors. The processing rate at the Surface Mounting station is 15 PCBs/minute, the processing rate for Baking is 5 PCBs/minute, and the processing rate for Final Assembly is 3 PCBs/minute. If there are on average 24 units of (work in process) inventory and the system is working at capacity, what is the flow (throughput) time for PCBs?arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.





